Abstract
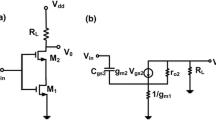
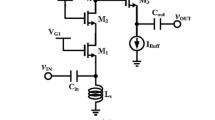
This paper presents a dual-wideband, common-gate, cascode low-noise amplifier (LNA) using gain–bandwidth product optimization technique. This approach shrinks the aspect ratio of the cascode MOS device, thereby reducing the equivalent parasitic capacitance of the resonator load to optimize the gain–bandwidth product of the LNA. The input impedance of the proposed LNA is analyzed, and the noise factor is well predicted through analytical equations. Measurement results that show well agreement with post-simulation results demonstrate the feasibility of this technique. In low-band mode, experimental results presented a maximum \(\left| S_{21} \right| \) of 13.4 dB over a \(-\)3-dB bandwidth of 3.1–4.8 GHz with a minimum noise figure of 4.5 dB. In high-band mode, the proposed LNA achieved a maximum \(\left| S_{21} \right| \) of 13.6 dB with a minimum noise figure of 6.2 dB over a \(-\)3-dB bandwidth of 7.3–9.4 GHz. A test chip with a die area of 0.83 mm\(^{2}\) was fabricated using a 0.18 \(\upmu \)m CMOS process. The proposed dual-wideband LNA consumes 9.1 mW, excluding the buffer, from a supply voltage of 1.8 V.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Cho, J. Bae, H.J. Yoo, A 10.8 mW body channel communication/MICS dual-band transceiver for a unified body sensor network controller. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 44(12), 3459–3468 (2009)
G.Z. Fatin, Z.D. Koozehkanani, H. Sjöland, A 90 nm CMOS +11 dBm IIP3 4 mW dual-band LNA for cellular handsets. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 20(9), 513–515 (2010)
Y. Gao, Y.J. Zheng, B.L. Ooi, 0.18 \(\upmu \)m CMOS dual-band UWB LNA with interference rejection. Electron. Lett. 43(20), 1096–1098 (2007)
H. Hashemi, A. Hajimiri, Concurrent multiband low-noise amplifiers—theory, design, and applications. IEEE Trans. Microw Theory Tech. 50(1), 288–301 (2002)
P. Heydari, Design and analysis of a performance-optimized CMOS UWB distributed LNA. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 42(9), 1892–1905 (2007)
Z.Y. Huang, C.C. Hung, CMOS dual-band low-noise amplifier for world-wide WiMedia ultra-wideband wireless personal area networks system. in Proceeding of Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, 2010 pp. 334–337
H.B. Kia, A.K. A’ain, I. Grout, I. Kamisian, A reconfigurable low-noise amplifier using a tunable active inductor for multistandard receivers. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32, 979–992 (2013)
T.H. Lee, The Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2004)
Z. Li, R. Quintal, K.O. Kenneth, A dual-band CMOS front-end with two gain modes for wireless LAN applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 39(11), 2069–2073 (2004)
J.Y. Lin, H.K. Chiou, Power-constrained third-order active notch filter applied in IR-LNA for UWB standards. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 58(1), 11–15 (2011)
L.H. Lu, H.H. Hsieh, Y.S. Wang, A compact 2.4/5.2-GHz CMOS dual-band low-noise amplifier. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 15(10), 685–687 (2005)
M.A. Martins, K. van Hartingsveldt, J.R. Fernandes, M.M. Silva, C.J.M. Verhoeven, Low noise amplifiers with double loop feedback. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32, 541–558 (2013)
N.M. Neihart, J. Brown, X. Yu, A dual-band 2.45/6 GHz CMOS LNA utilizing a dual-resonant transformer-based matching network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 59(8), 1743–1751 (2012)
B. Park, S. Choi, S. Hong, A low-noise amplifier with tunable interference rejection for 3.1- to 10.6-GHz UWB systems. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 20(1), 40–42 (2010)
Md.M. Reja, K. Moez, I. Filanovsky, An area-efficient multistage 3.0- to 8.5-GHz CMOS UWB LNA using tunable active inductors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 57(8), 587–591 (2010)
N. Shiramizu, T. Masuda, M. Tanabe, K. Washio, A 3-10 GHz bandwidth low-noise and low-power amplifier for full-band UWB communications in 0.25-\(\upmu \)m SiGe BiCMOS technology. in IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, 2005, pp. 39–42
H. Song, H. Kim, K. Han, J. Choi, C. Park, B. Kim, A sub-2 dB NF dual-band CMOS LNA for CDMA/WCDMA applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 18(3), 212–214 (2008)
G.M. Sung, X.J. Zhang, A 2.4-GHz/5.25-GHz CMOS variable gain low noise amplifier using gate voltage adjustment. in IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2013, pp. 776–779
X. Tang, F. Huang, Y. Zhang, S. Lin, Design of a reconfigurable low noise amplifier for IMT-A and UWB systems. in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Millimeter Wave Wireless Technology and Applications, 2012, pp. 1–4
T.K.K. Tsang, M.N. El-Gamal, Dual-band sub-1V CMOS LNA for 802.11a/b WLAN applications. in IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, I-217-I-220 2003
A. Vallese, A. Bevilacqua, C. Sandner, M. Tiebout, A. Gerosa, A. Neviani, Analysis and design of an integrated notch filter for the rejection of interference in UWB systems. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 44(2), 331–343 (2009)
K. Xuan, K.F. Tsang, W.C. Lee, S.C. Lee, 0.18 \(\upmu \)m CMOS dual-band low-noise amplifier for ZigBee development. Electron. Lett. 46(1), 85–86 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors would like to thank the Chung Yuan Christian University for financial support, and thank National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Hsin-Chu, Taiwan, for chip fabrication and measurement support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CC., Wang, YC. A Dual-Wideband CMOS LNA Using Gain–Bandwidth Product Optimization Technique. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 495–510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0322-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0322-7