Abstract
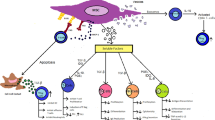
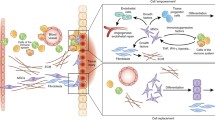
Bone marrow-derived stromal cells (BMSCs, or as they are frequently referred to as mesenchymal stem cells) have been long known to support hematopoiesis and to regenerate bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue. In the last decade, however, a vast amount of data surfaced in the literature to suggest new roles for these cells including tissue regeneration and immunomodulation. A great number of review articles appeared that summarize these new data and focus on different aspects of the physiology of these cells. In this present short review, we will try to summarize the available data based on both mouse and human cells describing how the function of BMSCs might be affected by an infectious environment. These data strongly support the idea that different toll-like receptor ligands can lead to substantial changes in the function of BMSCs that affect their proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and their production and release of immunomodulatory factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianco P, Kuznetsov SA, Riminucci M, Gehron Robey P (2006) Postnatal skeletal stem cells. Methods Enzymol 419:117–148
Mankani MH, Kuznetsov SA, Robey PG (2007) Formation of hematopoietic territories and bone by transplanted human bone marrow stromal cells requires a critical cell density. Exp Hematol 35:995–1004
Phinney DG (2007) Biochemical heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cell populations: clues to their therapeutic efficacy. Cell Cycle 6:2884–2889
Vayssade M, Nagel MD (2009) Stromal cells. Front Biosci 14:210–224
Mishra PJ, Glod JW, Banerjee D (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells: flip side of the coin. Cancer Res 69:1255–1258
Nasef A, Ashammakhi N, Fouillard L (2008) Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stromal cells: possible mechanisms. Regen Med 3:531–546
Crop M, Baan C, Weimar W, Hoogduijn M (2009) Potential of mesenchymal stem cells as immune therapy in solid-organ transplantation. Transpl Int 22:365–376
Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 8:726–736
Beutler B, Jiang Z, Georgel P, Crozat K, Croker B, Rutschmann S, Du X, Hoebe K (2006) Genetic analysis of host resistance: toll-like receptor signaling and immunity at large. Annu Rev Immunol 24:353–389
Apostolopoulos V, McKenzie IF (2001) Role of the mannose receptor in the immune response. Current Molecular Medicine 1:469–474
Strober W, Murray PJ, Kitani A, Watanabe T (2006) Signalling pathways and molecular interactions of NOD1 and NOD2. Nat Rev Immunol 6:9–20
Meylan E, Tschopp J (2006) Toll-like receptors and RNA helicases: two parallel ways to trigger antiviral responses. Mol. Cell 22:561–569
Liotta F, Angeli R, Cosmi L, Fili L, Manuelli C, Frosali F, Mazzinghi B, Maggi L, Pasini A, Lisi V, Santarlasci V, Consoloni L, Angelotti ML, Romagnani P, Parronchi P, Krampera M, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F (2008) Toll-like receptors 3 and 4 are expressed by human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and can inhibit their T cell modulatory activity by impairing Notch signaling. Stem Cells 26:279–289
Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Lutz C, Lanz TV, Tritschler I, Koppel A, Tolosa E, Hoberg M, Anderl J, Aicher WK, Weller M, Wick W, Platten M (2009) Toll-like receptor engagement enhances the immunosuppressive properties of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inducing indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase-1 via interferon-beta, and protein kinase R. Stem Cells 27:909–919
Tomchuck SL, Zwezdaryk KJ, Coffelt SB, Waterman RS, Danka ES, Scandurro AB (2008) Toll-like receptors on human mesenchymal stem cells drive their migration and immunomodulating responses. Stem Cells 26:99–107
Pevsner-Fischer M, Morad V, Cohen-Sfady M, Rousso-Noori L, Zanin-Zhorov A, Cohen S, Cohen IR, Zipori D (2007) Toll-like receptors and their ligands control mesenchymal stem cell functions. Blood 109:1422–1432
Nemeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller BH, Brown JM, Hu X, Jelinek I, Star RA, Mezey E (2009) Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med 15:42–49
Crisostomo PR, Wang Y, Markel TA, Wang M, Lahm T, Meldrum DR (2008) Human mesenchymal stem cells stimulated by TNF-alpha, LPS, or hypoxia produce growth factors by an NF kappa B- but not JNK-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:C675–C682
Wang ZJ, Zhang FM, Wang LS, Yao YW, Zhao Q, Gao X (2009) Lipopolysaccharides can protect mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and enhance proliferation of BMSCs via Toll-like receptor(TLR)-4 and PI3K/Akt. Cell Biol Int 33:665–674
Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, Joodi R, Brigham KL, Iyer S, Rojas M (2007) Prevention of endotoxin-induced systemic response by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L131–L141
Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH, Liles WC, Stewart DJ (2007) Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med 4:e269
Gonzalez-Rey E, Anderson P, Gonzalez MA, Rico L, Buscher D, Delgado M (2009) Human adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue protect against experimental colitis and sepsis. Gut 58:929–939
Parsons CH, Szomju B, Kedes DH (2004) Susceptibility of human fetal mesenchymal stem cells to Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Blood 104:2736–2738
Sundin M, Lindblom A, Orvell C, Barrett AJ, Sundberg B, Watz E, Wikman A, Broliden K, Le Blanc K (2008) Persistence of human parvovirus B19 in multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells expressing the erythrocyte P antigen: implications for transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 14:1172–1179
Rollin R, Alvarez-Lafuente R, Marco F, Jover JA, Hernandez-Garcia C, Rodriguez-Navas C, Lopez-Duran L, Fernandez-Gutierrez B (2007) Human parvovirus B19, varicella zoster virus, and human herpesvirus-6 in mesenchymal stem cells of patients with osteoarthritis: analysis with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Osteoarthr Cartil 15:475–478
Sundin M, Orvell C, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, Ringden O, Le Blanc K (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells are susceptible to human herpesviruses, but viral DNA cannot be detected in the healthy seropositive individual. Bone Marrow Transplant 37:1051–1059
Xie C, Zheng YB, Zhu HP, Peng L, Gao ZL (2009) Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are resistant to HBV infection during differentiation into hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro. Cell Biol Int 33:493–500
Karlsson H, Samarasinghe S, Ball LM, Sundberg B, Lankester AC, Dazzi F, Uzunel M, Rao K, Veys P, Le Blanc K, Ringden O, Amrolia PJ (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells exert differential effects on alloantigen and virus–specific T cell responses. Blood 112:532–541
Kang HS, Habib M, Chan J, Abavana C, Potian JA, Ponzio NM, Rameshwar P (2005) A paradoxical role for IFN-gamma in the immune properties of mesenchymal stem cells during viral challenge. Exp Hematol 33:796–803
Morandi F, Raffaghello L, Bianchi G, Meloni F, Salis A, Millo E, Ferrone S, Barnaba V, Pistoia V (2008) Immunogenicity of human mesenchymal stem cells in HLA-class I-restricted T cell responses against viral or tumor-associated antigens. Stem Cells 26:1275–1287
Rasmusson I, Uhlin M, Le Blanc K, Levitsky V (2007) Mesenchymal stem cells fail to trigger effector functions of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol 82:887–893
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, Gotherstrom C, Hassan M, Uzunel M, Ringden O (2004) Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 363:1439–1441
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the Division of Intramural Research of the NIDCR, Intramural Research Program of the NIH.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nemeth, K., Mayer, B. & Mezey, E. Modulation of bone marrow stromal cell functions in infectious diseases by toll-like receptor ligands. J Mol Med 88, 5–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0523-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0523-7