Abstract
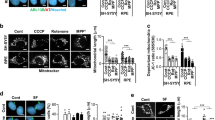
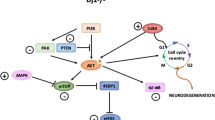
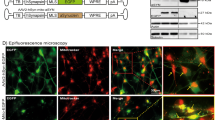
Aggregation of proteins in the centrosome is implicated in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. However, the relevance of the centrosome in neurodegeneration is still obscure. Centrosome duplication is initiated by the cyclin E/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) complex. The present study determined changes in cyclin E or Cdk2 expression and in the cen-trosomal structure in dopaminergic neuronal CATH.a cells exposed to 50, 100 and 150 μM dopamine (DA) for 24 h. DA induced significant increase in Cdk2 protein and cyclin E protein, but not cyclin e mRNA. In DA-treated cells, the intense cyclin E- and Cdk2-immunofluorescence signals were co-localized around large and supernumerary centrosomes, and these two parameters of centrosome amplification were significantly increased compared with the control. Simultaneous co-treatment with DA and a Cdk2 inhibitor blocked centrosome amplification and enhanced cell viability. Our results demonstrated that DA could lead to cyclin E accumulation and Cdk2 up-regulation triggering supernumerary centrosomes and apoptotic cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira D, M Tajes, E Verdaguer, SG de Arriba, C Allgaier, C Matute, R Trullas, A Jimenez, M Pallas and A Camins (2007) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases is neuroprotective in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis in neurons.Neuroscience 146, 350–365.
Andorfer C, CM Acker, Y Kress, PR Hof, K Duff and P Davies (2005) Cell-cycle reentry and cell death in transgenic mice expressing nonmutant human tau isoforms.J. Neurosci. 25, 5446–5454.
Asanuma M, I Miyazaki and N Ogawa (2003) Dopamine- or L-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: the role of dopamine qui-none formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson’s disease.Neurotox. Res. 5, 165–176.
Berman SB and TG Hastings (1999) Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria: implications for Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurochem. 73, 1127–1137.
Braak H, E Braak, D Yilmazer, C Schultz, RA de Vos and EN Jansen (1995) Nigral and extranigral pathology in Parkinson’s disease.J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 46, 15–31.
Ciciarello M, R Mangiacasale, M Casenghi, M Zaira Limongi, M D’Angelo, S Soddu, P Lavia and E Cundari (2001) p53 displacement from centrosomes and p53-mediated G1 arrest following transient inhibition of the mitotic spindle.J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19205–19213. Epub 12001 Feb 19228.
Conway KA, JC Rochet, RM Bieganski and PT Lansbury Jr (2001) Kinetic stabilization of the a-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-α-synuclein adduct.Science 294, 1346–1349.
Cyr M, JM Beaulieu, A Laakso, TD Sotnikova, WD Yao, LM Bohn, RR Gainetdinov and MG Caron (2003) Sustained elevation of extracellular dopamine causes motor dysfunction and selective degeneration of striatal GABAergic neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 11035–11040.
Delattre M and P Gonczy (2004) The arithmetic of centrosome biogenesis.J. Cell. Sci. 117, 1619–1630.
Diaz-Corrales FJ, M Asanuma, I Miyazaki, K Miyoshi and N Ogawa (2005) Rotenone induces aggregation of γ-tubulin protein and subsequent disorganization of the centrosome: relevance to formation of inclusion bodies and neurodegen-eration.Neuroscience 133, 117–135.
El-Khodor BF, TF Oo, N Kholodilov and RE Burke (2003) Ectopic expression of cell cycle markers in models of induced programmed cell death in dopamine neurons of the rat substantia nigra pars compacta.Exp. Neurol. 179, 17–27.
Emdadul Haque M, M Asanuma, Y Higashi, I Miyazaki, K Tanaka and N Ogawa (2003) Apoptosis-inducing neurotoxicity of dopamine and its metabolites via reactive quinone generation in neuroblastoma cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1619, 39–52.
Fahn S, D Oakes, I Shoulson, K Kieburtz, A Rudolph, A Lang, CW Olanow, C Tanner and K Marek (2004) Levodopa and the progression of Parkinson’s disease.N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 2498–2508.
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 259–272.
Honda R, ED Lowe, E Dubinina, V Skamnaki, A Cook, NR Brown and LN Johnson (2005) The structure of cyclin E1/ CDK2: implications for CDK2 activation and CDK2-independent roles.EMBO J. 24, 452–463.
Hoozemans JJ, MK Bruckner, AJ Rozemuller, R Veerhuis, P Eikelenboom and T Arendt (2002) Cyclin D1 and cyclin E are co-localized with cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX-2) in pyramidal neurons in Alzheimer disease temporal cortex.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61, 678–688.
Husseman JW, D Nochlin and I Vincent (2000) Mitotic activation: a convergent mechanism for a cohort of neurodegen-erative diseases.Neurobiol. Aging 21, 815–828.
Jellinger KA (2003) General aspects of neurodegeneration.J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 65, 101–144.
Johnson K, L Liu, N Majdzadeh, C Chavez, PC Chin, B Morrison, L Wang, J Park, P Chugh, HM Chen and SR D’Mello (2005) Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor GW8510: identification of 3’substituted indolones as a scaffold for the development of neuroprotective drugs.J. Neurochem. 93, 538–548.
Johnston JA, CL Ward and RR Kopito (1998) Aggresomes: a cellular response to misfolded proteins.J. Cell. Biol. 143, 1883–1898.
Kawamura K, H Izumi, Z Ma, R Ikeda, M Moriyama, T Tanaka, T Nojima, LS Levin, K Fujikawa-Yamamoto, K Suzuki and K Fukasawa (2004) Induction of centrosome amplification and chromosome instability in human bladder cancer cells by p53 mutation and cyclin E overexpression.Cancer Res. 64, 4800–4809.
Klein JA and SL Ackerman (2003) Oxidative stress, cell cycle, and neurodegeneration.J. Clin. Invest. 111, 785–793.
Kopito RR (2000) Aggresomes, inclusion bodies and protein aggregation.Trends Cell. Biol. 10, 524–530.
Lacey KR, PK Jackson and T Stearns (1999) Cyclin-dependent kinase control of centrosome duplication.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2817–2822.
LaVoie MJ, BL Ostaszewski, A Weihofen, MG Schlossmacher and DJ Selkoe (2005) Dopamine covalently modifies and functionally inactivates parkin.Nat. Med. 11, 1214–1221. Epub 2005 Oct 1216.
Lee SS, YM Kim, E Junn, G Lee, KH Park, M Tanaka, RD Ronchetti, MM Quezado and MM Mouradian (2003) Cell cycle aberrations by α-synuclein over-expression and cyclin B immunoreactivity in Lewy bodies.Neurobiol. Aging 24, 687–696.
Lingle WL, SL Barrett, VC Negron, AB D’Assoro, K Boeneman, W Liu, CM Whitehead, C Reynolds and JL Salisbury (2002) Centrosome amplification drives chromosomal instability in breast tumor development.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 1978–1983.
Marx FP, AS Soehn, D Berg, C Melle, C Schiesling, M Lang, S Kautzmann, KM Strauss, T Franck, S Engelender, J Pahnke, S Dawson, F von Eggeling, JB Schulz, O Riess and R Kruger (2007) The proteasomal subunit S6 ATPase is a novel synphilin-1 interacting protein - implications for Parkinson’s disease.FASEB J. 21, 1759–1767.
McNaught KS, P Shashidharan, DP Perl, P Jenner and CW Olanow (2002) Aggresome-related biogenesis of Lewy bodies.Eur. J. Neurosci. 16, 2136–2148.
Moroy T and C Geisen (2004) Cyclin E.Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36, 1424–1439.
Murray AW (2004) Recycling the cell cycle: cyclins revisited.Cell 116, 221–234.
Nguyen MD, WE Mushynski and JP Julien (2002) Cycling at the interface between neurodevelopment and neurodegener-ation.Cell Death Differ. 9, 1294–1306.
Oakley CE and BR Oakley (1989) Identification of γ-tubulin, a new member of the tubulin superfamily encoded by mipA gene of Aspergillus nidulans.Nature 338, 662–664.
Ogawa N, M Asanuma, I Miyazaki, FJ Diaz-Corrales and K Miyoshi (2005) L-DOPA treatment from the viewpoint of neuroprotection. Possible mechanism of specific and progressive dopaminergic neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurol. 252, IV23-IV31.
Olanow CW, DP Perl, GN DeMartino and KS McNaught (2004) Lewy-body formation is an aggresome-related process: a hypothesis.Lancet Neurol. 3, 496–503.
Petrozzi L, C Lucetti, R Scarpato, G Gambaccini, F Trippi, S Bernardini, P Del Dotto, L Migliore and U Bonuccelli (2002) Cytogenetic alterations in lymphocytes of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease patients.Neurol. Sci. 23 Suppl 2, S97-S98.
Sathasivam K, B Woodman, A Mahal, F Bertaux, EE Wanker, DT Shima and GP Bates (2001) Centrosome disorganization in fibroblast cultures derived from R6/2 Huntington’s disease (HD) transgenic mice and HD patients.Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 2425–2435.
Smith MZ, Z Nagy and MM Esiri (1999) Cell cycle-related protein expression in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 271, 45–48.
Smith PD, SJ Crocker, V Jackson-Lewis, KL Jordan-Sciutto, S Hayley, MP Mount, MJ O’Hare, S Callaghan, RS Slack, S Przedborski, H Anisman and DS Park (2003) Cyclin- dependent kinase 5 is a mediator of dopaminergic neuron loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13650–13655.
Stearns T, L Evans and M Kirschner (1991) γ-Tubulin is a highly conserved component of the centrosome.Cell 65, 825–836.
Sunkel CE, R Gomes, P Sampaio, J Perdigao and C Gonzalez (1995) γ-Tubulin is required for the structure and function of the microtubule organizing centre in Drosophila neuroblasts.EMBO J. 14, 28–36.
van Muiswinkel FL, RA de Vos, JG Bol, G Andringa, EN Jansen Steur, D Ross, D Siegel and B Drukarch (2004) Expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase in the normal and Parkinsonian substantia nigra.Neurobiol. Aging 25, 1253–1262.
Whitehead RE, JV Ferrer, JA Javitch and JB Justice (2001) Reaction of oxidized dopamine with endogenous cysteine residues in the human dopamine transporter.J. Neurochem. 76, 1242–1251.
Wigley WC, RP Fabunmi, MG Lee, CR Marino, S Muallem, GN DeMartino and PJ Thomas (1999) Dynamic association of proteasomal machinery with the centrosome.J. Cell. Biol. 145, 481–490.
Xu J, SY Kao, FJ Lee, W Song, LW Jin and BA Yankner (2002) Dopamine-dependent neurotoxicity of a-synuclein: a mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease.Nat. Med. 8, 600–606.
Xu Y, AH Stokes, RJ Roskoski and KE Vrana (1998) Dopamine, in the presence of tyrosinase, covalently modifies and inactivates tyrosine hydroxylase.J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 691–697.
Yoshimoto Y, K Nakaso and K Nakashima (2005) L-dopa and dopamine enhance the formation of aggregates under protea- some inhibition in PC12 cells.FEBS Lett. 579, 1197–1202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz-Corrales, F.J., Asanuma, M., Miyazaki, I. et al. Dopamine induces supernumerary centrosomes and subsequent cell death through Cdk2 up-regulation in dopaminergic neuronal cells. neurotox res 14, 295–305 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033854
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033854