Abstract
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a cytokine belonging to the IL-1 family, is crucially involved in inflammatory pathologies including liver injury and linked to various modes of cell death. However, a link between IL-33 and necroptosis or programmed necrosis in liver pathology remains elusive. We aimed to investigate the regulation of IL-33 during necroptosis-associated liver injury. The possible regulation of IL-33 during liver injury by receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) was investigated in mice in vivo and in hepatic stellate cells in vitro. The liver immunohistopathology, flow cytometry, serum transaminase measurement, ELISA, and qPCR-based cytokine measurement were carried out. By using a chemical approach, we showed that pretreatment of mice with Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) (inhibitor of RIPK1) and/or PJ34 (inhibitor of PARP-1) significantly protected mice against concanavalin A (ConA) liver injury (aspartate amino-transferase (AST)/alanine amino-transferase (ALT)) associated with down-regulated hepatocyte-specific IL-33 expression. In contrast, the expression level of most systemic cytokines (except for IL-6) or activation of liver immune cells was not altered by chemical inhibitors rather an increased infiltration of neutrophils in the liver. During polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (Poly(I:C))-induced acute hepatitis, liver injury and hepatocyte-specific IL-33 expression was also inhibited by PJ34 without any protective effect of PJ34 in CCl4-induced liver injury. Moreover, PJ34 down-regulated the protein expression of IL-33 in activated hepatic stellate cells by cocktail of cytokines or staurosporine in vitro. In conclusion, we evidenced that the Nec-1/PJ34 is a potent inhibitor of liver injury and Nec-1/PJ34 down-regulated hepatocyte-specific IL-33 expression in the liver in vivo or in hepatic stellate cells in vitro, suggesting IL-33 as a possible readout of necroptosis-involved liver pathologies.
Key message
-
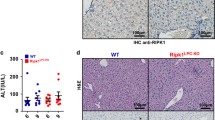
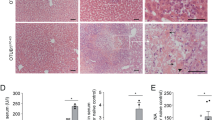
Necroptosis inhibitors can protect mice against liver injury induced by ConA or Poly(I:C).
-
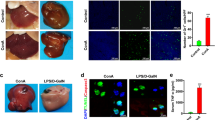
IL-33 expression in liver injury in vivo is inhibited by PJ34.
-
IL-33 expression in hepatic stellate cells in vitro is inhibited by PJ34.
-
Hepatocyte-specific IL-33 expression is down-regulated by Nec-1/PJ34 during hepatitis.
-
IL-33 is a new marker of necroptosis-associated liver injuries.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AST:
-
Aspartate amino-transferase
- ALT:
-
Alanine amino-transferase
- ConA:
-
Concanavalin A
- IL-33:
-
Interleukin 33
- IL-1RAcP:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein
- i.v.:
-
Intravenous
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- Nec-1:
-
Necrostatin-1
- PARP-1:
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
- P.I.:
-
Postinjection
- RIPK:
-
Receptor-interacting protein kinase
- Poly(I:C):
-
Polyinosine-polycytidylic acid
References
Malhi H, Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ (2010) Hepatocyte death: a clear and present danger. Physiol Rev 90:1165–1194
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G (2010) Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:700–714
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M et al (2009) Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 137:1112–1123
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L et al (2009) Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 137:1100–1111
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC et al (2009) RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science (New York, NY) 325:332–336
Jurisic V, Srdic-Rajic T, Konjevic G, Bogdanovic G, Colic M (2011) TNF-alpha induced apoptosis is accompanied with rapid CD30 and slower CD45 shedding from K-562 cells. The Journal of membrane biology 239:115–122
Zorde-Khvalevsky E, Abramovitch R, Barash H, Spivak-Pohis I, Rivkin L, Rachmilewitz J et al (2009) Toll-like receptor 3 signaling attenuates liver regeneration. Hepatology 50:198–206
Csak T, Dolganiuc A, Kodys K, Nath B, Petrasek J, Bala S et al (2011) Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein defect links impaired antiviral response and liver injury in steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 53:1917–1931
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest 90:196–203
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Van Kaer L, Matsuda H, Yagita H, Okumura K (2000) Critical contribution of liver natural killer T cells to a murine model of hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:5498–5503
Zheng SJ, Wang P, Tsabary G, Chen YH (2004) Critical roles of TRAIL in hepatic cell death and hepatic inflammation. J Clin Invest 113:58–64
Takeda K, Kojima Y, Ikejima K, Harada K, Yamashina S, Okumura K et al (2008) Death receptor 5 mediated-apoptosis contributes to cholestatic liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10895–10900
Beraza N, Malato Y, Sander LE, Al-Masaoudi M, Freimuth J, Riethmacher D et al (2009) Hepatocyte-specific NEMO deletion promotes NK/NKT cell- and TRAIL-dependent liver damage. J Exp Med 206:1727–1737
Ni HM, Chen X, Ding WX, Schuchmann M, Yin XM (2008) Differential roles of JNK in ConA/GalN and ConA-induced liver injury in mice. Am J Pathol 173:962–972
Kunstle G, Hentze H, Germann PG, Tiegs G, Meergans T, Wendel A (1999) Concanavalin A hepatotoxicity in mice: tumor necrosis factor-mediated organ failure independent of caspase-3-like protease activation. Hepatology 30:1241–1251
Liedtke C, Bangen JM, Freimuth J, Beraza N, Lambertz D, Cubero FJ et al (2011) Loss of caspase-8 protects mice against inflammation-related hepatocarcinogenesis but induces non-apoptotic liver injury. Gastroenterology 141:2176–2187
Zhou Y, Dai W, Lin C, Wang F, He L, Shen M et al (2013) Protective effects of necrostatin-1 against concanavalin A-induced acute hepatic injury in mice. Mediat Inflamm 2013:706156
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Martin-Chouly C, Le Moigne-Muller G, Van Herreweghe F et al (2012) TRAIL induces necroptosis involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent PARP-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 19:2003–2014
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732–738
Kawai T, Akira S (2008) Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1143:1–20
Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A (2003) Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol 33:105–136
Marvie P, Lisbonne M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Turlin B, Preisser L et al (2010) Interleukin-33 overexpression is associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans. J Cell Mol Med 14:1726–1739
Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Samson M (2012) IL-33 and HMGB1 alarmins: sensors of cellular death and their involvement in liver pathology. Liver Int 32:1200–1210
Arshad MI, Rauch M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Julia V, Leite-de-Moraes MC, Lucas-Clerc C et al (2011) NKT cells are required to induce high IL-33 expression in hepatocytes during ConA-induced acute hepatitis. Eur J Immunol 41:2341–2348
Arshad MI, Patrat-Delon S, Piquet-Pellorce C, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Genet V et al (2013) Pathogenic mouse hepatitis virus or poly(I:C) induce IL-33 in hepatocytes in murine models of hepatitis. PLoS One 8:e74278
Sakai N, Van Sweringen HL, Quillin RC, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Burns JM et al (2012) Interleukin-33 is hepatoprotective during liver ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Hepatology 56:1468–1478
Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Patrat-Delon S, Ezan F et al (2012) Tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL), but not FasL and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFa), regulates interleukin (IL)-33 expression in murine hepatocytes during acute hepatitis. Hepatology 56:2353–2362
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L et al (2007) IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:282–287
Ali S, Huber M, Kollewe C, Bischoff SC, Falk W, Martin MU (2007) IL-1 receptor accessory protein is essential for IL-33-induced activation of T lymphocytes and mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18660–18665
Volarevic V, Mitrovic M, Milovanovic M, Zelen I, Nikolic I, Mitrovic S et al (2012) Protective role of IL-33/ST2 axis in Con A-induced hepatitis. J Hepatol 56:26–33
Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM (2009) IL-33 raises alarm. Immunity 31:5–7
Cayrol C, Girard JP (2009) The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9021–9026
Luthi AU, Cullen SP, McNeela EA, Duriez PJ, Afonina IS, Sheridan C et al (2009) Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity 31:84–98
Talabot-Ayer D, Lamacchia C, Gabay C, Palmer G (2009) Interleukin-33 is biologically active independently of caspase-1 cleavage. J Biol Chem 284:19420–19426
Ali S, Nguyen DQ, Falk W, Martin MU (2010) Caspase 3 inactivates biologically active full length interleukin-33 as a classical cytokine but does not prohibit nuclear translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1512–1516
Bourd-Boittin K, Basset L, Bonnier D, L’Helgoualc’h A, Samson M, Theret N (2009) CX3CL1/fractalkine shedding by human hepatic stellate cells: contribution to chronic inflammation in the liver. J Cell Mol Med 13:1526–1535
Lisbonne M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Nauwelaers G, Turlin B, Lucas C, Herbelin A et al (2011) Invariant natural killer T-cell-deficient mice display increased CCl(4)-induced hepatitis associated with CXCL1 over-expression and neutrophil infiltration. Eur J Immunol 41:1720–1732
Diana J, Beaudoin L, Gautron AS, Lehuen A (2011) NKT and tolerance. Methods Mol Biol 677:193–206
Lu JV, Weist BM, van Raam BJ, Marro BS, Nguyen LV, Srinivas P et al (2011) Complementary roles of Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and receptor interacting protein kinase-3 (RIPK3) in T-cell homeostasis and antiviral immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:15312–15317
Duprez L, Takahashi N, Van Hauwermeiren F, Vandendriessche B, Goossens V, Vanden Berghe T et al (2011) RIP kinase-dependent necrosis drives lethal systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Immunity 35:908–918
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N et al (2005) Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 1:112–119
Welz PS, Wullaert A, Vlantis K, Kondylis V, Fernandez-Majada V, Ermolaeva M et al (2011) FADD prevents RIP3-mediated epithelial cell necrosis and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature 477:330–334
Gunther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, Amann K, Weigmann B, Neumann H et al (2011) Caspase-8 regulates TNF-alpha-induced epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature 477:335–339
An J, Mehrhof F, Harms C, Lattig-Tunnemann G, Lee SL, Endres M et al (2013) ARC is a novel therapeutic approach against acetaminophen-induced hepatocellular necrosis. J Hepatol 58:297–305
Takemoto K, Hatano E, Iwaisako K, Takeiri M, Noma N, Ohmae S et al (2014) Necrostatin-1 protects against reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced hepatotoxicity in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. FEBS open bio 4:777–787
Zhang YF, He W, Zhang C, Liu XJ, Lu Y, Wang H et al (2014) Role of receptor interacting protein (RIP)1 on apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated necroptosis during acetaminophen-evoked acute liver failure in mice. Toxicol Lett 225:445–453
Chang L, Kamata H, Solinas G, Luo JL, Maeda S, Venuprasad K et al (2006) The E3 ubiquitin ligase itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell 124:601–613
Kaufmann T, Jost PJ, Pellegrini M, Puthalakath H, Gugasyan R, Gerondakis S et al (2009) Fatal hepatitis mediated by tumor necrosis factor TNFalpha requires caspase-8 and involves the BH3-only proteins Bid and Bim. Immunity 30:56–66
Han J, Zhong CQ, Zhang DW (2011) Programmed necrosis: backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune system. Nat Immunol 12:1143–1149
Gantner F, Leist M, Lohse AW, Germann PG, Tiegs G (1995) Concanavalin A-induced T-cell-mediated hepatic injury in mice: the role of tumor necrosis factor. Hepatology 21:190–198
Kusters S, Gantner F, Kunstle G, Tiegs G (1996) Interferon gamma plays a critical role in T cell-dependent liver injury in mice initiated by concanavalin A. Gastroenterology 111:462–471
Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2011) Necroptosis turns TNF lethal. Immunity 35:849–851
Wang HX, Liu M, Weng SY, Li JJ, Xie C, He HL et al (2012) Immune mechanisms of Concanavalin A model of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 18:119–125
Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, Poli V et al (1996) Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science (New York, NY) 274:1379–1383
Wang K, Zhang S, Marzolf B, Troisch P, Brightman A, Hu Z et al (2009) Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4402–4407
Zhang Y, Jia Y, Zheng R, Guo Y, Wang Y, Guo H et al (2010) Plasma microRNA-122 as a biomarker for viral-, alcohol-, and chemical-related hepatic diseases. Clin Chem 56:1830–1838
Bala S, Petrasek J, Mundkur S, Catalano D, Levin I, Ward J et al (2012) Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.25873
Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N, Kelliher MA (2004) The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem 279:33185–33191
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch’en IL, Korkina O, Teng X et al (2008) Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 4:313–321
Knolle P, Schlaak J, Uhrig A, Kempf P, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Gerken G (1995) Human Kupffer cells secrete IL-10 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. J Hepatol 22:226–229
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh N, Peters AM, Chilvers ER (2010) Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol 31:318–324
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by INSERM, the Ministère de l’Education Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie, the University of Rennes 1, the Région Bretagne, the “Ligue contre le cancer, comités du grand Ouest”. Muhammad Imran Arshad was supported by a PhD fellowship from the Government of Pakistan and serving as an assistant professor under tenure track system (Higher Education Commission, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad). Sandrine Jouan-Lanhouet was supported by the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (doctoral fellowship). For immunohistochemistry, cytometry analysis, and animal house facilities, we would like to thank the dedicated platforms (i.e., H2P2 (Pascale Bellaud and Roselyne Viel), cytometry platform (Dr. Gersende Lacombe), and animal house platforms (Laurence Touami) of SFR BIOSIT, University of Rennes 1, France.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 539 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arshad, M.I., Piquet-Pellorce, C., Filliol, A. et al. The chemical inhibitors of cellular death, PJ34 and Necrostatin-1, down-regulate IL-33 expression in liver. J Mol Med 93, 867–878 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1270-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1270-6