Abstract
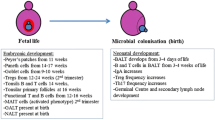
The intestinal mucosa faces the challenge of regulating the balance between immune tolerance towards commensal bacteria, environmental stimuli and food antigens on the one hand, and induction of efficient immune responses against invading pathogens on the other hand. This regulatory task is of critical importance to prevent inappropriate immune activation that may otherwise lead to chronic inflammation, tissue disruption and organ dysfunction. The most striking example for the efficacy of the adaptive nature of the intestinal mucosa is birth. Whereas the body surfaces are protected from environmental and microbial exposure during fetal life, bacterial colonization and contact with potent immunostimulatory substances start immediately after birth. In the present review, we summarize the current knowledge on the mechanisms underlying the transition of the intestinal mucosa during the neonatal period leading to the establishment of a stable, life-long host–microbial homeostasis. The environmental exposure and microbial colonization during the neonatal period, and also the influence of maternal milk on the immune protection of the mucosa and the role of antimicrobial peptides, are described. We further highlight the molecular mechanisms of innate immune tolerance in neonatal intestinal epithelium. Finally, we link the described immunoregulatory mechanisms to the increased susceptibility to inflammatory and infectious diseases during the neonatal period.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu J, Gordon JI (2003) Honor thy symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(18):10452–10459
Rescigno M (2011) The intestinal epithelial barrier in the control of homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol 32(6):256–264
Abreu MT (2010) Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: how bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat Rev Immunol 10(2):131–144. doi:10.1038/nri2707
Sansonetti PJ (2011) To be or not to be a pathogen: that is the mucosally relevant question. Mucosal Immunol 4(1):8–14
Artis D (2008) Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 8(6):411–420
Hooper LV, Macpherson AJ (2010) Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat Rev Immunol 10(3):159–169
Maloy KJ, Powrie F (2011) Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 474(7351):298–306
Eberl G, Boneca IG (2010) Bacteria and MAMP-induced morphogenesis of the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 22(4):448–454
Nenci A, Becker C, Wullaert A, Gareus R, van Loo G, Danese S, Huth M, Nikolaev A, Neufert C, Madison B, Gumucio D, Neurath MF, Pasparakis M (2007) Epithelial NEMO links innate immunity to chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature 446(7135):557–561
Zaph C, Troy AE, Taylor BC, Berman-Booty LD, Guild KJ, Du Y, Yost EA, Gruber AD, May MJ, Greten FR, Eckmann L, Karin M, Artis D (2007) Epithelial-cell-intrinsic IKK-beta expression regulates intestinal immune homeostasis. Nature 446(7135):552–556
Zaki MH, Boyd KL, Vogel P, Kastan MB, Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2010) The NLRP3 inflammasome protects against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during experimental colitis. Immunity 32(3):379–391
Kajino-Sakamoto R, Inagaki M, Lippert E, Akira S, Robine S, Matsumoto K, Jobin C, Ninomiya-Tsuji J (2008) Enterocyte-derived TAK1 signaling prevents epithelium apoptosis and the development of ileitis and colitis. J Immunol 181(2):1143–1152. doi:181/2/1143[pii]
Hansson GC, Johansson ME (2010) The inner of the two Muc2 mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Gut Microbes 1(1):51–54
Johansson ME, Larsson JM, Hansson GC (2011) The two mucus layers of colon are organized by the MUC2 mucin, whereas the outer layer is a legislator of host-microbial interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(Suppl 1):4659–4665
Van der Sluis M, De Koning BA, De Bruijn AC, Velcich A, Meijerink JP, Van Goudoever JB, Buller HA, Dekker J, Van Seuningen I, Renes IB, Einerhand AW (2006) Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology 131(1):117–129
Herbert DR, Yang JQ, Hogan SP, Groschwitz K, Khodoun M, Munitz A, Orekov T, Perkins C, Wang Q, Brombacher F, Urban JF Jr, Rothenberg ME, Finkelman FD (2009) Intestinal epithelial cell secretion of RELM-beta protects against gastrointestinal worm infection. J Exp Med 206(13):2947–2957. doi:10.1084/jem.20091268
Salzman NH, Hung K, Haribhai D, Chu H, Karlsson-Sjoberg J, Amir E, Teggatz P, Barman M, Hayward M, Eastwood D, Stoel M, Zhou Y, Sodergren E, Weinstock GM, Bevins CL, Williams CB, Bos NA (2010) Enteric defensins are essential regulators of intestinal microbial ecology. Nat Immunol 11(1):76–83
Ismail AS, Behrendt CL, Hooper LV (2009) Reciprocal interactions between commensal bacteria and gamma delta intraepithelial lymphocytes during mucosal injury. J Immunol 182(5):3047–3054
Niess JH, Brand S, Gu X, Landsman L, Jung S, McCormick BA, Vyas JM, Boes M, Ploegh HL, Fox JG, Littman DR, Reinecker HC (2005) CX3CR1-mediated dendritic cell access to the intestinal lumen and bacterial clearance. Science 307(5707):254–258
Chieppa M, Rescigno M, Huang AY, Germain RN (2006) Dynamic imaging of dendritic cell extension into the small bowel lumen in response to epithelial cell TLR engagement. J Exp Med 203(13):2841–2852
Coombes JL, Powrie F (2008) Dendritic cells in intestinal immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol 8(6):435–446
Niess JH, Adler G (2010) Enteric flora expands gut lamina propria CX3CR1 + dendritic cells supporting inflammatory immune responses under normal and inflammatory conditions. J Immunol 184(4):2026–2037. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0901936
Sawa S, Lochner M, Satoh-Takayama N, Dulauroy S, Berard M, Kleinschek M, Cua D, Di Santo JP, Eberl G (2011) RORgammat + innate lymphoid cells regulate intestinal homeostasis by integrating negative signals from the symbiotic microbiota. Nat Immunol 12(4):320–326
Wang Y, Koroleva EP, Kruglov AA, Kuprash DV, Nedospasov SA, Fu YX, Tumanov AV (2010) Lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells orchestrates innate immune responses against mucosal bacterial infection. Immunity 32(3):403–413
Rimoldi M, Chieppa M, Salucci V, Avogadri F, Sonzogni A, Sampietro GM, Nespoli A, Viale G, Allavena P, Rescigno M (2005) Intestinal immune homeostasis is regulated by the crosstalk between epithelial cells and dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 6(5):507–514
Fukata M, Michelsen KS, Eri R, Thomas LS, Hu B, Lukasek K, Nast CC, Lechago J, Xu R, Naiki Y, Soliman A, Arditi M, Abreu MT (2005) Toll-like receptor-4 is required for intestinal response to epithelial injury and limiting bacterial translocation in a murine model of acute colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288(5):G1055–G1065
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R (2004) Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 118(2):229–241
Vijay-Kumar M, Sanders CJ, Taylor RT, Kumar A, Aitken JD, Sitaraman SV, Neish AS, Uematsu S, Akira S, Williams IR, Gewirtz AT (2007) Deletion of TLR5 results in spontaneous colitis in mice. J Clin Invest 117(12):3909–3921
Tapiainen T, Ylitalo S, Eerola E, Uhari M (2006) Dynamics of gut colonization and source of intestinal flora in healthy newborn infants. Apmis 114(11):812–817
Fanaro S, Chierici R, Guerrini P, Vigi V (2003) Intestinal microflora in early infancy: composition and development. Acta Paediatr Suppl 91(441):48–55
Dominguez-Bello MG, Costello EK, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Fierer N, Knight R (2010) Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(26):11971–11975
Levy O (2007) Innate immunity of the newborn: basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Nat Rev Immunol 7(5):379–390
Decker E, Hornef M, Stockinger S (2011) Cesarean delivery is associated with celiac disease but not inflammatory bowel disease in children. Gut Microbes 2(2):91–98
Lecuit M, Abachin E, Martin A, Poyart C, Pochart P, Suarez F, Bengoufa D, Feuillard J, Lavergne A, Gordon JI, Berche P, Guillevin L, Lortholary O (2004) Immunoproliferative small intestinal disease associated with Campylobacter jejuni. N Engl J Med 350(3):239–248
Ott SJ, Musfeldt M, Wenderoth DF, Hampe J, Brant O, Folsch UR, Timmis KN, Schreiber S (2004) Reduction in diversity of the colonic mucosa associated bacterial microflora in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 53(5):685–693
Fell JM (2005) Neonatal inflammatory intestinal diseases: necrotising enterocolitis and allergic colitis. Early Hum Dev 81(1):117–122
Frank DN, Zhu W, Sartor RB, Li E (2011) Investigating the biological and clinical significance of human dysbioses. Trends Microbiol (in press)
Grapin-Botton A, Melton DA (2000) Endoderm development: from patterning to organogenesis. Trends Genet 16(3):124–130
Beaulieu JF, Menard D, Calvert R (1985) Influence of epidermal growth factor on the maturation of the fetal mouse duodenum in organ culture. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 4(3):476–481
Hirano S, Kataoka K (1986) Histogenesis of the mouse jejunal mucosa, with special reference to proliferative cells and absorptive cells. Arch Histol Jpn 49(3):333–348
Crosnier C, Stamataki D, Lewis J (2006) Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat Rev Genet 7(5):349–359
Dolowschiak T, Chassin C, Ben Mkaddem S, Fuchs TM, Weiss S, Vandewalle A, Hornef MW (2010) Potentiation of epithelial innate host responses by intercellular communication. PLoS Pathog 6(11):e1001194
Amerongen HM, Mack JA, Wilson JM, Neutra MR (1989) Membrane domains of intestinal epithelial cells: distribution of Na+ , K+ -ATPase and the membrane skeleton in adult rat intestine during fetal development and after epithelial isolation. J Cell Biol 109(5):2129–2138
Pacha J (2000) Development of intestinal transport function in mammals. Physiol Rev 80(4):1633–1667
Richmond CA, Breault DT (2010) Regulation of gene expression in the intestinal epithelium. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 96:207–229
Jones RG, Li X, Gray PD, Kuang J, Clayton F, Samowitz WS, Madison BB, Gumucio DL, Kuwada SK (2006) Conditional deletion of beta1 integrins in the intestinal epithelium causes a loss of Hedgehog expression, intestinal hyperplasia, and early postnatal lethality. J Cell Biol 175(3):505–514
Hermiston ML, Green RP, Gordon JI (1993) Chimeric-transgenic mice represent a powerful tool for studying how the proliferation and differentiation programs of intestinal epithelial cell lineages are regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(19):8866–8870
Mustata RC, Van Loy T, Lefort A, Libert F, Strollo S, Vassart G, Garcia MI (2011) Lgr4 is required for Paneth cell differentiation and maintenance of intestinal stem cells ex vivo. EMBO Rep 12(6):558–564
Chassin C, Kocur M, Pott J, Duerr CU, Gutle D, Lotz M, Hornef MW (2010) miR-146a mediates protective innate immune tolerance in the neonate intestine. Cell Host Microbe 8(4):358–368
Rhee SJ, Walker WA, Cherayil BJ (2005) Developmentally regulated intestinal expression of IFN-gamma and its target genes and the age-specific response to enteric Salmonella infection. J Immunol 175(2):1127–1136
van der Flier LG, Clevers H (2009) Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol 71:241–260
Harper J, Mould A, Andrews RM, Bikoff EK, Robertson EJ (2011) The transcriptional repressor Blimp1/Prdm1 regulates postnatal reprogramming of intestinal enterocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(26):10585–10590
McKenna LB, Schug J, Vourekas A, McKenna JB, Bramswig NC, Friedman JR, Kaestner KH (2010) MicroRNAs control intestinal epithelial differentiation, architecture, and barrier function. Gastroenterology 139(5):1654–1664
Biton M, Levin A, Slyper M, Alkalay I, Horwitz E, Mor H, Kredo-Russo S, Avnit-Sagi T, Cojocaru G, Zreik F, Bentwich Z, Poy MN, Artis D, Walker MD, Hornstein E, Pikarsky E, Ben-Neriah Y (2011) Epithelial microRNAs regulate gut mucosal immunity via epithelium—T cell crosstalk. Nat Immunol 12(3):239–246
Zeng L, Carter AD, Childs SJ (2009) miR-145 directs intestinal maturation in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(42):17793–17798
Hino K, Fukao T, Watanabe M (2007) Regulatory interaction of HNF1-alpha to microRNA-194 gene during intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf) (51):415–416
Liao Y, Lonnerdal B (2010) Global microRNA characterization reveals that miR-103 is involved in IGF-1 stimulated mouse intestinal cell proliferation. PLoS One 5(9):e12976
Dalmasso G, Nguyen HT, Yan Y, Laroui H, Charania MA, Obertone TS, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D (2011) MicroRNA-92b regulates expression of the oligopeptide transporter PepT1 in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300(1):G52–G59
Husband AJ, Gleeson M (1996) Ontogeny of mucosal immunity—environmental and behavioural influences. Brain Behav Immun 10(3):188–204
DiSanto JP, Muller W, Guy-Grand D, Fischer A, Rajewsky K (1995) Lymphoid development in mice with a targeted deletion of the interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(2):377–381
Yoshida H, Honda K, Shinkura R, Adachi S, Nishikawa S, Maki K, Ikuta K, Nishikawa SI (1999) IL-7 receptor alpha + CD3(−) cells in the embryonic intestine induces the organizing center of Peyer’s patches. Int Immunol 11(5):643–655
Friedberg SH, Weissman IL (1974) Lymphoid tissue architecture. II. Ontogeny of peripheral T and B cells in mice: evidence against Peyer’s patches as the site of generation of B cells. J Immunol 113(5):1477–1492
Brandtzaeg P (2010) Function of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in antibody formation. Immunol Invest 39(4–5):303–355. doi:10.3109/08820131003680369
Cummins AG, Thompson FM (1997) Postnatal changes in mucosal immune response: a physiological perspective of breast feeding and weaning. Immunol Cell Biol 75(5):419–429
Kollmann TR, Crabtree J, Rein-Weston A, Blimkie D, Thommai F, Wang XY, Lavoie PM, Furlong J, Fortuno ES 3rd, Hajjar AM, Hawkins NR, Self SG, Wilson CB (2009) Neonatal innate TLR-mediated responses are distinct from those of adults. J Immunol 183(11):7150–7160
Wang G, Miyahara Y, Guo Z, Khattar M, Stepkowski SM, Chen W (2010) “Default” generation of neonatal regulatory T cells. J Immunol 185(1):71–78. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903806
Pabst R, Russell MW, Brandtzaeg P (2008) Tissue distribution of lymphocytes and plasma cells and the role of the gut. Trends Immunol 29(5):206–208; author reply 209-210. doi:S1471-4906(08)00086-0 [pii] 10.1016/j.it.2008.02.006
Wagner CL, Taylor SN, Johnson D (2008) Host factors in amniotic fluid and breast milk that contribute to gut maturation. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34(2):191–204
Minekawa R, Takeda T, Sakata M, Hayashi M, Isobe A, Yamamoto T, Tasaka K, Murata Y (2004) Human breast milk suppresses the transcriptional regulation of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB signaling in human intestinal cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287(5):C1404–C1411
Kosaka N, Izumi H, Sekine K, Ochiya T (2010) microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk. Silence 1(1):7
LeBouder E, Rey-Nores JE, Raby AC, Affolter M, Vidal K, Thornton CA, Labeta MO (2006) Modulation of neonatal microbial recognition: TLR-mediated innate immune responses are specifically and differentially modulated by human milk. J Immunol 176(6):3742–3752
Robinson G, Volovitz B, Passwell JH (1991) Identification of a secretory IgA receptor on breast-milk macrophages: evidence for specific activation via these receptors. Pediatr Res 29(5):429–434
Muller CA, Autenrieth IB, Peschel A (2005) Innate defenses of the intestinal epithelial barrier. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(12):1297–1307
Boehm G, Stahl B (2007) Oligosaccharides from milk. J Nutr 137(3 Suppl 2):847S–849S
Halpern MD, Dominguez JA, Dvorakova K, Holubec H, Williams CS, Meza YG, Ruth MC, Dvorak B (2003) Ileal cytokine dysregulation in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis is reduced by epidermal growth factor. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 36(1):126–133
Clark JA, Doelle SM, Halpern MD, Saunders TA, Holubec H, Dvorak K, Boitano SA, Dvorak B (2006) Intestinal barrier failure during experimental necrotizing enterocolitis: protective effect of EGF treatment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291(5):G938–G949
Fusunyan RD, Nanthakumar NN, Baldeon ME, Walker WA (2001) Evidence for an innate immune response in the immature human intestine: toll-like receptors on fetal enterocytes. Pediatr Res 49(4):589–593
Gioannini TL, Teghanemt A, Zhang D, Coussens NP, Dockstader W, Ramaswamy S, Weiss JP (2004) Isolation of an endotoxin-MD-2 complex that produces Toll-like receptor 4-dependent cell activation at picomolar concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(12):4186–4191
Lotz M, Gutle D, Walther S, Menard S, Bogdan C, Hornef MW (2006) Postnatal acquisition of endotoxin tolerance in intestinal epithelial cells. J Exp Med 203(4):973–984
Hornef MW, Frisan T, Vandewalle A, Normark S, Richter-Dahlfors A (2002) Toll-like receptor 4 resides in the Golgi apparatus and colocalizes with internalized lipopolysaccharide in intestinal epithelial cells. J Exp Med 195(5):559–570
Li L, Cousart S, Hu J, McCall CE (2000) Characterization of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase in normal and endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Biol Chem 275(30):23340–23345. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001950200M001950200[pii]
Bens M, Bogdanova A, Cluzeaud F, Miquerol L, Kerneis S, Kraehenbuhl JP, Kahn A, Pringault E, Vandewalle A (1996) Transimmortalized mouse intestinal cells (m-ICc12) that maintain a crypt phenotype. Am J Physiol 270(6 Pt 1):C1666–C1674
Barbalat R, Barton GM (2010) MicroRNAs and LPS: developing a relationship in the neonatal gut. Cell Host Microbe 8(4):303–304
Leavy O (2010) (micro)Tolerance in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 10(12):810
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D (2006) NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(33):12481–12486
Boldin MP, Taganov KD, Rao DS, Yang L, Zhao JL, Kalwani M, Garcia-Flores Y, Luong M, Devrekanli A, Xu J, Sun G, Tay J, Linsley PS, Baltimore D (2011) miR-146a is a significant brake on autoimmunity, myeloproliferation, and cancer in mice. J Exp Med 208(6):1189–1201
Mege JL, Mehraj V, Capo C (2011) Macrophage polarization and bacterial infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis 24(3):230–234
Bevins CL, Salzman NH (2011) Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(5):356–368
Hornef MW, Putsep K, Karlsson J, Refai E, Andersson M (2004) Increased diversity of intestinal antimicrobial peptides by covalent dimer formation. Nat Immunol 5(8):836–843
Ayabe T, Satchell DP, Wilson CL, Parks WC, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2000) Secretion of microbicidal alpha-defensins by intestinal Paneth cells in response to bacteria. Nat Immunol 1(2):113–118
Narushima Y, Unno M, Nakagawara K, Mori M, Miyashita H, Suzuki Y, Noguchi N, Takasawa S, Kumagai T, Yonekura H, Okamoto H (1997) Structure, chromosomal localization and expression of mouse genes encoding type III Reg, RegIII alpha, RegIII beta, RegIII gamma. Gene 185(2):159–168
Salzman NH, Underwood MA, Bevins CL (2007) Paneth cells, defensins, and the commensal microbiota: a hypothesis on intimate interplay at the intestinal mucosa. Semin Immunol 19(2):70–83
Wilson CL, Ouellette AJ, Satchell DP, Ayabe T, Lopez-Boado YS, Stratman JL, Hultgren SJ, Matrisian LM, Parks WC (1999) Regulation of intestinal alpha-defensin activation by the metalloproteinase matrilysin in innate host defense. Science 286(5437):113–117
Salzman NH, Ghosh D, Huttner KM, Paterson Y, Bevins CL (2003) Protection against enteric salmonellosis in transgenic mice expressing a human intestinal defensin. Nature 422(6931):522–526
Cash HL, Whitham CV, Behrendt CL, Hooper LV (2006) Symbiotic bacteria direct expression of an intestinal bactericidal lectin. Science 313(5790):1126–1130
Brandl K, Plitas G, Schnabl B, DeMatteo RP, Pamer EG (2007) MyD88-mediated signals induce the bactericidal lectin RegIII gamma and protect mice against intestinal Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Exp Med 204(8):1891–1900
Mukherjee S, Partch CL, Lehotzky RE, Whitham CV, Chu H, Bevins CL, Gardner KH, Hooper LV (2009) Regulation of C-type lectin antimicrobial activity by a flexible N-terminal prosegment. J Biol Chem 284(8):4881–4888
Lehotzky RE, Partch CL, Mukherjee S, Cash HL, Goldman WE, Gardner KH, Hooper LV (2010) Molecular basis for peptidoglycan recognition by a bactericidal lectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(17):7722–7727
Lai Y, Gallo RL (2009) AMPed up immunity: how antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense. Trends Immunol 30(3):131–141
Calvert R, Pothier P (1990) Migration of fetal intestinal intervillous cells in neonatal mice. Anat Rec 227(2):199–206
Bry L, Falk P, Huttner K, Ouellette A, Midtvedt T, Gordon JI (1994) Paneth cell differentiation in the developing intestine of normal and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(22):10335–10339
Putsep K, Axelsson LG, Boman A, Midtvedt T, Normark S, Boman HG, Andersson M (2000) Germ-free and colonized mice generate the same products from enteric prodefensins. J Biol Chem 275(51):40478–40482
Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2005) Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat Immunol 6(6):551–557
Darmoul D, Brown D, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (1997) Cryptdin gene expression in developing mouse small intestine. Am J Physiol 272(11):G197–G206
Menard S, Forster V, Lotz M, Gutle D, Duerr CU, Gallo RL, Henriques-Normark B, Putsep K, Andersson M, Glocker EO, Hornef MW (2008) Developmental switch of intestinal antimicrobial peptide expression. J Exp Med 205(1):183–193
Inoue R, Tsuruta T, Nojima I, Nakayama K, Tsukahara T, Yajima T (2008) Postnatal changes in the expression of genes for cryptdins 1–6 and the role of luminal bacteria in cryptdin gene expression in mouse small intestine. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 52(3):407–416
Ouellette AJ, Greco RM, James M, Frederick D, Naftilan J, Fallon JT (1989) Developmental regulation of cryptdin, a corticostatin/defensin precursor mRNA in mouse small intestinal crypt epithelium. J Cell Biol 108(5):1687–1695
Linden SK, Sutton P, Karlsson NG, Korolik V, McGuckin MA (2008) Mucins in the mucosal barrier to infection. Mucosal Immunol 1(3):183–197
Schaedler RW, Dubos R, Costello R (1965) The development of the bacterial flora in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. J Exp Med 122:59–66
Savage DC, Dubos R, Schaedler RW (1968) The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med 127(1):67–76
Davis CP, McAllister JS, Savage DC (1973) Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun 7(4):666–672
Hirayama K, Miyaji K, Kawamura S, Itoh K, Takahashi E, Mitsuoka T (1995) Development of intestinal flora of human-flora-associated (HFA) mice in the intestine of their offspring. Exp Anim 44(3):219–222
Adlerberth I, Wold AE (2009) Establishment of the gut microbiota in Western infants. Acta Paediatr 98(2):229–238
Rook GA (2011) Hygiene and other early childhood influences on the subsequent function of the immune system. Dig Dis 29(2):144–153
Hascoet JM, Hubert C, Rochat F, Legagneur H, Gaga S, Emady-Azar S, Steenhout PG (2011) Effect of formula composition on the development of infant gut microbiota. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 52(6):756–762
Koenig JE, Spor A, Scalfone N, Fricker AD, Stombaugh J, Knight R, Angenent LT, Ley RE (2011) Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(Suppl 1):4578–4585
Inoue R, Otsuka M, Ushida K (2005) Development of intestinal microbiota in mice and its possible interaction with the evolution of luminal IgA in the intestine. Exp Anim 54(5):437–445. doi:JST.JSTAGE/expanim/54.437[pii]
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(44):15718–15723
Stappenbeck TS, Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2002) Developmental regulation of intestinal angiogenesis by indigenous microbes via Paneth cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(24):15451–15455
MacDonald TT, Gordon JN (2005) Bacterial regulation of intestinal immune responses. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 34(3):401–412, vii–viii
Velagapudi VR, Hezaveh R, Reigstad CS, Gopalacharyulu P, Yetukuri L, Islam S, Felin J, Perkins R, Boren J, Oresic M, Backhed F (2010) The gut microbiota modulates host energy and lipid metabolism in mice. J Lipid Res 51(5):1101–1112
Neu J, Chen M, Beierle E (2005) Intestinal innate immunity: how does it relate to the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 14(3):137–144
Leaphart CL, Cavallo J, Gribar SC, Cetin S, Li J, Branca MF, Dubowski TD, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ (2007) A critical role for TLR4 in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis by modulating intestinal injury and repair. J Immunol 179(7):4808–4820
Jilling T, Simon D, Lu J, Meng FJ, Li D, Schy R, Thomson RB, Soliman A, Arditi M, Caplan MS (2006) The roles of bacteria and TLR4 in rat and murine models of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol 177(5):3273–3282
Gribar SC, Sodhi CP, Richardson WM, Anand RJ, Gittes GK, Branca MF, Jakub A, Shi XH, Shah S, Ozolek JA, Hackam DJ (2009) Reciprocal expression and signaling of TLR4 and TLR9 in the pathogenesis and treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol 182(1):636–646
McElroy SJ, Prince LS, Weitkamp JH, Reese J, Slaughter JC, Polk DB (2011) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-dependent depletion of mucus in immature small intestine: a potential role in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol (in press)
Ye D, Guo S, Al-Sadi R, Ma TY (2011) MicroRNA regulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. Gastroenterology (in press)
WHO (2004) Global deaths under age five attributable to rotavirus infection. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wolf JL, Cukor G, Blacklow NR, Dambrauskas R, Trier JS (1981) Susceptibility of mice to rotavirus infection: effects of age and administration of corticosteroids. Infect Immun 33(2):565–574
Pott J, Mahlakoiv T, Mordstein M, Duerr CU, Michiels T, Stockinger S, Staeheli P, Hornef MW (2011) IFN-lambda determines the intestinal epithelial antiviral host defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(19):7944–7949
Vazquez-Boland JA, Kuhn M, Berche P, Chakraborty T, Dominguez-Bernal G, Goebel W, Gonzalez-Zorn B, Wehland J, Kreft J (2001) Listeria pathogenesis and molecular virulence determinants. Clin Microbiol Rev 14(3):584–640
Genovese F, Mancuso G, Cuzzola M, Biondo C, Beninati C, Delfino D, Teti G (1999) Role of IL-10 in a neonatal mouse listeriosis model. J Immunol 163(5):2777–2782
Byun HJ, Jung WW, Lee JB, Chung HY, Sul D, Kim SJ, Park CG, Choi I, Hwang KW, Chun T (2007) An evaluation of the neonatal immune system using a listeria infection model. Neonatology 92(2):83–90
Bonazzi M, Lecuit M, Cossart P (2009) Listeria monocytogenes internalin and E-cadherin: from structure to pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 11(5):693–702
Lecuit M, Vandormael-Pournin S, Lefort J, Huerre M, Gounon P, Dupuy C, Babinet C, Cossart P (2001) A transgenic model for listeriosis: role of internalin in crossing the intestinal barrier. Science 292(5522):1722–1725
Fernandez MI, Thuizat A, Pedron T, Neutra M, Phalipon A, Sansonetti PJ (2003) A newborn mouse model for the study of intestinal pathogenesis of shigellosis. Cell Microbiol 5(7):481–491
Fernandez MI, Regnault B, Mulet C, Tanguy M, Jay P, Sansonetti PJ, Pedron T (2008) Maturation of paneth cells induces the refractory state of newborn mice to Shigella infection. J Immunol 180(7):4924–4930
Shim DH, Ryu S, Kweon MN (2010) Defensins play a crucial role in protecting mice against oral Shigella flexneri infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 401(4):554–560
Burns-Guydish SM, Olomu IN, Zhao H, Wong RJ, Stevenson DK, Contag CH (2005) Monitoring age-related susceptibility of young mice to oral Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection using an in vivo murine model. Pediatr Res 58(1):153–158
Echeverry A, Schesser K, Adkins B (2007) Murine neonates are highly resistant to Yersinia enterocolitica following orogastric exposure. Infect Immun 75(5):2234–2243
Echeverry A, Saijo S, Schesser K, Adkins B (2010) Yersinia enterocolitica promotes robust mucosal inflammatory T-cell immunity in murine neonates. Infect Immun 78(8):3595–3608
Acknowledgments
S.S. was recipient of an APART fellowship at the Institute for Medical Microbiology at Hanover Medical School. S.S. present address is: Institute of Animal Breeding and Genetics, University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria. C.C. was supported by a post-doctoral fellowship from the Alexander Von Humboldt foundation. M.W.H. was supported by the German Research Foundation (Ho2236/5-3), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (DLR 01GU0825) as well as the Collaborative Research Center SFB 621 and SFB900.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stockinger, S., Hornef, M.W. & Chassin, C. Establishment of intestinal homeostasis during the neonatal period. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 3699–3712 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0831-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0831-2