Abstract
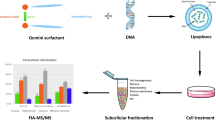
In this study, the in vitro and in vivo transfection capacity of novel pH-sensitive sugar-based gemini surfactants was investigated. In an aqueous environment at physiological pH, these compounds form bilayer vesicles, but they undergo a lamellar-to-micellar phase transition in the endosomal pH range as a consequence of an increased protonation state. In the same way, lipoplexes made with these amphiphiles exhibit a lamellar morphology at physiological pH and a non-lamellar phase at acidic pH. In this study, we confirm that the gemini surfactants are able to form complexes with plasmid DNA at physiological pH and are able to transfect efficiently CHO cells in vitro. Out of the five compounds tested here, two of these amphiphiles, GS1 and GS2, led to 70% of transfected cells with a good cell survival. These two compounds were tested further for in vivo applications. Because of their lamellar organisation, these lipoplexes exhibited a good colloidal stability in salt and in serum at physiological pH compatible with a prolonged stability in vivo. Indeed, when injected intravenously to mice, these stable lipoplexes apparently did not substantially accumulate, as inferred from the observation that transfection of the lungs was not detectable, as examined by in vivo bioluminescence. This potential of avoiding ‘preliminary capture’ in the lungs may, thus, be further exploited in developing devices for specific targeting of gemini lipoplexes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- lipolexes:
-
Complexes of DNA and cationic lipids
- PEG:
-
Poly(ethylene glycol)
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GS:
-
Gemini surfactant
- DOPE:
-
1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
- DOTAP:
-
N-[1-(2,3-dioleyl)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonim chloride
- Saint-2:
-
N-methyl-4-(dioleyl)methylpyridinium
- N-Rh-PE:
-
N-(lissamine rhodamine B sulphonyl)phosphatidylethanolamine
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- SAXS:
-
Small angle X-ray scattering
- HEPES:
-
N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- MES:
-
2-[N-morpholino]ethanesulfonic acid
- HBS solution:
-
HEPES buffered saline solution
- CHO cells:
-
Chinese hamster ovarian cells
- AU:
-
Arbitrary unit
References
Felgner PL (1996) Improvements in cationic liposomes for in vivo gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther 7(15):1791–1793
Romano G, Claudio PP, Kaiser HE, Giordano A (1998) Recent advances, prospects and problems in designing new strategies for oligonucleotide and gene delivery in therapy. In Vivo 12(1):59–67
Felgner PL (1997) Nonviral strategies for gene therapy. Sci Am 276(6):102–106
van der Woude I, Wagenaar A, Meekel AA, ter Beest MB, Ruiters MH, Engberts JB, Hoekstra D (1997) Novel pyridinium surfactants for efficient, nontoxic in vitro gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(4):1160–1165
Shi F, Nomden A, Oberle V, Engberts JB, Hoekstra D (2001) Efficient cationic lipid-mediated delivery of antisense oligonucleotides into eukaryotic cells: down-regulation of the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor. Nucleic Acids Res 29(10):2079–2087
Garcia-Chaumont C, Seksek O, Grzybowska J, Borowski E, Bolard J (2000) Delivery systems for antisense oligonucleotides. Pharmacol Ther 87(2-3):255–277
Chien PY, Wang J, Carbonaro D, Lei S, Miller B, Sheikh S, Ali SM, Ahmad MU, Ahmad I (2005) Novel cationic cardiolipin analogue-based liposome for efficient DNA and small interfering RNA delivery in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 12(3):321–328
Zelphati O, Wang Y, Kitada S, Reed JC, Felgner PL, Corbeil J (2001) Intracellular delivery of proteins with a new lipid-mediated delivery system. J Biol Chem 276(37):35103–35110
Simberg D, Weisman S, Talmon Y, Barenholz Y (2004) DOTAP (and other cationic lipids): chemistry, biophysics, and transfection. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carr Syst 21(4):257–317
Simeoni F, Morris MC, Heitz F, Divita G (2003) Insight into the mechanism of the peptide-based gene delivery system MPG: implications for delivery of siRNA into mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 31(11):2717–2724
Mountain A (2000) Gene therapy: the first decade. Trends Biotechnol 18(3):119–128
de Lima MC, Simoes S, Pires P, Faneca H, Duzgunes N (2001) Cationic lipid-DNA complexes in gene delivery: from biophysics to biological applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47(2–3):277–294
Simberg D, Weisman S, Talmon Y, Faerman A, Shoshani T, Barenholz Y (2003) The role of organ vascularization and lipoplex-serum initial contact in intravenous murine lipofection. J Biol Chem 278(41):39858–39865
Mahato RI, Anwer K, Tagliaferri F, Meaney C, Leonard P, Wadhwa MS, Logan M, French M, Rolland A (1998) Biodistribution and gene expression of lipid/plasmid complexes after systemic administration. Hum Gene Ther 9(14):2083–2099
Niven R, Pearlman R, Wedeking T, Mackeigan J, Noker P, Simpson-Herren L, Smith JG (1998) Biodistribution of radiolabeled lipid-DNA complexes and DNA in mice. J Pharm Sci 87(11):1292–1299
Li S, Tseng WC, Stolz DB, Wu SP, Watkins SC, Huang L (1999) Dynamic changes in the characteristics of cationic lipidic vectors after exposure to mouse serum: implications for intravenous lipofection. Gene Ther 6(4):585–594
Li S, Rizzo MA, Bhattacharya S, Huang L (1998) Characterization of cationic lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) complexes for intravenous gene delivery. Gene Ther 5(7):930–937
Tam P, Monck M, Lee D, Ludkovski O, Leng EC, Clow K, Stark H, Scherrer P, Graham RW, Cullis PR (2000) Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles for systemic gene therapy. Gene Ther 7(21):1867–1874
Bartsch M, Weeke-Klimp AH, Hoenselaar EP, Stuart MC, Meijer DK, Scherphof GL, Kamps JA (2004) Stabilized lipid coated lipoplexes for the delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to liver endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. J Drug Target 12(9–10):613–621
Holland JW, Cullis PR, Madden TD (1996) Poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugates promote bilayer formation in mixtures of non-bilayer-forming lipids. Biochemistry 35(8):2610–2617
Shi F, Wasungu L, Nomden A, Stuart MCA, Polushkin E, Engberts JBFN, Hoekstra D (2002) Interference of polyethylene glycol-lipid analogues with cationic lipid-mediated delivery of oligonucleotides; role of lipid exchangeability and non-lamellar transitions. Biochem J 366:333–341
Martin-Herranz A, Ahmad A, Evans HM, Ewert K, Schulze U, Safinya CR (2004) Surface functionalized cationic lipid-DNA complexes for gene delivery: PEGylated lamellar complexes exhibit distinct DNA-DNA interaction regimes. Biophys J 86(2):1160–1168
Woodle MC (1998) Controlling liposome blood clearance by surface-grafted polymers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 32(1–2):139–152
Song LY, Ahkong QF, Rong Q, Wang Z, Ansell S, Hope MJ, Mui B (2002) Characterization of the inhibitory effect of PEG-lipid conjugates on the intracellular delivery of plasmid and antisense DNA mediated by cationic lipid liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1558(1):1–13
Bergstrand N, Arfvidsson MC, Kim JM, Thompson DH, Edwards K (2003) Interactions between pH-sensitive liposomes and model membranes. Biophys Chem 104(1):361–379
Li W, Huang Z, MacKay JA, Grube S, Szoka FC Jr (2005) Low-pH-sensitive poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-stabilized plasmid nanolipoparticles: effects of PEG chain length, lipid composition and assembly conditions on gene delivery. J Gene Med 7(1):67–79
Guo X, MacKay JA, Szoka FC Jr (2003) Mechanism of pH-triggered collapse of phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes stabilized by an ortho ester polyethyleneglycol lipid. Biophys J 84(3):1784–1795
Ambegia E, Ansell S, Cullis P, Heyes J, Palmer L, MacLachlan I (2005) Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles containing PEG-diacylglycerols exhibit extended circulation lifetimes and tumor selective gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669(2):155–163
Rejman J, Wagenaar A, Engberts JB, Hoekstra D (2004) Characterization and transfection properties of lipoplexes stabilized with novel exchangeable polyethylene glycol-lipid conjugates. Biochim Biophys Acta 1660(1-2):41–52
Johnsson M, Wagenaar A, Stuart MCA, Engberts JBFN (2003) Sugar-based gemini surfactants with pH-dependent aggregation behavior: vesicle-to-micelle transition, critical micelle concentration, and vesicle surface charge reversal. Langmuir 19(11):4609–4618
Johnsson M, Wagenaar A, Engberts JBFN (2003) Sugar-based gemini surfactant with a vesicle-to-micelle transition at acidic pH and a reversible vesicle flocculation near neutral pH. J Am Chem Soc 125(3):757–760
Johnsson M, Engberts JBFN (2004) Novel sugar-based gemini surfactants: aggregation properties in aqueous solution. J Phys Org Chem 17(11):934–944
Scarzello M, Klijn JE, Wagenaar A, Stuart MCA, Hulst R, Engberts JBFN (2006) pH-dependent aggregation properties of mixtures of sugar-based gemini surfactants with phospholipids and single-tailed surfactants. Langmuir 22(6):2558–2568
Fielden ML, Perrin C, Kremer A, Bergsma M, Stuart MCA, Camilleri P, Engberts JBFN (2001) Sugar-based tertiary amino gemini surfactants with a vesicle-to-micelle transition in the endosomal pH range mediate efficient transfection in vitro. Eur J Biochem 268(5):1269–1279
Bell PC, Bergsma M, Dolbnya IP, Bras W, Stuart MCA, Rowan AE, Feiters MC, Engberts JBFN (2003) Transfection mediated by gemini surfactants: engineered escape from the endosomal compartment. J Am Chem Soc 125(6):1551–1558
Smisterova J, Wagenaar A, Stuart MCA, Polushkin E, ten Brinke G, Hulst R, Engberts JBFN, Hoekstra D (2001) Molecular shape of the cationic lipid controls the structure of cationic lipid/dioleylphosphatidylethanolamine-DNA complexes and the efficiency of gene delivery. J Biol Chem 276(50):47615–47622
Zuhorn IS, Bakowsky U, Polushkin E, Visser WH, Stuart MCA, Engberts JBFN, Hoekstra D (2005) Nonbilayer phase of lipoplex-membrane mixture determines endosomal escape of genetic cargo and transfection efficiency. Mol Ther 11(5):801–810
Scarzello M, Chupin V, Wagenaar A, Stuart MCA, Engberts JBFN, Hulst R (2005) Polymorphism of pyridinium amphiphiles for gene delivery: influence of ionic strength, helper lipid content, and plasmid DNA complexation. Biophys J 88(3):2104–2113
Oberle V, Bakowsky U, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D (2000) Lipoplex formation under equilibrium conditions reveals a three-step mechanism. Biophys J 79(3):1447–1454
Zuhorn IS, Visser WH, Bakowsky U, Engberts JB, Hoekstra D (2002) Interference of serum with lipoplex-cell interaction: modulation of intracellular processing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1560(1–2):25–36
McElroy WD, DeLuca MA (1983) Firefly and bacterial luminescence: basic science and applications. J Appl Biochem 5(3):197–209
Wilson T, Hastings JW (1998) Bioluminescence. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 14:197–230
Scarzello M, Smisterova J, Wagenaar A, Stuart MC, Hoekstra D, Engberts JB, Hulst R (2005) Sunfish cationic amphiphiles: toward an adaptative lipoplex morphology. J Am Chem Soc 127(29):10420–10429
Audouy SA, de Leij LF, Hoekstra D, Molema G (2002) In vivo characteristics of cationic liposomes as delivery vectors for gene therapy. Pharm Res 19(11):1599–1605
Iyer M, Berenji M, Templeton NS, Gambhir SS (2002) Noninvasive imaging of cationic lipid-mediated delivery of optical and PET reporter genes in living mice. Mol Ther 6(4):555–562
Stuart MCA, van de Pas JC, Engberts JBFN (2005) The use of Nile Red to monitor the aggregation behavior in ternary surfactant-water-organic solvent systems. J Phys Org Chem 18(9):929–934
Li W, Ishida T, Okada Y, Oku N, Kiwada H (2005) Increased gene expression by cationic liposomes (TFL-3) in lung metastases following intravenous injection. Biol Pharm Bull 28(4):701-706
Audouy S, Molema G, de Leij L, Hoekstra D (2000) Serum as a modulator of lipoplex-mediated gene transfection: dependence of amphiphile, cell type and complex stability. J Gene Med 2(6):465-476
Crook K, Stevenson BJ, Dubouchet M, Porteous DJ (1998) Inclusion of cholesterol in DOTAP transfection complexes increases the delivery of DNA to cells in vitro in the presence of serum. Gene Ther 5(1):137-143
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO)/NDRF Innovative Drug Research (940-70-001). The authors would like to thank Dr. Marc Stuart and Dr. Jaap Klijn for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wasungu, L., Scarzello, M., van Dam, G. et al. Transfection mediated by pH-sensitive sugar-based gemini surfactants; potential for in vivo gene therapy applications. J Mol Med 84, 774–784 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0067-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0067-z