Abstract
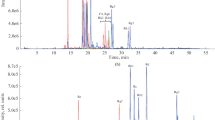
A fast isocratic HPLC method for analysis of steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana leaves was developed with a high selectivity for nine known steviol glycosides and low eluent consumption. The analytical method was performed on a Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped 3 μm Hibar® RT 250-4.6 column at 50 °C with an eluent composition of water (65 vol. %) and acetonitrile (35 vol. %). With a flow rate of 1 mL min−1, nine known steviol glycosides were detected selectively after 15 min. Method validation for rebaudioside A showed a LOD of 0.0004 mg mL−1 and a LOQ of 0.0038 mg mL−1. Particularly with regard to moderate solubility, the method is linear up to a concentration of rebaudioside A of 4.8 mg mL−1. The linear calibration curve was obtained with a coefficient of determination of 0.9997 ± 0.0002 and a total error of 2.01 % RSD (n = 12). The accuracy of the method was determined by the percentage mean recovery rate to 100.99 ± 2.01 %. The intra-day precision was in a range of 0.12 to 1.96 % RSD and the inter-day precision varies from 0.02 to 1.89 % RSD. Small changes in operating conditions like eluent composition (65 ± 2 vol. %), temperature (50 ± 10 °C) or flow rate (1 ± 0.2 mL min−1) do not affect the performance of the analytical method. The reliable and robust proposed HPLC method can be applied for quantification of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves in laboratories and quality control in industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adduci J, Buddhasukh D, Ternai B (1987) Improved isolation and purification of stevioside. J Sci Soc Thailand 13:179–183
Ahmed MS, Dobberstein RH (1982a) Stevia rebaudiana. II. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and quantitation of stevioside, rebaudioside A and rebaudioside C. J Chromatogr 236(2):523–526
Ahmed MS, Dobberstein RH (1982b) Stevia rebaudiana. III. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and quantitation of rebaudiosides B, D, and E, dulcoside A, and steviolbioside. J Chromatogr 245(3):373–376
Bovanová L, Brandsteterová E, Baxa S (1998) HPLC determination of stevioside in plant material and food samples. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 207(5):352–355
Carakastos M, Curry L, Boileau A, Brusick D (2008) Overview: the history, technical function and safety of rebaudioside A, a naturally occurring steviol glycoside, for use in food and beverages. Food Chem Toxicol 46(7):S1. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2008.05.003
Crammer B, Ikan R (1986) Sweet glycosides from the Stevia plant. Chem Br 22:915–917
Dacome AS, Da Silva CC, Da Costa CEM, Fontana JD, Adelmann J, Da Costa SC (2005) Sweet diterpenic glycosides balance of a new cultivar of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.) Bertoni: isolation and quantitative distribution by chromatographic, spectroscopic, and electrophoretic methods. Process Biochem 40(11):3587–3594
FAO (2010) Steviol glycosides. FAO JECFA Mono 10
Gardana C, Scaglianti M, Simonetti P (2010) Evaluation of steviol and its glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana leaves and commercial sweetener by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217(9):1463–1470
Hashimoto Y, Moriyasu M, Nakamura S (1978) High performance liquid chromatographic determination of Stevia components on a hydrophilic packed column. J Chromatogr 161:403–405
Hearn LK, Subedi PP (2009) Determining levels of steviol glycosides in the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J Food Compos Anal 22(2):165–168
Henderson J, Berry J (2009) Isocratic Stevia sweetener analyses using selective ZORBAX column
Huang XY, Fu JF, Di DL (2010) Preparative isolation and purification of steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni using high-speed counter-current chromatography. Sep Purif Technol 71(2):220–224
ICH (2005) Harmonized tripartite guideline validation on analytical procedures: text and methodology. In: International conference on harmonization Q2(R1)
Jaitak V, Gupta AP, Kaul VK, Ahuja PS (2008) Validated high-performance thin-layer chromatography method for steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47(4–5):790–794
Kalandia A, Papunidze G, Vanidze M, Papunidze S (2004) HPLC of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) diterpene glycosides. Bull Georg Acad Sci 169(1):147–150
Kedik SA, Fedorov SV, Yanul’ NA, Prokhorova LV, Smirnova EV, Panov AV (2003) Chromatographic determination of stevioside in raw plant material. Pharm Chem J 37(10):529–532
Kitada Y, Sasaki M, Yamazoe Y, Nakazawa H (1989) Simultaneous determination of stevioside, rebaudioside A and C and dulcoside A in foods by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 474(2):447–451
Kovylyaeva GI, Bakaleinik GA, Strobykina IY, Gubskaya VI, Sharipova RR, Al’Fonsov VA, Kataev VE, Tolstikov AG (2007) Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana. Chem Nat Compd 43(1):81–85
Makapugay HC, Nanayakkara NPD, Kinghorn AD (1984) Improved high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of the Stevia rebaudiana sweet diterpene glycosides using linear gradient elution. J Chromatogr A 283(C):390–395
Nikolova-Damyanova B, Bankova V, Popov S (1994) Separation and quantitation of stevioside and rebaudioside A in plant extracts by normal-phase high performance liquid chromatography and thin-layer chromatography: a comparison. Phytochem Anal 5(2):81–85
Nishiyama P (1992) Quantitative analysis of stevioside in the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J Sci Food Agric 59(3):277–281
Schmidt-Traub H (ed) (2005) Preparative chromatography of fine chemicals and pharmaceutical agents, 1st edn. Wiley, Weinheim
Woelwer-Rieck U, Lankes C, Wawrzun A, Wüst M (2010) Improved HPLC method for the evaluation of the major steviol glycosides in leaves of Stevia rebaudiana. Eur Food Res Technol 231(4):581–588
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the German Federal Ministry of Research and Education (Förderkennziffer: 0315663) and CLIB2021—Cluster Industrial Biotechnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergs, D., Burghoff, B., Joehnck, M. et al. Fast and isocratic HPLC-method for steviol glycosides analysis from Stevia rebaudiana leaves. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 7, 147–154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-012-0760-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-012-0760-5