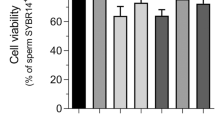
Abstract
The spermicidal and microbicidal activity of Asiatic acid isolated from Shorea robusta resin was explored earlier using rat spermatozoa. The current investigation is aimed at examining the spermicidal efficacy of the molecule against human spermatozoa along with the plausible pathway involved in its spermicidal action. Spermicidal efficacy of Asiatic acid against human spermatozoa was evaluated in vitro by modified Sander-Cramer test and the subsequent mode of spermicidal action was assessed by (a) hypo-osmotic swelling test, (b) double fluoroprobe staining, (c) flow cytometric detection of apoptosis by fluorescein isothiocyanate-Annexin V labelling and (d) JC-1 labelling. The minimum effective concentration of the molecule against human spermatozoa was found to be 500 µg/ml which is comparable to the standard spermicide nonoxynol-9 (minimum effective concentration 550 µg/ml). The mechanistic pathway of spermicidal action of the molecule involves apoptosis rather than general cell necrosis. The molecule Asiatic acid may be explored as an ingredient for the formulation of a new generation non-detergent type microbicidal contraceptive.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzar M, He L, Buhr MM, Kroetsch TG, Pauls KP (2002) Sperm apoptosis in fresh and cryopreserved bull semen detected by flow cytometry and its relationship with fertility. Biol Reprod 66:354–360
Bains R, Moe MC, Larsen GA, Berg-Johnsen J, Vinje ML (2006) Volatile anaesthetics depolarize neural mitochondria by inhibition of the electron transport chain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 50:572–579
Banerjee M, Hazra A, Bharitkar YP, Mondal NB (2014) Insights of spermicidal research: an update. JFIV Reprod Med Genet 3:138. doi:10.4172/2375-4508.1000138
Bharitkar YP, Banerjee M, Kumar S, Paira R, Meda R, Kuotsu K, Mondal NB (2013) Search for a potent microbicidal spermicide from the isolates of Shroea robusta resin. Contraception 88:133–140
Bhowal SK, Lala S, Hazra A, Paira P, Banerjee S, Mondal NB, Chakraborty S (2008) Synthesis and assessment of fertility regulating potential of 2-(2″-chloroacetamidobenzyl)-3-(3′-indolyl)quinoline in adult rats as a male contraceptive agent. Contraception 77:214–222
Cho CW, Choi DS, Cardone MH, Kim CW, Sinskey AJ, Rha C (2006) Glioblastoma cell death induced by asiatic acid. Cell Biol Toxicol 22:393–408
D’Cruz OJ, Venkatachalam TK, Uckun FM (2000) Structural requirements for potent human spermicidal activity of dual-functionaryl phosphate derivative of bromo-methoxy zidovudine (Compound WHI-07). Biol Reprod 62:37–44
De Lamirande E, Leclerc P, Gagnon C (1997) Capacitation as a regulatory event that primes spermatozoa for the acrosome reaction and fertilization. Mol Hum Reprod 3:175–94
Flajshans M, Cosson J, Rodina M, Linhart O (2004) The application of image cytometry to viability assessment in dual fluorescence-stained fish spermatozoa. Cell Biol Int 28:955–959
Garner DL, Johnson LA (1995) Viability assessment of mammalian sperm using SYBR-14 and propidium iodide. Biol Reprod 53:276–284
Hardy E, De Padua KS, Jimenez AL, Zaneveld LJD (1998) Women’s preferences for vaginal antimicrobial contraceptives. II. Preferred characteristics according to women’s age and socioeconomic status. Contraception 58:239–44
Jain RK, Jain A, Kumar R, Verma V, Maikhuri PJ, Sharma VL, Mitra K, Batra S, Gupta G (2010) Functional attenuation of human sperm by novel, non-surfactantspermicides: precise targeting of membrane physiology without affecting structure. Hum Reprod 25:1165–1176
Jayendran RS, Van der Ven HH, Perag-Pelaez M, Crabo BG, Zaneveld LJ (1984) Development of an assay to assess the functional integrity of the human sperm membrane and its relationship to other semen characteristics. J Reprod Fertil 70:219–228
Khillare B, Shrivastav TG (2003) Spermicidal activity of Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf extract. Contraception 68:225–229
Kim IC, Waller DP, Marcelle GB, Cordell GA, Fong HH, Pirkle WH, Pilla L, Matlin SA (1984) Comparative in vitro spermicidal effects of (+/-)-gossypol, (+)-gossypol, (-)-gossypol and gossypolone. Contraception 30:253–259
Kumar S, Biswas S, Banerjee S, Mondal NB (2011) Evaluation of safety margins of Chenopodium album seed decoction: 14-day subacute toxicity and microbicidal activity studies. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 9:102
Kumar S, Biswas S, Mandal D, Roy HN, Chakraborty S, Kabir SN, Banerjee S, Mondal NB (2007) Chenopodium album seed extract: a potent sperm-immobilizing agent both in vitro and in vivo. Contraception 75:71–78
Kumar S, Chatterjee R, Dolai S, Adak S, Kabir SN, Banerjee S, Mondal NB (2008) Chenopodium album seed extract induced sperm cell death: exploration of a plausible pathway. Contraception 77:456–462
Martin HL, Richardson BA, Nyange PM, Lavreys L, Hillier SL, Chohan BH, Mandaliya K, Ndinya-Achola JO, Bwayo J, Kreiss J (1999) Vaginal lactobacilli, microbial flora and risk of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and sexually transmitted disease acquisition. J Infect Dis 180:1863–1868
Mukherjee M, Datta M, Biswas S, Pal AK, Malabar D, Bhattacharyya AK, Bhatacharya S, Kobayashi H (2003) Immotilin, a novel sperm immobilizing protein. Fertil Steril 79:1673–1675
Norzaharaini MG, Wan Norshazwani WS, Hasmah A (2011) A Preliminary study on antimicrobial activities of asiaticoside and asiatic acid against selected gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Health Environ J 2:23–26
Paira P, Hazra A, Kumar S, Paira R, Sahu KB, Naskar S, Saha P, Mondal S, Maity A, Banerjee S, Mondal NB (2009) Efficient synthesis of 3,3-diheteroaromatic oxindole analogues and their in vitro evaluation for spermicidal potential. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:4786–4789
Pal D, Chakraborty P, Ray HN, Pal BC, Mitra D, Kabir SN (2009) Acaciaside-B-enriched fraction of Acacia auriculiformis is a prospective spermicide with no mutagenic property. Reproduction 138:453–462
Reddy KV, Aranha C, Gupta SM, Yedery RD (2004) Evaluation of antimicrobial peptide nisin as a safe vaginal contraceptive agent in rabbits: in vitro and in vivo studies. Reproduction 128:117–126
Richardson BA, Martin HL, Stevens CE, Hillier SL, Mwatha AK, Chohan BH, Nyange PM, Mandaliya K, Ndinya-Achola J, Kreiss JK (1998) Use of nonoxynol-9 and changes in vaginal lactobacilli. J Infect Dis 178:441–445
Saha P, Majumdar S, Pal D, Pal BC, Kabir SN (2010) Evaluation of spermicidal activity of MI-saponin A. Reprod sci 17:454–464
Yun KJ, Kim JY, Kim JB, Lee KW, Jeong SY, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Cho YW, Yun K, Lee KT (2008) Inhibition of LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the IKK and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 8:431–441
Zaneveld LJD (1994) Vaginal contraception since 1994: chemical agents and barrier devices. In: Van Look PFA, Perez-Palacios G, (eds). Contraceptive Research and Developmen, Oxford, p 69–90. Oxford University Press
Zaneveld LJD, Waller DP, Anderson RA, Chany 2nd C, Rencher WF, Feathergill K, Diao XH, Doncel GF, Herold B, Cooper M (2002) Efficacy and safety of a new vaginal contraceptive antimicrobial formulation containing high molecular weight poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate). Biol Reprod 66:886–894
Acknowledgement
The authors express their thanks and gratitude to Department of Science and Technology (DST, Women Scientist scheme (SR/WOS-A/LS491/2013(G)) for providing the financial support for this work and fellowship to SK. NBM and YPB are indebted to CSIR for the award of Emeritus Scientist scheme and Research Associate ship, respectively. The authors are also thankful to the Director, IICB, for laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Bharitkar, Y.P., Kumar, G.S. et al. Asiatic acid, a non-detergent type spermicide: exploration of plausible pathway of spermicidal action. Med Chem Res 25, 1908–1915 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1623-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1623-x