Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the potential benefits on students’ eating habits, of incorporating healthy nutrition education as part of a school food aid program.
Methods
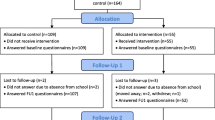
146 schools participating in the DIATROFI Program in Greece during the 2013–2014 school year were randomly allocated to the environmental intervention (received a healthy daily meal) and the multicomponent intervention (MI) group (in addition to the meal, a healthy nutrition educational program was applied). The analysis, based on 3627 pre–post intervention questionnaire pairs, was stratified for children (ages 4–11 years) and adolescents (ages 12–18 years).
Results
Children participating in the MI group displayed 25 % higher odds of increasing the weekly consumption of milk/yoghurt and fruits, 61 % higher odds of improving BMI from overweight/obese to normal and 2.5 times higher odds of improving from underweight to normal. For adolescents in the MI group, the odds of increasing the consumption of vegetables were 40 % higher. In both intervention groups, approximately one in four overweight/obese adolescents reached normal weight.
Conclusions
Educational programs on healthy nutrition might be considered worth implementing in the framework of school food aid programs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonogeorgos G, Panagiotakos DB, Grigoropoulou D, Papadimitriou A, Anthracopoulos M, Nicolaidou P, Priftis KN (2013) The mediating effect of parents’ educational status on the association between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and childhood obesity: the PANACEA study. Int J Public Health 58:401–408
Bountziouka V, Bathrellou E, Giotopoulou A, Katsagoni C, Bonou M, Vallianou N, Barbetseas J, Avgerinos PC, Panagiotakos DB (2012) Development, repeatability and validity regarding energy and macronutrient intake of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: methodological considerations. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 22:659–667
Busch V, de Leeuw JR, de Harder A, Schrijvers AJ (2013) Changing multiple adolescent health behaviors through school-based interventions: a review of the literature. J Sch Health 83:514–523
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Cole TJ, Flegal KM, Nicholls D, Jackson AA (2007) Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: international survey. BMJ 335:194
Coleman-Jensen A, Nord M, Singh A (2013) Household Food Security in the United States in 2012. In: ERR-155. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service
Cook B, Wayne GF, Valentine A, Lessios A, Yeh E (2013) Revisiting the evidence on health and health care disparities among the Roma: a systematic review 2003–2012. Int J Public Health 58:885–911
Currie C, Molcho M, Boyce W, Holstein B, Torsheim T, Richter M (2008) Researching health inequalities in adolescents: the development of the Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) family affluence scale. Soc Sci Med 66:1429–1436
Dalma A, Kastorini C-M, Zota D, Veloudaki A, Petralias A, Yannakoulia M, Linos A (2016) Perceptions of parents and children, participating in a school-based feeding program in disadvantaged areas in Greece: a qualitative study. Care Health Dev, Child. doi:10.1111/cch.12315
Deitchler M, Ballard T, Swindale A, Coates J (2011) Introducing a simple measure of household hunger for cross-cultural use. In: Food and nutrition technical assistance II project, AED, Washington, D.C
Foltz JL, May AL, Belay B, Nihiser AJ, Dooyema CA, Blanck HM (2012) Population-level intervention strategies and examples for obesity prevention in children. Annu Rev Nutr 32:391–415
Gonzalez-Suarez C, Worley A, Grimmer-Somers K, Dones V (2009) School-based interventions on childhood obesity: a meta-analysis. Am J Prev Med 37:418–427
Ickes MJ, McMullen J, Haider T, Sharma M (2014) Global school-based childhood obesity interventions: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:8940–8961
Jacka FN, Kremer PJ, Berk M, de Silva-Sanigorski AM, Moodie M, Leslie ER, Pasco JA, Swinburn BA (2011) A prospective study of diet quality and mental health in adolescents. PLoS One 6:e24805
Kastorini CM, Lykou A, Yannakoulia M, Petralias A, Riza E, Linos A, On behalf of the DIATROFI Program Research Team (2016) The influence of a school-based intervention program regarding adherence to a healthy diet in children and adolescents of disadvantaged areas in Greece: the DIATROFI Study. J Epidemiol Community Health. doi:10.1136/jech-2015-205680
Khambalia AZ, Dickinson S, Hardy LL, Gill T, Baur LA (2012) A synthesis of existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses of school-based behavioural interventions for controlling and preventing obesity. Obes Rev 13:214–233
Kokkevi A, Stavrou M, Kanavou E, Fotiou A (2015) Eating behaviour, physical activity and body weight in adolescents. Series of short reports: adolescents, behaviours & health. University Mental Health Research Institute, Athens
Krolner R, Rasmussen M, Brug J, Klepp KI, Wind M, Due P (2011) Determinants of fruit and vegetable consumption among children and adolescents: a review of the literature. Part II: qualitative studies. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 8:112
Lapalme J, Bisset S, Potvin L (2014) Role of context in evaluating neighbourhood interventions promoting positive youth development: a narrative systematic review. Int J Public Health 59:31–42
Lien N, Haerens L, Te Velde SJ, Mercken L, Klepp KI, Moore L, de Bourdeaudhuij I, Faggiano F, van Lenthe FJ (2014) Exploring subgroup effects by socioeconomic position of three effective school-based dietary interventions: the European TEENAGE project. Int J Public Health 59:493–502
Livingstone MB (1995) Assessment of food intakes: are we measuring what people eat? Br J Biomed Sci 52:58–67
Lorson BA, Melgar-Quinonez HR, Taylor CA (2009) Correlates of fruit and vegetable intakes in US children. J Am Diet Assoc 109:474–478
McAloney K, Graham H, Law C, Platt L, Wardle H, Hall J (2014) Fruit and vegetable consumption and sports participation among UK Youth. Int J Public Health 59:117–121
Mindell JS, Coombs N, Stamatakis E (2014) Measuring physical activity in children and adolescents for dietary surveys: practicalities, problems and pitfalls. Proc Nutr Soc 73:218–225
Noel A, Stark P, Redford J, Zukerberg A (2013) Parent and family involvement in education, from the National Household Educations Surveys Program of 2012 (NCES 2013-028). U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Washington, DC
Peltzer K, Pengpid S (2015) Correlates of healthy fruit and vegetable diet in students in low, middle and high income countries. Int J Public Health 60:79–90
Perikkou A, Gavrieli A, Kougioufa MM, Tzirkali M, Yannakoulia M (2013) A novel approach for increasing fruit consumption in children. J Acad Nutr Diet 113:1188–1193
Petralias A, Papadimitriou E, Riza E, Karagas RM, Zagouras A, Linos A, On behalf of the DIATROFI Program Research Team (2016) The impact of a school food aid program on household food insecurity. Eur J Public Health. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckv223
Reinaerts E, Crutzen R, Candel M, De Vries NK, De Nooijer J (2008) Increasing fruit and vegetable intake among children: comparing long-term effects of a free distribution and a multicomponent program. Health Educ Res 23:987–996
Shepherd J, Harden A, Rees R, Brunton G, Garcia J, Oliver S, Oakley A (2006) Young people and healthy eating: a systematic review of research on barriers and facilitators. Health Educ Res 21:239–257
Silveira JA, Taddei JA, Guerra PH, Nobre MR (2011) Effectiveness of school-based nutrition education interventions to prevent and reduce excessive weight gain in children and adolescents: a systematic review. J Pediatr (Rio J) 87:382–392
St George SM, Wilson DK (2012) A qualitative study for understanding family and peer influences on obesity-related health behaviors in low-income African-American adolescents. Child Obes 8:466–476
Stang J, Story M (2005) Guidelines for adolescent nutrition services. Center for Leadership, Education and Training in Maternal and Child Nutrition, Division of Epidemiology and Community Health, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
Story M, Neumark-Sztainer D, French S (2002) Individual and environmental influences on adolescent eating behaviors. J Am Diet Assoc 102:S40–S51
Story M, Kaphingst KM, French S (2006) The role of schools in obesity prevention. Future Child 16:109–142
Van Cauwenberghe E, Maes L, Spittaels H, van Lenthe FJ, Brug J, Oppert JM, De Bourdeaudhuij I (2010) Effectiveness of school-based interventions in Europe to promote healthy nutrition in children and adolescents: systematic review of published and ‘grey’ literature. Br J Nutr 103:781–797
Verstraeten R, Roberfroid D, Lachat C, Leroy JL, Holdsworth M, Maes L, Kolsteren PW (2012) Effectiveness of preventive school-based obesity interventions in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 96:415–438
Yannakoulia M, Lykou A, Kastorini CM, Saranti Papasaranti E, Petralias A, Veloudaki A, Linos A (2015) Socio-economic and lifestyle parameters associated with diet quality of children and adolescents using classification and regression tree analysis: the DIATROFI study. Public Health Nutr, pp 1–9. doi:10.1017/S136898001500110X
Acknowledgments
Over 100 volunteers participated in the DIATROFI Program and deserve our sincere thanks.
The Food Aid and Promotion of Healthy Nutrition Program—DIATROFI (http://diatrofi.prolepsis.gr/) is implemented by the Institute of Preventive Medicine, Environmental and Occupational Health, Prolepsis, and has been approved and conducted under the auspices of the Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs. The DIATROFI Program was funded by the Stavros Niarchos Foundation.
The DIATROFI Program research team (in alphabetical order): Belogianni Katerina, MSc; Dalma Archontoula, MSc; Giannikou Dafni MSc; Gioti Natalia, BSc; Haviaris Anna Maria, MSc; Karagas R Margaret, PhD; Karnaki Pania, MA; Kastorini Christina Maria, PhD; Linos Athena, MD, MPH, PhD; Linos Constantinos, BSc; Lykou Anastasia, PhD; Mitraka Kallis, MA; Pantazopoulou Anastasia, MD, PhD; Papadimitriou Eleni, MD, PhD; Peppas Manolis, BSc; Petralias Athanassios, PhD; Riza Elena, PhD; Saranti Papasaranti Eirini, MSc; Spyridis Ioannis, MSc; Veloudaki Afroditi, MA; Yannakoulia Mary, PhD; Zota Dina, MSc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The DIATROFI Program was funded by the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and has been approved and runs under the auspices of the Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The DIATROFI Program was conducted under the auspices of the Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs. All questionnaires collected were anonymous.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Additional information
On behalf of the DIATROFI Program Research Team: The members are listed in the Acknowledgments section.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zota, D., Dalma, A., Petralias, A. et al. Promotion of healthy nutrition among students participating in a school food aid program: a randomized trial. Int J Public Health 61, 583–592 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-016-0813-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-016-0813-0