Abstract
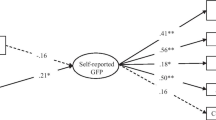
We present a psychometric test of life history theory as applied to human individual differences using MIDUS survey data (Brim et al. 2000). Twenty scales measuring cognitive and behavioral dimensions theoretically related to life history strategy were constructed using items from the MIDUS survey. These scales were used to construct a single common factor, the K-factor, which accounted for 70% of the reliable variance. The scales used included measures of personal, familial, and social function. A second common factor, Covitality, was constructed from scales for physical and mental health. Finally, a single general factor, Personality, was constructed from scales for the “Big Five” factors of personality. The K-factor, covitality factor, and general personality factor correlated significantly with each other, supporting the prediction that high K predicts high somatic effort and also manifests in behavioral display. Thus, a single higher-order common factor, the Super-K factor, was constructed that consisted of the K-factor, covitality factor, and personality factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrow, K., S. Bowles, and S. Durlauf 2000Meritocracy and Economic Inequality. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Belsky, J. 2000 Conditional and Alternative Reproductive Strategies: Individual Differences in Susceptibility to Rearing Experiences. InGenetic Influences on Human Fertility and Sexuality, J. L. Rodgers, D. C. Rowe, and W. B. Miller, eds. Pp. 127–146 Boston: Kluwer.
Belsky, J., L. Steinberg, and P. Draper 1991 Childhood Experience, Interpersonal Development, and Reproductive Strategy: An Evolutionary Theory of Socialization.Child Development 62:647–670.
Blackburn, R., S. J. D. Renwick, J. P. Donnelly, and C. Logan 2004 Big Five or Big Two? Superordinate Factors in the NEO Five Factor Inventory and the Antisocial Personality Questionnaire.Personality and Individual Differences 37:957–970.
Brim, O. G., P. B. Baltes, L. L. Bumpass, P. D. Cleary, D. L. Featherman, W. R. Hazzard, R. C. Kessler, M. E. Lachman, H. R. Markus, M. G. Marmot, A. S. Rossi, C. D. Ryff, and R. A. Shweder 2000National Survey of Midlife Development in the United States (MIDUS), 1995–1996 [Computer file]. ICPSR version. DataStat and Harvard Medical School, Dept. of Health Care Policy [producers], 1996. Ann Arbor: Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research [distributor].
Brim, O. G., C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler 2004 The MIDUS National Survey: An Overview. InHow Healthy Are We? A National Study of Well-being at Midlife, O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler, eds. Pp. 64–89. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Buss, D. M. 1989 Sex Differences in Human Mate Preferences: Evolutionary Hypotheses Tested in 37 Cultures.Behavioral and Brain Science 12:1–49.
Buss, D. M. 1999 Adaptive Individual Differences.Journal of Personality 67:209–243.
Charlesworth, B. 1980Evolution and Age-Structured Populations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, J. S. 1996 The Evolutionary Ecology of Attachment Organization.Human Nature 7:1–38.
Cohen, J., and P. Cohen 1983Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Costa, P. T., and R. R. McCrae 1992Revised NEO Personality Inventory (NEO PI-R) and NEO Five-Factor Inventory (NEOFFI): Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Digman, J. 1997 Higher-Order Factors of the Big Five.Journal ofPersonality and Social Psychology 73:1246–1256.
Ellis, B. J. 2004 Timing of Pubertal Maturation in Girls: An Integrated Life History Approach.Psychological Bulletin 130:920–958.
Eysenck, H. J., and S. B. G. Eysenck 1975Manual of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire. London: Hodder and Stoughton.
Figueredo, A. J., J. Sefcek, and D. N. Jones 2005 The Ideal Romantic Partner Personality.Personality and Individual Differences 41:431–441.
Figueredo, A. J., J. Corral-Verdugo, M. Frias-Armenta, K. J. Bachar, J. White, P. L. McNeill, B. R. Kirsner, and I. P. Castell-Ruiz 2001 Blood, Solidarity, Status, and Honor: The Sexual Balance of Power and Spousal Abuse in Sonora, Mexico.Evolution and Human Behavior 22:295–328.
Figueredo, A. J., J. Sefcek, G. Vásquez, B. H. Brumbach, J. E. King, and W. J. Jacobs 2005 Evolutionary Personality Psychology. InHandbook of Evolutionary Psychology, D. M. Buss, ed. Pp. 851–877. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Figueredo, A. J., G. Vásquez, B. H. Brumbach, J. A. Sefcek, B. R. Kirsner, and W. J. Jacobs 2005 The K-Factor: Individual Differences in Life History Strategy.Personality and Individual Differences 39:1349–1360.
Fleeson, W. 2001 Judgments of One’s Own Contributions to the Welfare of Others: Life-Course Trajectories and Predictors. InCaring and Doing for Others: Social Responsibility in the Domains of Family, Work, and Community, A. S. Rossi, ed. Pp. 75–96 Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Fouts, H. N., B. S. Hewlett, and M. E. Lamb 2005 Parent-Offspring Weaning Conflicts among the Bofi Farmers and Foragers of Central Africa.Current Anthropology 46:29–50.
Gadgil, M., and O. T. Solbrig 1972 The Concept of r and K Selection: Evidence from Wild Flowers and Some Theoretical Considerations.American Naturalist 106:14–31.
Geary, D. C. 2005The Origin of Mind: Evolution of Brain, Cognition, and General Intelligence. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association Press.
Gottfredson, L. S. 2006 Social Consequences of Group Differences in Cognitive Ability (Consequencias sociais das diferencas de grupo em habilidade cognitiva). InIntroducau a psicologia das diferencas individuals, C. E. Flores-Mendoza and R. Colom, eds. Pp. 433–456. Porto Allegre, Brazil: ArtMed Publishers.
Grzywacz, J. G., and C. L. M. Keyes 2004 Toward Health Promotion: Physical and Social Behaviors in Complete Health.American Journal of Health Behavior 28(2):99–111.
Grzywacz, J. G., and N. F. Marks 1999 Family Solidarity and Health Behaviors: Evidence from the National Survey of Midlife Development in the United States.Journal of Family Issues 20:243–268.
Grzywacz, J. G., D. M. Almeida, and D. A. McDonald 2002 Work-Family Spillover and Daily Reports of Work and Family Stress in the Adult Labor Force.Family Relations 51:28–36.
Hewlett, B. S., and M. E. Lamb 2002 Integrating Evolution, Culture, and Developmental Psychology: Explaining Caregiver-Infant Proximity and Responsiveness in Central Africa and the USA. InBetween Culture and Biology: Perspectives on Ontogenetic Development, H. Keller, ed. Pp. 241–269. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Kawachi, I., B. P. Kennedy, and R. G. Wilkinson 1999Income Inequality and Health. The Society and Population Health Reader, Vol. I. New York: New Press.
Kerckhoff, A. C. 2000Generating Social Stratification: Toward a New Research Agenda. Boulder: Greenwood Press.
King, V. 2003 The Influence of Religion on Fathers’ Relationships with Their Children.Journal of Marriage and Family 65:382–395.
Krebs, C. J., M. S. Gaines, B. L. Keller, J. H. Myers, and R. H. Tamarin 1973 Population Cycles in Small Rodents.Science 179:35–41.
Leggett, W. C., and J. E. Carscadden 1978 Latitudinal Variation in Reproductive Characteristics of American Shad (Alosa sapidissima): Evidence for Population Specific Life History Stages in Fish.Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 35:1469–1478.
MacArthur, R. H., and E. O. Wilson 1967The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Marks, N. F., L. L. Bumpass, and H. Jun 2004 Family Roles and Well-being during Middle Life Course. InHow Healthy Are We? A National Study of Well-being at Midlife, O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler, eds. Pp. 514–549. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Marmot, M. G., and R. Fuhrer 2004 Socioeconomic Position and Health across Midlife. InHow Healthy Are We? A National Study of Well-being at Midlife, O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler, eds. Pp. 64–89. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Marmot, M. G., R. Fuhrer, S. L. Ettner, N. F. Marks, L. L. Bumpass, and C. D. Ryff 1998 Contributions of Psychosocial Factors to Socioeconomic Differences in Health.Milbank Quarterly 76:403–448.
Martin, M., and G. J. Westerhof 2003 Do You Need Them or Should You Believe You Have Them? Resources, Their Appraisal, and Well-being in Adulthood.Journal of Adult Development 10(2):99–112.
Miller, G. 2000 Mental Traits as Fitness Indicators. InEvolutionary Perspectives on Human Reproductive Behavior, D. LeCrosy and P. Moller, eds. Pp. 62–74. New York: New York Academy of Sciences.
Pianka, E. R. 1970 On r- and K-selection.American Naturalist 104:592–596.
Quinlan, R. J. 2003 Father Absence, Parental Care and Female Reproductive Development.Evolution and Human Behavior 24:376–390.
Reznick, B., M. J. Bryant, and F. Bashey 2002 r- and K-selection Revisited: The Role of Population Regulation in Life-History Evolution.Ecology 83:1509–1520.
Rossi, A. S. 2001a Contemporary Dialogue on Civil Society and Social Responsibility. InCaring and Doing for Others: Social Responsibility in the Domains of Family, Work, and Community, A. S. Rossi, ed. Pp. 3–75. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Rossi, A. S. 2001b Domains and Dimensions of Social Responsibility: A Sociodemographic Profile. InCaring and Doing for Others: Social Responsibility in the Domains of Family, Work, and Community, A. S. Rossi, ed. Pp. 97–134. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Rossi, A. S. 2001c Impact of Family Problems on Social Responsibility. InCaring and Doing for Others: Social Responsibility in the Domains of Family, Work, and Community, A. S. Rossi, ed. Pp. 312–347. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Rossi, A. S. 2004 Social Responsibility to Family and Community. InHow Healthy Are We? A National Study of Well-being at Midlife, O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler, eds. Pp. 550–585. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Rowe, D. C. 2000 Environmental and Genetic Influences on Pubertal Development: Evolutionary Life History Traits? InGenetic Influences on Human Fertility and Sexuality: Recent Empirical and Theoretical Findings, J. L. Rodgers, D. C. Rowe, and W. B. Miller, eds. Pp. 147–168. Boston: Kluwer.
Rushton, J. P. 1985 Differential K Theory: The Sociobiology of Individual and Group Differences.Personality and Individual Differences 6:441–452.
Rushton, J. P. 2000Race, Evolution, and Behavior: A Life-History Perspective, third ed. Port Huron, MI: Charles Darwin Research Institute.
Rushton, J. P. 2004 Placing Intelligence into an Evolutionary Framework, or How g Fits into the r-K Matrix of Life History Traits, Including Longevity.Intelligence 32:321–328.
Ryff, C. D., B. H. Singer, and K. A. Palmersheim 2001 Social Inequalities in Health and Well-being: The Role of Relational and Religious Protective Factors. InHow Healthy Are We? A National Study of Well-being at Midlife, O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, and R. C. Kessler, eds. Pp. 90–123. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1999SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Version 8, 3 vols. Cary, NC: SAS Institute.
Schlichting, C. D., and M. Pigliucci 1998Phenotypic Evolution: A Reaction Norm Perspective. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates.
Stearns, S. C. 1992The Evolution of Life Histories. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Tal, I., D. Hill, A. J. Figueredo, M Frias-Armenta, and V Corral-Verdugo 2006 An Evolutionary Approach to Explaining and Water Conservation.Medio Ambiente y Comportamiento Humano 7(1):7–27.
Taylor, C. E., and C. Condra 1980 r- and K-selection inDrosophila pseudoobscura.Evolution 34:1183–1193.
Thornhill, R., and C. T. Palmer 2004 Evolutionary Life History Perspective on Rape. InEvolutionary Psychology, Public Policy and Personal Decisions, C. Crawford and C. Salmon, eds. Pp. 249–274. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Vásquez, G. 2004Female Personality, Risk, and Mate Selection. Unpublished Masters Thesis, Department of Psychology, University of Arizona, Tucson.
Weiss, A., J. E. King, and R. M. Enns 2002 Subjective Well-being Is Heritable and Genetically Correlated with Dominance in Chimpanzees.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 83:1141–1149.
West-Eberhard, M. J. 2003Developmental Plasticity and Evolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Wilbur, H. M., D. W. Tinkle, and J. P. Collins 1974 Environmental Certainty, Trophic Level, and Resource Availability in Life History Evolution.American Naturalist 108:805–817.
Wilkinson, R. 1996Unhealthy Societies: The Afflictions of Inequality. Routledge: London.
Zuckerman, M., D. M. Kuhlman, J. Joireman, P. Teta, and M. Kraft 1993 A Comparison of Three Structural Models for Personality: The Big Three, the Big Five, and the Alternative Five.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 65:757–768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figueredo, A.J., Vásquez, G., Brumbach, B.H. et al. The K-factor, Covitality, and personality. Hum Nat 18, 47–73 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02820846
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02820846