Abstract
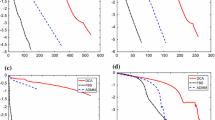
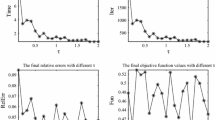
Compressive sensing has achieved great success in many scientific research fields. It has revealed that sparse signals can be stably recovered from a small number of noisy measurements by solving the constrained convex \({\ell }_1\)-minimization problem. In practice, a faster algorithm for solving this optimization problem is the key to compressive sensing. The Douglas–Rachford splitting method is a well-known operator splitting method that has been widely applied for solving a certain class of convex composite problems. In particular, its dual application results in the popular alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). In this paper, we reformulate the constrained convex \({\ell }_1\)-minimization problem as a convex composite problem with a special structure and then apply the primal Douglas–Rachford splitting method to solve it. The computational cost of the developed algorithm in each iteration is dominated by the projection onto the constraint set. A fast and efficient method of computing the projection is proposed. Numerical results show that the developed algorithm performs better than the popular NESTA and LADMM (inexact ADMM) in terms of accuracy and run time for large-scale sparse signal recovery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Artacho, J. Borwein, M. Tam, Douglas–Rachford feasibility methods for matrix completion problems. ANZIAM J. 55(4), 299–326 (2014)
B. Alexeev, J. Cahill, D. Mixon, Full spark frames. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 18(6), 1167–1194 (2012)
A. Beck, M. Teboulle, A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(1), 183–202 (2009)
H. Bauschke, P. Combettes, Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces (Springer, New York, 2011). CMS Books in Mathematics
J. Benedetto, P. Ferreira, Modern Sampling Theory: Mathematics and Applications (Birkhäuser, Boston, 2001). Applied and Numerical Harmonic Analysis
P. Bühlmann, S. van de Geer, Statistics for High-Dimensional Data (Springer, Berlin, 2011). Springer Series in Statistics
J. Bobin, J. Starck, R. Ottensamer, Compressed sensing in astronomy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2(5), 718–726 (2008)
S. Becker, J. Bobin, E. Candès, NESTA: a fast and accurate first-order method for sparse recovery. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 4(1), 1–39 (2011)
T. Blumensath, M. Davies, Sampling theorems for signals from the union of finite-dimensional linear subspaces. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 55(4), 1872–1882 (2009)
S. Chen, D. Donoho, M. Saunders, Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20(1), 33–61 (1998)
E. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
E. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 59(8), 1207–1223 (2006)
E. Candès, T. Tao, Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51(12), 4203–4215 (2005)
E. Candès, B. Recht, Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Found. Comput. Math. 9(6), 717–772 (2009)
P. Combettes, V. Wajs, Signal recovery by proximal forward–backward splitting. SIAM J. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4(4), 1168–1200 (2005)
P. Combettes, J. Pesquet, A Douglas–Rachford splitting approach to nonsmooth convex variational signal recovery. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 1(4), 564–574 (2007)
D. Donoho, Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(8), 1289–1306 (2006)
D. Donoho, De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 41(3), 613–627 (1995)
A. Daneshmand, F. Facchinei, V. Kungurtsev, G. Scutari, Hybrid random/deterministic parallel algorithms for convex and nonconvex big data optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(15), 3914–3929 (2015)
A. Daneshmand, F. Facchinei, V. Kungurtsev, G. Scutari, Flexible selective parallel algorithms for big data optimization. in 2014 48th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, IEEE (2014), pp. 3–7
I. Dassios, K. Fountoulakis, J. Gondzio, A second-order method for compressed sensing problems with coherent and redundant dictionaries. http://arxiv.org/abs/1405.4146, (2014)
I. Dassios, K. Fountoulakis, J. Gondzio, A preconditioner for a primal-dual newton conjugate gradients method for compressed sensing problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37(6), A2783–A2812 (2015)
Y. Dong, Douglas–Rachford splitting method for semidefinite programming. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 51(1), 569–591 (2016)
L. Demanet, X. Zhang, Eventual linear convergence of the Douglas–Rachford iteration for basis pursuit. Math. Comput. 85, 209–238 (2015)
J. Douglas, H. Rachford, On the numerical solution of the heat conduction problem in 2 and 3 space variables. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 82, 421–439 (1956)
M. Duarte, M. Davenport, D. Takhar, J. Laska, S. Ting, K. Kelly, R. Baraniuk, Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25(2), 83–91 (2008)
J. Eckstein, D. Bertsekas, On the Douglas–Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program. 55(3), 293–318 (1992)
M. Elad, Sparse and Redundant Representations: From Theory to Applications in Signal and Image Processing (Springer, New York, 2010)
Y. Eldar, G. Kutyniok, Compressed Sensing Theory and Applications (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2012)
J. Eckstein, Augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for convex optimization: a tutorial and some illustrative computational results, RUTCOR Research Report (RRR) (2012)
S. Foucart, H. Rauhut, A Mathematical Introduction to Compressive Sensing (Birkhäuser, Basel, 2013)
M. Fazel, Matrix Rank Minimization with Applications. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University (2002)
B. He, X. Yuan, On the convergence rate of Douglas–Rachford operator splitting method. Math. Program. 153(2), 715–722 (2015)
E. Hale, W. Yin, Y. Zhang, Fixed-point continuation for \(\ell _1\)-minimization: methodology and convergence. SIAM J. Optim. 19(3), 1107–1130 (2008)
F. Herrmann, M. Friedlander, O. Yilmaz, Fighting the curse of dimensionality: compressive sensing in exploration seismology. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 29(3), 88–100 (2012)
D. Holland, M. Bostock, L. Gladden, D. Nietlispach, Fast multidimensional NMR spectroscopy using compressed sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50(29), 6548–6551 (2011)
M. Herman, T. Strohmer, High-resolution radar via compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(6), 2275–2284 (2009)
A. Lenoir, P. Mahey, A survey on operator splitting and decomposition of convex programs. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_FILE/2015/07/5039 (2015)
G. Li, T. Pong, Douglas–Rachford splitting for nonconvex feasibility problems. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.8444v1 (2014)
M. Lustig, D. Donoho, J. Pauly, Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 58, 1182–1195 (2007)
M. Lai, J. Wang, An unconstrained \(\ell _q\) minimization with \(0<q\le 1\) for sparse solution of underdetermined linear systems. SIAM J. Optim. 21(1), 82–101 (2011)
Z. Lu, T. Pong, Y. Zhang, An alternating direction method for finding Dantzig selectors. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 35(8), 4037–4046 (2012)
F. Masao, The primal Douglas–Rachford splitting algorithm for a class of monotone mappings with application to the traffic equilibrium problem. Math. Program. 72(1), 1–15 (1996)
M. Murphy, M. Alley, J. Demmel, K. Keutzer, S. Vasanawala, M. Lustig, Fast \(\ell _1\)-SPIRiT compressed sensing parallel imaging MRI: scalable parallel implementation and clinically feasible runtime. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31(6), 1250–1262 (2012)
M. Mishali, Y. Eldar, From theory to practice: sub-nyquist sampling of sparse wideband analog signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 375–391 (2010)
\(\ell _1\)-Magic. http://www.acm.caltech.edu/l1magic/ (2006)
T. Ni, J. Zhai, A matrix-free smoothing algorithm for large-scale support vector machines. Inf. Sci. 358–359(3), 29–43 (2016)
NESTA. http://statweb.stanford.edu/~candes/nesta/ (2011)
D. O’Connor, L. Vandenberghe, Primal-dual decomposition by operator splitting and applications to image deblurring. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7(3), 1724–1754 (2014)
S. Osher, Y. Mao, B. Dong, W. Yin, Fast linearized Bregman iteration for compressive sensing and sparse denoising. Commun. Math. Sci. 8(1), 93–111 (2010)
G. Pfander, H. Rauhut, J. Tanner, Identification of matrices having a sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(11), 5376–5388 (2008)
Y. Pfeffer, Compressive Sensing for Hyperspectral Imaging. Research thesis, Israel Institute of Technology (2010)
H. Rauhut, G. Pfander, Sparsity in time-frequency representations. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 16(2), 233–260 (2010)
R. Rockafellar, Convex Analysis (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1970)
G. Steidl, T. Teuber, Removing multiplicative noise by Douglas–Rachford splitting methods. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 36(2), 168–184 (2010)
Y. Shrot, L. Frydman, Compressed sensing and the reconstruction of ultrafast 2D NMR data: principles and biomolecular applications. J. Magn. Reson. 209(2), 352–358 (2011)
J. Tropp, J. Laska, M. Duarte, J. Romberg, R. Baraniuk, Beyond Nyquist: efficient sampling of sparse bandlimited signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 56(1), 520–544 (2010)
S. Vasanawala, M. Alley, B. Hargreaves, R. Barth, J. Pauly, M. Lustig, Improved pediatric MR imaging with compressed sensing. Radiology 256(2), 607–616 (2010)
J. Yang, Y. Zhang, Alternating direction algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33(1), 250–278 (2011)
J. Yang, X. Yuan, Linearized augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for nuclear norm minimization. Math. Comput. 82(281), 301–329 (2013)
W. Yin, S. Osher, D. Goldfarb, J. Darbon, Bregman iterative algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-minimization with applications to compressed sensing. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 1(1), 143–168 (2008)
YALL1. http://yall1.blogs.rice.edu/ (2011)
C. Zhang, Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann. Stat. 38(2), 894–942 (2010)
W. Zhu, S. Shu, L. Cheng, Proximity point algorithm for low-rank matrix recovery from sparse noise corrupted data. Appl. Math. Mech. 35(2), 259–268 (2014)
S. Zhang, J. Xin, Minimization of transformed \(\ell _1\) penalty: closed form representation and iterative thresholding algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.5240 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the associate editor and editor-in chief for their constructive comments, which significantly improved this paper. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grants 11131006, 41390450, 91330204 and 11271297 and in part supported by the National Basic Research Program of China under the Grant 2013CB329404.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Peng, J., Han, X. et al. A Primal Douglas–Rachford Splitting Method for the Constrained Minimization Problem in Compressive Sensing. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 4022–4049 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0498-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0498-5