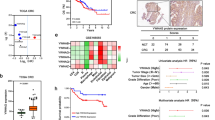
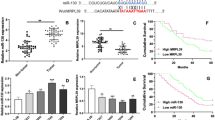
Abstract
Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 (PRL-3) has been implicated in controlling cancer cell invasiveness. Deregulated expression of PRL-3 is involved in cancer progression and predicts poor overall survival. Recent studies have revealed critical roles for microRNAs in various cellular processes, including tumorigenic development. In this study, we aimed to explore the linkage between PRL-3 and microRNAs in gastric cancer. We found that PRL-3 transcript levels were positively correlated with miR-210 levels in gastric cancer tissues. In gastric cancer cells, PRL-3 upregulated miR-210 expression in a HIF-1α-dependent fashion under normoxia and hypoxia. In addition, PRL-3 activated NF-κB signaling and promoted HIF-1α expression through modulating phosphorylation of p65. NF-κB signaling, HIF-1α, and miR-210 partially contributed to PRL-3-induced migration and invasion. Furthermore, the levels of PRL-3, HIF-1α, and miR-210 transcripts inversely affected the overall survival of gastric cancer patients. Our work identified the existence of a PRL-3-NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis, thus providing new insight into the role of PRL-3 in promoting gastric cancer invasiveness.
Key Message
-
PRL-3 regulates microRNA in gastric cancer.
-
PRL-3 elevates hsa-miR-210 by upregulating HIF-1α.
-
PRL-3 activates a NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis by enhancing the phosphorylation of p65.
-
PRL-3 promotes cell migration and invasion via the NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis.
-
High levels of PRL-3 and miR-210 are related with poor OS in gastric cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bessette DC, Qiu D, Pallen CJ (2008) PRL PTPs: mediators and markers of cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27(2):231–252
Wang H, Vardy LA, Tan CP, Loo JM, Guo K, Li J, Lim SG, Zhou J, Chng WJ, Ng SB et al (2010) PCBP1 suppresses the translation of metastasis-associated PRL-3 phosphatase. Cancer Cell 18(1):52–62
Fiordalisi JJ, Keller PJ, Cox AD (2006) PRL tyrosine phosphatases regulate rho family GTPases to promote invasion and motility. Cancer Res 66(6):3153–3161
Fiordalisi JJ, Dewar BJ, Graves LM, Madigan JP, Cox AD (2013) Src-mediated phosphorylation of the tyrosine phosphatase PRL-3 is required for PRL-3 promotion of Rho activation, motility and invasion. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64309
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang JP, Zeng Q (2007) PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals through PI3K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 67(7):2922–2926
Peng L, Xing X, Li W, Qu L, Meng L, Lian S, Jiang B, Wu J, Shou C (2009) PRL-3 promotes the motility, invasion, and metastasis of LoVo colon cancer cells through PRL-3-integrin beta1-ERK1/2 and-MMP2 signaling. Mol Cancer 8:110
Lian S, Meng L, Liu C, Xing X, Song Q, Dong B, Han Y, Yang Y, Peng L, Qu L et al (2013) PRL-3 activates NF-kappaB signaling pathway by interacting with RAP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 430(1):196–201
Liang F, Liang J, Wang WQ, Sun JP, Udho E, Zhang ZY (2007) PRL3 promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down-regulation of Csk leading to Src activation. J Biol Chem 282(8):5413–5419
Al-Aidaroos AQ, Yuen HF, Guo K, Zhang SD, Chung TH, Chng WJ, Zeng Q (2013) Metastasis-associated PRL-3 induces EGFR activation and addiction in cancer cells. J Clin Invest 123(8):3459–3471
Guo K, Li J, Tang JP, Tan CP, Hong CW, Al-Aidaroos AQ, Varghese L, Huang C, Zeng Q (2011) Targeting intracellular oncoproteins with antibody therapy or vaccination. Sci Transl Med 3(99):99ra85
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3(10):721–732
Kim YH, Yoo KC, Cui YH, Uddin N, Lim EJ, Kim MJ, Nam SY, Kim IG, Suh Y, Lee SJ (2014) Radiation promotes malignant progression of glioma cells through HIF-1alpha stabilization. Cancer Lett 354(1):132–141
Martinengo C, Poggio T, Menotti M, Scalzo MS, Mastini C, Ambrogio C, Pellegrino E, Riera L, Piva R, Ribatti D et al (2014) ALK-dependent control of hypoxia-inducible factors mediates tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res 74(21):6094–6106
Ma L, Li G, Zhu H, Dong X, Zhao D, Jiang X, Li J, Qiao H, Ni S, Sun X (2014) 2-Methoxyestradiol synergizes with sorafenib to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma by simultaneously dysregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and −2. Cancer Lett 355(1):96–105
Marhold M, Tomasich E, El-Gazzar A, Heller G, Spittler A, Horvat R, Krainer M, Horak P (2014) HIF-1alpha regulates mTOR signaling and viability of prostate cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer Res MCR. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0153-T
Ren H, Jia L, Zhao T, Zhang H, Chen J, Yang S, Liu J, Yu M, Hao J (2014) Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha directly activates leptin receptor (Ob-R) in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett 354(1):172–180
Chan SY, Loscalzo J (2010) MicroRNA-210: a unique and pleiotropic hypoxamir. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 9(6):1072–1083
Chan YC, Banerjee J, Choi SY, Sen CK (2012) miR-210: the master hypoxamir. Microcirculation 19(3):215–223
He J, Wu J, Xu N, Xie W, Li M, Li J, Jiang Y, Yang BB, Zhang Y (2013) MiR-210 disturbs mitotic progression through regulating a group of mitosis-related genes. Nucleic Acids Res 41(1):498–508
Lou YL, Guo F, Liu F, Gao FL, Zhang PQ, Niu X, Guo SC, Yin JH, Wang Y, Deng ZF (2012) miR-210 activates notch signaling pathway in angiogenesis induced by cerebral ischemia. Mol Cell Biochem 370(1–2):45–51
Bianchi N, Zuccato C, Lampronti I, Borgatti M, Gambari R (2009) Expression of miR-210 during erythroid differentiation and induction of gamma-globin gene expression. BMB Rep 42(8):493–499
Gee HE, Ivan C, Calin GA, Ivan M (2014) HypoxamiRs and cancer: from biology to targeted therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(8):1220–1238
Zhang J, Xiao Z, Lai D, Sun J, He C, Chu Z, Ye H, Chen S, Wang J (2012) miR-21, miR-17 and miR-19a induced by phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promote the proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer. Br J Cancer 107(2):352–359
Li Z, Cao Y, Jie Z, Liu Y, Li Y, Li J, Zhu G, Liu Z, Tu Y, Peng G et al (2012) miR-495 and miR-551a inhibit the migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by directly interacting with PRL-3. Cancer Lett 323(1):41–47
Tian W, Qu L, Meng L, Liu C, Wu J, Shou C (2012) Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 directly interacts with integrin beta1 and regulates its phosphorylation at tyrosine 783. BMC Biochem 13:22
Smith TG, Robbins PA, Ratcliffe PJ (2008) The human side of hypoxia-inducible factor. Br J Haematol 141(3):325–334
Mazzone M, Dettori D, Leite de Oliveira R, Loges S, Schmidt T, Jonckx B, Tian YM, Lanahan AA, Pollard P, Ruiz de Almodovar C et al (2009) Heterozygous deficiency of PHD2 restores tumor oxygenation and inhibits metastasis via endothelial normalization. Cell 136(5):839–851
Al-Aidaroos AQ, Zeng Q (2010) PRL-3 phosphatase and cancer metastasis. J Cell Biochem 111(5):1087–1098
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J (2003) HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J 22(16):4082–4090
Semenza GL (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell 148(3):399–408
Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM (2004) Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 279(37):38458–38465
Bordoli MR, Stiehl DP, Borsig L, Kristiansen G, Hausladen S, Schraml P, Wenger RH, Camenisch G (2011) Prolyl-4-hydroxylase PHD2- and hypoxia-inducible factor 2-dependent regulation of amphiregulin contributes to breast tumorigenesis. Oncogene 30(5):548–560
Gorlach A, Bonello S (2008) The cross-talk between NF-kappaB and HIF-1: further evidence for a significant liaison. Biochem J 412(3):e17–e19
Michiels C, Minet E, Mottet D, Raes M (2002) Regulation of gene expression by oxygen: NF-kappaB and HIF-1, two extremes. Free Radic Biol Med 33(9):1231–1242
Walmsley SR, Print C, Farahi N, Peyssonnaux C, Johnson RS, Cramer T, Sobolewski A, Condliffe AM, Cowburn AS, Johnson N et al (2005) Hypoxia-induced neutrophil survival is mediated by HIF-1alpha-dependent NF-kappaB activity. J Exp Med 201(1):105–115
Yoshida T, Hashimura M, Mastumoto T, Tazo Y, Inoue H, Kuwata T, Saegusa M (2013) Transcriptional upregulation of HIF-1alpha by NF-kappaB/p65 and its associations with beta-catenin/p300 complexes in endometrial carcinoma cells. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 93(11):1184–1193
Van Uden P, Kenneth N, Rocha S (2008) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kappaB. Biochem J 412:477–484
Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Maroni P, Desiderio MA (2009) NF-kappaB activation, dependent on acetylation/deacetylation, contributes to HIF-1 activity and migration of bone metastatic breast carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res MCR 7(8):1328–1341
Wang H, Flach H, Onizawa M, Wei L, McManus MT, Weiss A (2014) Negative regulation of Hif1a expression and TH17 differentiation by the hypoxia-regulated microRNA miR-210. Nat Immunol 15(4):393–401
Qi J, Qiao Y, Wang P, Li S, Zhao W, Gao C (2012) microRNA-210 negatively regulates LPS-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines by targeting NF-kappaB1 in murine macrophages. FEBS Lett 586(8):1201–1207
Giannakakis A, Sandaltzopoulos R, Greshock J, Liang S, Huang J, Hasegawa K, Li C, O’Brien-Jenkins A, Katsaros D, Weber BL et al (2008) miR-210 links hypoxia with cell cycle regulation and is deleted in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 7(2):255–264
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, Tong RT, Welford SM, Ang KK, Story M, Le QT, Giaccia AJ (2009) Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell 35(6):856–867
Zhang Z, Sun H, Dai H, Walsh RM, Imakura M, Schelter J, Burchard J, Dai X, Chang AN, Diaz RL et al (2009) MicroRNA miR-210 modulates cellular response to hypoxia through the MYC antagonist MNT. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 8(17):2756–2768
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP, de Weerd V, Boersma AW, Klijn JG, Wiemer EA, Martens JW (2008) Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(35):13021–13026
Ying Q, Liang L, Guo W, Zha R, Tian Q, Huang S, Yao J, Ding J, Bao M, Ge C et al (2011) Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-210 augments the metastatic potential of tumor cells by targeting vacuole membrane protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (Baltim, Md) 54(6):2064–2075
Wang Z, He YL, Cai SR, Zhan WH, Li ZR, Zhu BH, Chen CQ, Ma JP, Chen ZX, Li W et al (2008) Expression and prognostic impact of PRL-3 in lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer: its molecular mechanism was investigated using artificial microRNA interference. Int J Cancer 123(6):1439–1447
Miskad UA, Semba S, Kato H, Matsukawa Y, Kodama Y, Mizuuchi E, Maeda N, Yanagihara K, Yokozaki H (2007) High PRL-3 expression in human gastric cancer is a marker of metastasis and grades of malignancies: an in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch Int J Pathol 450(3):303–310
Li ZR, Wang Z, Zhu BH, He YL, Peng JS, Cai SR, Ma JP, Zhan WH (2007) Association of tyrosine PRL-3 phosphatase protein expression with peritoneal metastasis of gastric carcinoma and prognosis. Surg Today 37(8):646–651
Wang Z, Cai SR, He YL, Zhan WH, Chen CQ, Cui J, Wu WH, Wu H, Song W, Zhang CH et al (2009) High expression of PRL-3 can promote growth of gastric cancer and exhibits a poor prognostic impact on patients. Ann Surg Oncol 16(1):208–219
Bessette DC, Wong PC, Pallen CJ (2007) PRL-3: a metastasis-associated phosphatase in search of a function. Cells Tissues Organs 185(1–3):232–236
Acknowledgments
We deeply appreciate Jingyan Han, Chunshui Pan (Peking University Health Science Center), Caiyun Liu and Lixin Wang (Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute) for the helpful suggestions on study design and experimental procedures and Dr. Lorenzo Finci (Tsinghua University) for the meticulous editing of this manuscript. This study was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB553906, 2013CB910504) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81230046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None. The experiments described in the manuscript comply with the current laws of the countries in which they were performed.
Additional information
Cheng Zhang and Wei Tian contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Tian, W., Meng, L. et al. PRL-3 promotes gastric cancer migration and invasion through a NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis. J Mol Med 94, 401–415 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1350-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1350-7