Abstract
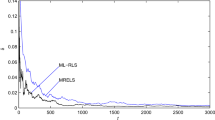
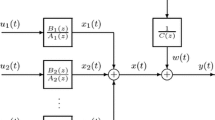
In this paper, we focus on the recursive computation of the cost functions for the least-squares-type algorithms for multivariable linear regressive models. It is shown that the proposed recursive computation formulas for the cost functions can also be extended to the estimation algorithm of the multivariable equation error models, e.g., the controlled autoregressive models. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm is effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Ahmad, O. Kukrer, A. Hocanin, Robust recursive inverse adaptive algorithm in impulsive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(2), 703–710 (2012)
A. Al–Smadi, A least-squares-based algorithm for identification of non-Gaussian ARMA models. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 26(5), 715–731 (2007)
H.I. Ashiba, K.H. Awadalla, S.M. EI-Halfawy, F.E. Abd EI-Samie, Adaptive least squares interpolation of infrared images. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(3), 543–551 (2011)
M. Ayatai, Adaptive fuzzy control of nonlinear in parameters uncertain chaotic systems using improved speed gradient method. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(2), 911–926 (2012)
B. Bao, Y.Q. Xu, J. Sheng, R.F. Ding, Least squares based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable controlled ARMA system modelling with finite measurement data. Math. Comput. Model. 53(9–10), 1664–1669 (2011)
Y.N. Cao, Z.Q. Liu, Signal frequency and parameter estimation for power systems using the hierarchical identification principle. Math. Comput. Model. 51(5–6), 854–861 (2010)
J. Chen, Y. Zhang, R.F. Ding, Auxiliary model based multi-innovation algorithms for multivariable nonlinear systems. Math. Comput. Model. 52(9–10), 1428–1434 (2010)
F. Ding, Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apm.2012.04.039
F. Ding, Several multi-innovation identification methods. Digit. Signal Process. 20(4), 1027–1039 (2010)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Hierarchical gradient-based identification of multivariable discrete-time systems. Automatica 41(2), 315–325 (2005)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Hierarchical least squares identification methods for multivariable systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(3), 397–402 (2005)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Hierarchical identification of lifted state-space models for general dual-rate systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Regul. Pap. 52(6), 1179–1187 (2005)
J. Ding, F. Ding, Bias compensation based parameter estimation for output error moving average systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 25(12), 1100–1111 (2011)
J. Ding, F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Hierarchical least squares identification for linear SISO systems with dual-rate sampled-data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(11), 2677–2683 (2011)
J. Ding, L.L. Han, X.M. Chen, Time series AR modeling with missing observations based on the polynomial transformation. Math. Comput. Model. 51(5–6), 527–536 (2010)
F. Ding, P.X. Liu, G. Liu, Multi-innovation least squares identification for linear and pseudo-linear regression models. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B, Cybern. 40(3), 767–778 (2010)
F. Ding, G. Liu, X.P. Liu, Partially coupled stochastic gradient identification methods for non-uniformly sampled systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(8), 1976–1981 (2010)
F. Ding, Y.J. Liu, B. Bao, Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(1), 43–55 (2012)
F. Ding, G. Liu, X.P. Liu, Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 47(8), 1646–1655 (2011)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
J. Ding, Y. Shi et al., A modified stochastic gradient based parameter estimation algorithm for dual-rate sampled-data systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(4), 1238–1249 (2010)
F. Ding, Y.S. Xiao, A finite-data-windows least squares algorithm with a forgetting factor for dynamical modeling. Appl. Math. Comput. 186(1), 184–192 (2007)
W. Dong, J.D. Li, Z. Lu, Parameter estimation for correlated MIMO channels with frequency-selective fading. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 52(4), 813–828 (2010)
W. Dong, J.D. Li, Z. Lu, W. Zhang, Joint frequency offset and channel estimation for MIMO systems in the presence of timing error. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(2), 275–293 (2010)
F. Felici, J. van Wingerden, M. Verhaegen, Subspace identification of MIMO LPV systems using a periodic scheduling sequence. Automatica 43(10), 1684–1697 (2007)
S. Gibson, B. Ninness, Robust maximum-likelihood estimation of multivariable dynamic systems. Automatica 41(10), 1667–1682 (2005)
G.C. Goodwin, K.S. Sin, Adaptive Filtering Prediction and Control (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1984)
L.L. Han, F. Ding, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Digit. Signal Process. 19(4), 545–554 (2009)
L.L. Han, J. Sheng et al., Auxiliary models based recursive least squares identification for multirate multi-input systems. Math. Comput. Model. 50(7–8), 1100–1106 (2009)
H.Q. Han, L. Xie et al., Hierarchical least squares based iterative identification for multivariable systems with moving average noises. Math. Comput. Model. 51(9–10), 1213–1220 (2010)
J.H. Li, F. Ding, Maximum likelihood stochastic gradient estimation for Hammerstein systems with colored noise based on the key term separation technique. Comput. Math. Appl. 62(11), 4170–4177 (2011)
J.H. Li, F. Ding, G.W. Yang, Maximum likelihood least squares identification method for input nonlinear finite impulse response moving average systems. Math. Comput. Model. 55(3–4), 442–450 (2012)
Y.J. Liu, F. Ding, Y. Shi, Least squares estimation for a class of non-uniformly sampled systems based on the hierarchical identification principle. Circuits Syst. Signal Proces. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00034-012-9421-2
Y.J. Liu, J. Sheng, R.F. Ding, Convergence of stochastic gradient estimation algorithm for multivariable ARX-like systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(8), 2615–2627 (2010)
Y.J. Liu, Y.S. Xiao, X.L. Zhao, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Y.J. Liu, L. Yu et al., Multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(4), 649–667 (2010)
J.X. Ma, W.L. Xiong, E. Ding, Recursive relations of the criterion functions for the recursive least squares algorithms, in The 2012 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2012 CCDC), May 23–25, 2012, Taiyuan, China (2012), pp. 2081–2086
T.J. Moir, A unified family of recursive algorithms using feedback. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(5), 1047–1054 (2011)
R. Pintelon, J. Schoukens, P. Guillaume, Box–Jenkins identification revisited—part III: multivariable systems. Automatica 43(5), 868–875 (2007)
M. Rachid, B. Maamar, D. Said, Multivariable fractional system approximation with initial conditions using integral state space representation. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(5), 1842–1851 (2010)
M.S. Radenkovic, T. Bose, A recursive blind adaptive equalizer for IIR channels with common zeros. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 28(3), 467–486 (2009)
T. Schon, A. Wills, B. Ninness, System identification of nonlinear state-space models. Automatica 47(1), 39–49 (2011)
R.M. Udrea, D.N. Vizireanu, Quantized multiple sinusoids signal estimation algorithm. J. Instrum. 3(2), 1–7 (2008)
M. Viberg, Subspace-based state-space system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 21(1), 23–27 (2002)
D.N. Vizireanu, Quantized sine signals estimation algorithm for portable DSP based instrumentation. Int. J. Electron. 96(11), 1175–1181 (2009)
D.N. Vizireanu, A simple and precise real-time four point single sinusoid signals instantaneous frequency estimation method for portable DSP based instrumentation. Measurement 44(2), 500–502 (2011)
D.N. Vizireanu, A fast, simple and accurate time-varying frequency estimation method for single-phase electric power systems. Measurement 45(5), 1331–1333 (2012)
D.N. Vizireanu, S.V. Halunga, Simple, fast and accurate eight points amplitude estimation method of sinusoidal signals for DSP based instrumentation. J. Instrum. 7(2), 1–10 (2012)
J. Vörös, Iterative algorithm for parameter identification of Hammerstein systems with two-segment nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 44(11), 2145–2149 (1999)
D.Q. Wang, Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Least squares based and gradient based iterative identification for Wiener nonlinear systems. Signal Process. 91(5), 1182–1189 (2011)
W. Wang, F. Ding, J.Y. Dai, Maximum likelihood least squares identification for systems with autoregressive moving average noise. Appl. Math. Model. 36(5), 1842–1853 (2012)
W. Wang, J.H. Li, R.F. Ding, Maximum likelihood parameter estimation algorithm for controlled autoregressive models. Int. J. Comput. Math. 88(16), 3458–3467 (2011)
Y.S. Xiao, F. Ding, Y. Zhou, M. Li, J.Y. Dai, On consistency of recursive least squares identification algorithms for controlled auto-regression models. Appl. Math. Model. 32(11), 2207–2215 (2008)
Y. Zhang, Unbiased identification of a class of multi-input single-output systems with correlated disturbances using bias compensation methods. Math. Comput. Model. 53(9–10), 1810–1819 (2011)
Z.N. Zhang, F. Ding, X.G. Liu, Hierarchical gradient based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable output error moving average systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(3), 672–682 (2011)
J.B. Zhang, F. Ding, Y. Shi, Self-tuning control based on multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation. Syst. Control Lett. 58(1), 69–75 (2009)
Z.N. Zhang, J. Jia, R.F. Ding, Hierarchical least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for multivariable Box–Jenkins-like systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(9), 5580–5587 (2012)
Z. Zheng, G. Li, Y. Teng, Simplified estimation of 2D DOA for coherently distributed sources. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 62(4), 907–922 (2012)
L. Zhong, Robust maximum-likelihood parameter estimation of stochastic state-space systems based on EM algorithm. Prog. Nat. Sci. 17(9), 1095–1103 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60973043) and the 111 Project (B12018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Ding, F. Recursive Relations of the Cost Functions for the Least-Squares Algorithms for Multivariable Systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 32, 83–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9448-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9448-4