Abstract
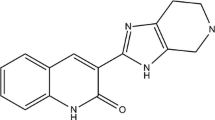
The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR2) is an attractive target for the development of novel anticancer agents. Molecular docking and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) were used to investigate how inhibitors’ chemical structures relate to the inhibitory activities. The molecular docking studies show that at least one hydrogen bond with LYS866 residue is one of the essential requirements for the optimum binding of a series of 42 pyridylmethylthio inhibitors. The obtained QSAR model indicates that the inhibitory activity can be described by solvent-accessible molecular surface area, topological electronic indices, local dipole index, steric interaction, and hydrogen bonding energies between the receptor and the inhibitors. Furthermore, several validation methods were used to evaluate the predictive capacity of the generated models. The satisfactory results (R 2L25 %O = 0.819, Q 2LOO = 0.838, R 2p = 0.866, RMSELOO = 0.315, and RMSEL25 %O = 0.337) suggest that the models exhibited considerable predictive power which can be used in prediction of activity of new pyridylmethylthio inhibitors. Also the docking analysis showed that the interaction of the inhibitors with residues ALA879, ASP(1044, 1026), LEU880, PHE843, and LYS866 plays an important role in the activities of the inhibitors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahman T, Eisen T (2004) Kinase Inhibition with BAY 43–9006 in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:6388–6392
Cho SJ, Pasha FA, Muddassar M, Neaz MM (2009) Pharmacophore and docking-based combined in silico study of KDR inhibitors. J Mol Graph Model 28:54–61
Cross MJ, Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2: structure, function, intracellular signaling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell Signal 19:2003–2012
Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Annal. Stat 19:1–141
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2009) Shuffling multivariate adaptive regression splines and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system as tools for QSAR study of SARS inhibitors. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:853–860
Klebl BM, Muller G (2005) Second-generation kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9:975–993
Neaz MM, Pasha FA, Muddassar M, Lee SH, Sim T, Hah J, Cho SJ (2009) Pharmacophore based 3D-QSAR study of VEGFR-2 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 18:127–142
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386:671–674
Roy Roy P (2002) On some aspects of variable selection for partial least squares regression models. QSAR Comb Sci 27:302–313
Shahbazikhah P, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Khaksar R, Alamdari RF, Zare-Shahabadi V (2011) Predicting partition coefficients of migrants in food simulant/polymer systems using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. J Braz Chem Soc 22:1446–1451
Suykens J, Gestel J, Brabanter J, Moor B, Vandewalle J (2002) Least squares support vector machines. World Scientifics, Singapore
Tajima H, Honda T, Kawashima K, Sasabuchi Y, Yamamoto M, Ban M, Okamoto K, Inoue K, Inaba T, Takeno Y, Aono H (2010) Pyridylmethylthio derivatives as VEGF inhibitors Part 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:7234–7238
Tajima H, Honda T, Kawashima K, Sasabuchi Y, Yamamoto M, Ban M, Okamoto K, Inoue K, Inaba T, Takeno Y, Tsuboi T, Tonouchi A, Aono H (2011) Pyridylmethylthio derivatives as VEGF inhibitors Part 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:1232–1235
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2000) Handbook of Molecular Descriptors. Wiley/VCH, Weinheim
Tropsha A, Golbraikh A (2002) Beware of q2. J Mol Graph Model 20:269–276
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York
Walsh DA, Haywood L (2001) Angiogenesis: a therapeutic target in arthritis. Curr Opin Invest Drugs 2:1054–1063
Yao X, Du J, Lei B, Qin J, Liu H (2009) Molecular modeling studies of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors using QSAR and docking. J Mol Graph Model 27:642–654
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asadollahi-Baboli, M., Mani-Varnosfaderani, A. Shuffling multivariate adaptive regression splines as a predictive method for modeling of novel pyridylmethylthio derivatives as VEGFR2 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 22, 2645–2653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0266-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0266-9