Abstract
Purpose
Submental intubation is widely accepted as a safe and effective alternative to nasal intubation or tracheostomy in head and neck surgery patients. Forceful or careless technique can cause significant bleeding and trauma to the soft tissues at this point, increasing the likelihood of troublesome sublingual haematoma.
Methods
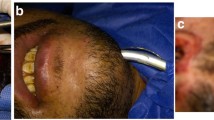
We describe the use of a percutaneous tracheostomy horn (Cook Medical Blue Rhino®) to allow minimally traumatic submental intubation without the need for serial dilations. A patient with severe midfacial injuries requiring surgery was intubated via a standard oral technique. Following this, submental access was achieved using a novel dilational technique with a tracheostomy dilator. This resulted in a very secure and safe submental intubation and unrestricted access to the entire surgical field.
Results
The single instrument, one-pass dilation technique to achieve submental intubation was found to be easy, quick, and avoided excessive trauma to the floor of mouth.
Conclusion
Patients will sometimes require a protected airway that allows surgeons unrestricted and simultaneous access to the dental occlusion, oral cavity, midface, and nose. In our case, this simple, easy, and quick adaptation of an established technique using a tracheostomy dilator is an excellent alternative to the traditional blunt dissection used to achieve submental intubation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisemann B, Eisemann M, Rizvi M, Urata M, Lypka M. Defining the role for submental intubation. J Clin Anesth. 2014;26:238–42.
Amin M, Dill-Russell P, Manisali M, Lee R, Sinton I. Facial fractures and submental tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia. 2002;57:1195–212.
Chandu A, Witherow H, Stewart A. Submental intubation in orthognathic surgery: initial experience. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46:561–3.
Saheb A, Nath V, Kumar K, Padmaja P. A novel method using Seldinger’s technique for submental intubation in major craniomaxillofacial fractures: a case series. Indian J Anaesth. 2014;58:48–50.
Biswas B, Joshi S, Bhattacharyya P, Gupta P. Percutaneous dilational tracheostomy kit: an aid to submental intubation. Anesth Analg. 2006;103(4):1055.
Yadav S, Deo G. Submental intubation including extubation: airway complications of Maxillmandibular fixation. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2012;2012:841051.
Cools-Lartigue J, Aboalsaud A, Gill H, Ferri L. Evolution of percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy—a review of current techniques and their pitfalls. World J Surg. 2013;37:1633–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Atheer Ujam and Michael Perry declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ujam, A., Perry, M. Minimally traumatic submental intubation: a novel dilational technique. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 43, 359–362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-016-0675-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-016-0675-4