Abstract
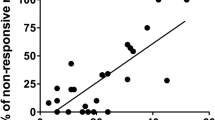
Presumably unrelated behaviors (e.g. psychiatric admissions, seizures, heart failures) have been correlated with increased global geomagnetic activity. We have suggested that all of these behaviors share a common source of variance. They are evoked by transient, dopamine-mediated paroxysmal electrical patterns that are generated within the amygdala and the hippocampus of the temporal lobes. Both the probability and the propagation of these discharges to distal brain regions are facilitated when nocturnal melatonin levels are suppressed by increased geomagnetic activity. In support of this hypothesis, the present study demonstrated a significant correlation of Pearsonr=0.60 between mortality during the critical 4-day period that followed induction of libic seizures in rats and the ambient geomagnetic activity during the 3 to 4 days that preceded death; the risk increased when the 24 h geomagnetic indices exceeded 20 nT for more than 1 to 2 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahtee L, Vahala M-L (1985) Taurine and its derivatives alter brain dopamine metabolism similarly to GABA in mice and rats. Prog Clin Biol Res 179:331–334.
Anton-Tay F (1971) Pineal-brain relationships. In: Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) The pineal gland. Churchill Livingston. London, pp 213–227.
Bardsano JL, Cos S, Picazo ML (1989) Veränderungen der Anzahl synaptischer Bänder in der Pinealdrüse der Ratte an geomagnetischen Ruhetagen und Gewittertagen. J Hirnforsch 30:639–643
Baron P, Palma V, DeBartolomies A, Tedeschi E, Muscettola G, Campanella G (1991) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptors mediate opposite functions in seizures induced by lithium-pilocarpine. Eur J Pharmacol 195:157–162.
Bureau YRJ, Persinger MA (1991) Transient blocking of persistent gnawing by haloperidol in rats with seizure-induced damage in the substantia nigra reticulata. Submitted to Psychopharmacology.
Carpenter MC, Sutton J (1983) Human neuroanatomy, 8th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Dakshinamurti K, Paulose CS, Viswanathan M, Siow AY (1988) Neuroendocrinology of pyridoxine deficiency. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 12:189–193.
De Olmos J, Alheid GF, Beltramino CA (1985) Amygdala. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, New York. pp 223–317.
Foley PB, Cairncross KD, Foldes A (1986) Pineal indoles: significance and measurement. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 10:273–293.
Friedman H, Becker RO, Bachman CH (1963) Geomagnetic parameters and psychiatric hospital admissions. Nature 200:626–628.
Gloor P, Olivier A, Wuesney LF, Andermann F, Horowitz S (1982) The role of the limbic system in experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 12:129–144.
Honchar MP, Olney JW, Sherman WR (1983) Systemic cholinergic agents induce seizures and brain damage in lithium-treated rats. Science 220:323–325.
Kavaliers M, Ossenkopp KP (1988) Day-night rhythms of opioid and non-opioid stress-induced analgesia: differential inhibitory effects of exposure to magnetic fields. Pain 32:223–229.
Keshavan MS, Gangadhar BN, Guatam RU, Ajit VB, Kapur RL (1981) Convulsive threshold in humans and rats and magnetic changes: observations during total solar eclipse. Neurosci Lett 22:205–208.
Lerchl A, Reiter RJ, Howes KA, Nonaka KO, Stokkan KA (1991) Evidence that extremely low frequency Ca++-cyclotron resonance depresses pineal melatonin synthesis in vitro. Neurosci Lett 124:213–215
Mayaud PN (1973) A hundred-year series of geomagnetic data 1868–1967. IAGA Bull.
McDonald RMP (1991) Course of recovery from seizure-induced brain trauma in rats. Unpublished fourth year thesis; Laurentian University.
McIntyre DC, Plant JR (1989) Pyriform cortex involvement in kindling. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:277–280.
Novikova KF, Gnevyshev MN, Tokareva NV, Ol Ai, Panov TN (1968) The effect of solar activity on the development of myocardial infarction and mortality resulting therefrom. Cardiology 4:109–112.
Olcese J, Reuss S (1986) Magnetic field effects on pineal gland melatonin synthesis: comparative studies on albino and pigmented rats. Brain Res 369:365–368.
Oppenheimer SM, Wilson JX, guirarudon C, Cechetto DF (1991) Insular cortex stimulation produces lethal cardiac arrhythmias: a mechanism of sudden death? Brain Res 550:115–121
Ormandy GC, Jope RS, Snead OC (1989) Anticonvulsant actions of MK801 on the lithium-pilocarpine model of status epilepticus in rats. Exp Neurol 106:172–180
Ossenkopp KP, Kavaliers M, Prato FS, Hirst M (1983) Reduced nocturnal morphine analgesia in mice following a geomagnetic disturbance. Neurosci Lett 90:321–325.
Persinger MA (1980) The weather matrix and human behavior. Praeger, New York.
Persinger MA (1983) The effects of transient or intense geomagnetic or related global perturbations upon human group behavior. In: Calhoun JB (ed) Environment and population: problems of adaptation. Praeger, New York, pp 28–30
Persinger MA (1988) Increased geomagnetic activity and the occurrence of bereavement hallucinations: evidence for melatonin-mediated microseizuring in the temporal lobe?. Neurosci Lett 88:271–274.
Persinger MA (1991) Canonical correlation of a temporal lobe signs scale with schizoid and hypomania scales in a normal population. Men and women are similar but for different reasons. Percep Mot Skil 73:615–618.
Persinger MA, Makarec K (1987) Temporal lobe epileptic signs and correlative behaviors displayed by normal populations. J Gen Psychol 114:179–195
Persinger MA, Ludwig HW, Ossenkopp KP (1973) Psychophysiological effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields: a review. Percept Mot Skills 36:131–159.
Persinger MA, Makarec K, Bradley JC (1988) Characteristics of limbic seizures evoked by peripheral injections of lithium and pilocarpine. Physiol Behav 44:27–37.
Persinger MA, Bureau Y, Kostakos M, Peredery O (1992a) Behaviors of rats with insidious brain damage induced by seizures following single peripheral injections of lithium and pilocarpine. Physiol Behav (in press)
Persinger MA, Koren SA, Makarec K, Richards P, Youlton S (1992b) Differential effects of wave form and the subject’s possible temporal lobe signs upon experiences during cerebral exposure to weak intensity magnetic fields. J Bioelectr (in press)
Rajaram M, Mitra S (1981) Correlations between convulsive seizure and geomagnetic activity. Neurosci Lett 24:187–191
Randall W, Randall S (1991) The solar wind and hallucinations — a possible relation to magnetic disturbances. Bioelectromagnetics 12:67–70
Roberts GW, Bruton CJ (1990) Notes from the graveyard: neuropathology and schizophrenia. Neuropath Appl Neurobiol 16:3–16
Roberts RJ, Varney NR, Hulbert JR, Paulsen JS, Richardson ED, Springer JA, Shepard JS, Swan CM, Legrand JA, Harvey JH, Struchen MA (1990) The neuropathology of everyday life: the frequency of partial seizure symptoms among normals. Neuropsychology 4:65–85
Rockhold RW, Acuff CG, Clower BR (1990) Excitotoxic lesions of the paraventricular hypothalamus: metabolic and cardiac effects. Neuropharmacology 29:663–673
Rosenstein RE, Estevez A, Cardinali DP (1989) Time-dependent effect of melatonin on glutamic acid decarboxylase activity and 36Cl-influx in rat hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 1:443–447
Ruttan LA, Persinger MA, Koren S (1990) Enhancement of temporal lobe-related experiences during brief exposures to milligauss intensity extremely low frequency magnetic fields. J Bioelectr 9:33–54
Seidman LJ (1983) Schizophrenia and brain dysfunction: an integration of recent neurodiagnostic findings. Psychol Bull 94:195–238
Semm P (1988) The magnetic detection system of the pigeon: involvement of pineal and retinal photoreceptors and the vestibular system. In: Connor ME, Lovely RH (eds) Electromagnetic fields and neurobehavioral function. Liss, New York, pp 47–61
Spencer SE, Sawyer WB, Loewy AD (1989) Cardiovascular effects produced byl-glutamate stimulation of the lateral hypothalamic area. Am J Physiol 257:H540-H552
Stevens JR (1982) Sleep is for seizures: a new interpretation of the role of phasic events in sleep and wakefulness. In: Sterman MB, Shouse MN, Passoaunt P (eds) Sleep and epilepsy. Academic Press, New York, pp 249–264
Subrahmanyam S, Sanker Narayan PV, Srinivasan TM (1985) Effect of magnetic micropulsations on biological symptoms — a bioenvironmental study. Int J Biometerol 29:293–305.
Swerdlow NR, Koob GF (1987) Dopamine, schizophrenia, mania and depression; toward a unified hypothesis of cortico-striatopallido-thalamic function. Behav Brain Sci 10:197–245
Traute V, Duell B (1935) Correlation between geomagnetic storms and death rate. Dtsch Wochensch (January):95
Vanecek J, Pavlik A, Illnerova H (1989) Hypothalamic melatonin receptor sites revealed by autoradiography. Brain Res 435:359–362.
Walton NY, Gunawan S, Trieman DM (1990) Brain amino acid concentration changes during status epilepticus induced by lithium and pilocarpine. Exp Neurol 108:61–71.
Wilson BW, Wright CW, Morris JE, Buschbom RL, Brown DP, Miller DL, Sommers-Flanningan R, Anderson LE (1990) Evidence of an effect of ELF electromagnetic fields on human pineal gland function. J Pineal Res 9:259–269
Welker HA, Semm P, Willing RP, Commentz JC, Wiltscho W, Vollrath L (1983) Effects of an artificial magnetic field on serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity and melatonin content of the rat pineal gland. Exp Brain Res 50:426–432
Zeise ML, Semm P (1985) Melatonin lowers excitability of guinea pig hippocampus neurons in vitro. J Comp Physiol A 157:23–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bureau, Y.R.J., Persinger, M.A. Geomagnetic activity and enhanced mortality in rats with acute (epileptic) limbic lability. Int J Biometeorol 36, 226–232 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726403
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726403