Abstract
Objective: The effects of histamine and of histamine receptor agonists and antagonists on the coronary outflow and on the generation of nitric oxide (NO) were evaluated on isolated guinea pig hearts.
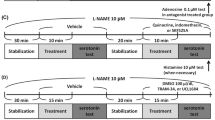
Methods: Isolated guinea pig hearts were perfused for 50 min in a Langendorff apparatus with histamine (10–7– 10–8 M), in the absence or in the presence of NG-monome-thyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA, 10–4 M), a NO synthase inhibitor and of triprolidine (3⋅10–8 M) and cimetidine (10–7 M), H1 receptor and H2 receptor antagonists, and with trifluoromethyl-phenylhistamine (TFMPH, 10–7 M) and dimaprit (10–7 M), H1 and H2 receptor agonists. The effects of (R)-α-methylhistamine (10–7 M), a H3 receptor agonist and of FUB 181 (10–7 M), a H3 receptor antagonist, were studied in the presence of bradykinin (10–7 M).
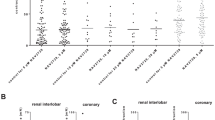
Results: Histamine increases the coronary outflow and the generation of NO in a concentration-dependent fashion. The effects were completely abolished by blocking NO-synthase (NOS) with L-NMMA (10 –4 M). The effects were also abolished by cimetidine (10 –7 M), H 2 receptor antagonist, and only scarcely affected by triprolidine (3⋅10 –8 M), H 1 receptor antagonist. The effects were reproduced by dimaprit (10 –7 M), H 2 receptor agonist, and only scarcely by TFMPH (10 –7 M), a selective H 1 receptor agonist. Bradykinin (10 –7 M) produces a sustained coronary dilation paralleled by a marked increase in the generation of NO; the effects were significantly reduced by L-NMMA. The stimulation of H 3 receptors by (R)-α-methylhistamine (10 –7 M) significantly reduced both effects, which reverted to normal with FUB 181 (10 –7 M), an H 3 receptor antagonist.
Conclusion: These results suggest that, in isolated guinea pig hearts, histamine produces coronary dilation through an H 2 /H 3 -dependent mechanism involving the generation of nitric oxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 3 December 2002; returned for revision 8 April 2003; accepted by M. Parnham 26 May 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierpaoli, S., Marzocca, C., Bello, M.G. et al. Histaminergic receptors modulate the coronary vascular response in isolated guinea pig hearts. Role of nitric oxide. Inflamm. res. 52, 390–396 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1191-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1191-7