Abstract
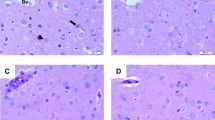
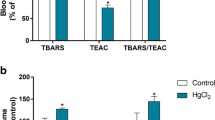
Parenteral administration of methyl mercuric chloride (MMC, CH3HgCl) to rats enhanced lipid peroxidation in liver of rats, as measured by the thiobarbituric acid reaction for malondialdehyde (MDA) in fresh tissue homogenates. After sc injection of CH3HgCl (5 mg/kg body wt), MDA concentration in liver became significantly increased at 24 h and further increased at 48 h. Dose-response studies were carried out with male albino rats of the Fisher-344 strain (body wt 170–280 g) injected with 3 or 5 mg Hg/kg as CH3HgCl and sacrificed after 24 h. In time-response studies, animals were administered 5 mg Hg/kg as CH3HgCl and sacrificed after 24 and 48 h. Studies in the authors’ laboratory have shown that (1) mercury is accumulated in liver; (2) concentration of MDA is increased in liver of CH3HgCl-treated rats; (3) severity of hepatotoxicity is generally proportional to the elevation of MDA concentration, based upon the dose-effect relationships observed after administration of CH3HgCl to rats. The results of this study implicate that the lipid peroxidation is one of the molecular mechanisms for cell injury in acute CH3HgCl poisoning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. P. Junghans, A review of the toxicity of methylmercury compounds with application to occupational exposures associated with laboratory uses,Environ. Res. 31, 1–31 (1983).
R. Von Burg, F. K. Northington, and A. Shamoo, Methylmercury inhibition of rat brain muscarinic receptors,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 53, 285–292 (1980).
R. Klein, S. P. Herman, B. C. Bullock, and F. A. Tally, Methyl mercury intoxication in rat kidneys,Arch. Patho. 96, 83–90.
D. L. Brown, K. R. Reuhl, S. Bormann, and J. E. Little, Effects of methyl mercury on the microtubule system of mouse lymphocytes,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 96, 66–75 (1988).
D. O. Marsh, C. J. Meyers, T. W. Clarkson, L. Amin-Zaki, and S. Tikriti, Fetal methylmercury poisoning: New data on clinical and toxicological aspects,Trans. Am. Neurol. Assoc. 102, 1–3 (1977).
D. O. Marsh, C. J. Meyers, T. W. Clarkson, L. Amin-Zaki, S. Tikriti, and M. A. Majeed, Fetal methylmercury poisoning: Clinical and toxicological data,Ann. Neurol. 7, 348–353 (1980).
D. O. Marsh, C. J. Meyers, T. W. Clarkson, L. Amin-Zaki, S. Tikriti, M. A. Majeed, and A. R. Dabbagh, Dose-response relationship for human fetal exposure to methylmercury. Presented at the International Congress of Neurotoxicology, Varese, Italy (1979).
L. W. Chang and S. Yamaguchi, Ultrastructure changes of the liver following long term diet of mercury contaminated tuna,Environ. Res. 7, 133–148 (1974).
P. A. Desnoyers and L. W. Chang, Ultrastructure changes of the liver after chronic exposure to methylmercury.Environ. Res. 10, 59–75 (1975).
P. A. Desnoyers and L. W. Chang, Ultrastructure changes in the hepatocytes following acute methylmercury intoxication,Environ. Res. 9, 224–239 (1975).
L. W. Chang and K. R. Reuhl, Mercury in human and animal health, inTrace Elements in Health, Chapter 6, J. Rose, ed., Butterworth, London, pp. 132–149 (1983).
S. M. Charbonneau, I. C. Munro, E. A. Nera, F. A. Armstrong, R. F. Willes, F. Bryce, and R. F. Nelson, Chronic toxicity of methylmercury in the adult cat, Interim report,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 5, 337–349 (1976).
F. W. Sunderman Jr., Metals and lipid peroxidation,Acta pharmacol. Toxicol. 5, 137–143 (1986).
F. W. Sunderman Jr., A. Marzouk, S. M. Hopfer, O. Zaharia, and M. C. Reid, Increased lipid peroxidation in tissues of nickel chloride-treated rats.Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 15, 229–236 (1985).
S. M. Lin, C. H. Chiang, C. L. Tseng, and M. H. Yang, Determination of mercury contents in head hair of dentists by instrumental neutron activation analysis.Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett. 56, 261–272 (1983).
T. Takahashi, T. Kimura, Y. Jato, H. Shiraki, and T. Ukita, Time dependent distribution of 203 Hg-mercury compound in cat and monkeys as studied by whole body autoradiography,J. Hyg. Chem. 17, 93–107 (1971).
T. Norseth and T. W. Clarkson, Intestinal transport of 203Hg labeled methylmercury chloride in rats,Arch. Environ. Hlth.,21, 717–727 (1970).
R. Klein, S. P. Herman, P. E. Brubaker, G. W. Lucier, and M. R. Krigman, A model of acute methylmercury intoxication in rats.Arch. Pathol. 93, 408–418 (1972).
P. D. Simplicio, M. Gorelli, R. Vignani, and C. Leonzio, The differential modulation of the enzymes of glutathione metabolism. Indication of overlapping effects of toxicity and repair in mouse liver and kidney after dietary treatment with methyl mercury and sodium selenite,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 36, 167–181 (1993).
M. Younes and C-P. Siegers, Interrelation between lipid peroxidation and other hepatotoxic events,Biochem. Pharmacol. 33, 2001–2003 (1984).
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge, Oxygen toxity, oxygen radicals, transition metal, and disease,Biochem. J. 219, 1–14 (1984).
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge, Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage, and antioxidant therapy,Lancet,1, 1396, 1397 (1985).
J. P. Clavel, J. Emerit, and A. Thuillier, Lipid peroxidation and free radicals. Role in cellular biology and in pathology,Path. Biol. 33, 61–69 (1985).
N. Sugawara and C. Sugawara, Selenium protection against testicular lipid peroxidation from cadmium,J. Appl. Biochem. 6, 199–204 (1984).
H. Fukino, M. Hirai, Y. M. Hsueh, and Y. Yamane, Effect of zinc pretreatment on mercuric chloride-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat kidney,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 73, 395–401 (1984).
J. J. Doughery and W. C. Hoekstra, Effects of vitamin E and selenium on copper-induced lipid peroxidation in vivo and on acute copper toxicity,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 169, 201–208 (1982).
O. A. Levander, V. C. Morris, and R. J. Ferretti, Filterability of erythrocytes from vitamin E-deficient lead poisoned rats,J. Nutri. 107, 363–372 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TH., Huang, YL. & Huang, SF. Lipid peroxidation in liver of rats administrated with methyl mercuric chloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 54, 33–41 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785318
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785318