Abstract
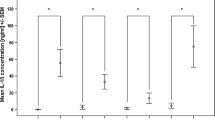
In humans, eight monosaccharides are required for the synthesis of glycoproteins. Dietary supplements that supply these crucial sugars are known as glyconutrients. A glyconutrient compound was added to Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) isolated from normal controls and patients with the Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), a disease associated with immune dysregulation. The in vitro immunomodulatory effects were investigated. Cell surface expression of the glycoproteins CD5, CD8, and CD11a were significantly lower in patients with CFS compared to normal controls. Addition of glyconutrient homogenate to PBMC from patients with CFS stimulated with phytohemagglutinin significantly increased the expression of each glycoprotein. Furthermore, natural killer (NK) cell function was reduced in CFS patients. The glyconutrient preparation significantly enhanced NK cell activity versus human herpes virus 6 (HHV-6)-infected H9 cells in an 8 h51Cr release assay compared to placebo for PBMC from patients with CFS (p<.01). Finally, apoptosis was significantly higher in patients with CSF. The percentage of apoptotic cells was significantly decreased in PBMC from patients with CFS that had been incubated for 48 h with glyconutrients. Thus, glyconutrients improved abnormal immune parameters in vitro in patients with CFS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann, C., Laratt, K., Golubjatnikov, R., Kirmani, N., Rytel, M. (1988). Immunologic markers in the chronic fatigue syndrome.Clinical Research 36:845A.
Behan, P., Behan, W., Bell, E. (1985). The postviral fatigue syndrome—An analysis of the findings in 50 cases.Journal of Infection 10:21–222.
Buchwald, D., Freedman, A., Ablashi, D., Sullivan, J., Caliguri, M., Weinberg, D.A. (1990). Chronic postinfectious fatigue syndrome associated with benign lymphoproliferation, B-cell proliferation, and active replication of human herpesvirus-6.Journal of Clinical Immunology 10:335–344.
Demitrack, M., Dale, J., Straus, S., Laue, L., Listwak, S., Kruesi, M., Chrousos, G., Gold P. (1991). Evidence for impaired activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome.Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 73: 1224–1234.
Dykman, K., Tone, C., Dykman, R. (1997). Analysis of retrospective survey on the effects of nutritional supplements on chronic fatigue syndrome and/or fibromyalgia.Journal of the American Neutraceutical Association Suppl 1:28–31.
Dykman, K., Tone, C., Ford, C., Dykman, R. (1998). The effects of nutritional supplements on the symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 31(1) 61–70.
Fakuda, K., Straus, S., Hickie, I., Sharpe, M., Dobbins, J., Komaroff, A. (1994). The chronic fatigue syndrome: A comprehensive approach to its definition and study.Annals of Internal Medicine 121: 953–959.
Gupta, S., Aggarwhal, S., See, D., Starr, A. (1997). Cytokine production by adherent and non-adherent mononuclear cells in chronic fatigue syndrome.Journal of Psychiatric Research 31:149–156.
Gupta, S., Vayuvegula, B. (1991). A comprehensive immunological analysis in chronic fatigue syndrome.Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 33:319–327.
Holmes, G., Kaplan, J., Gantz, N., Komaroff, A., Schonberger, L., Straus, S., Jones, J., DuBois, R., Cunningham-Rundles, C., Pahwa, S., Tosato, G., Zegans, L., Purtilo, D., Brown, N., Schooley, R. (1988). Chronic fatigue syndrome: A working case definition.Annals of Internal Medicine 108:387–389.
Klimas, N., Salvato, F., Morgan, R., Fletcher, M. (1990). Immunologic abnormalities in chronic fatigue syndrome.Journal of Clinical Microbiology 28:1403–1410.
Kruesi, M., Dale, J., Straus, S. (1989). Psychiatric diagnoses in patients who have chronic fatigue syndrome.Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 50:53–56.
Lloyd, A., Wakefield, D., Boughton, C., Dwyer, J. (1989). Immunological abnormalities in the chronic fatigue syndrome.Medical Journal of Australia 151:122–124.
Mordechai, E., Vojdani, A., Choppa, P., Magtoto, L., Lapp, C. (1997). Elevated apoptotic cell population in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome: The pivotal role of PKR.Journal of Internal Medicine 242:465–478.
Morrison, L., Behan, W., Nehan, P. (1991). Changes in natural killer cell phenotypes with patients with post-viral fatigue syndrome.Clinical and Experimental Immunology 83:441–446.
Murray, R.K. (1996).Harper’s Biochemistry. A Lange Medical Book, 24th Edition. Stamford, Conn: Appleton and Lange.
Ojo-Amaize, A., Conley, E., Peter, J. (1994). Decreased natural killer cell function is associated with severity of chronic fatigue immunodeficiency syndrome.Clinical Infectious Diseases 19 (Suppl 1): S157–159.
Pross, H., Baines, M., Rubin, P., Shragge, P., Patterson, M. (1981). Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity.Journal of Clinical Immunology 1:51–63.
Russel, I., Michalek, J., Vipraio, G. (1991). Platelet 3H-imiprimine uptake receptor density and serum seratonin levels in patients with fibromyalgia/fibrositis syndrome.Journal of Rheumatology 19:104–109.
See, D., Broumand, N., Sahl, L., Tilles, J. (1996). In vitro effects of echinacea and ginseng on natural killer and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in healthy subjects and chronic fatigue syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients.Immunopharmacology 39:229–235.
See, D., Khemka, P., Sahl, L., Bui, T., Tilles, J. (1997). The role of natural killer cells in viral infections.Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 46:217–224.
See, D., Tilles, J. (1996). Alpha interferon treatment of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.Immunological Investigations 25:153–164.
See, D., Tilles, J. (1998). Alpha interferon treatment of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome: A prospective study of patients with decreased natural killer cell function. (submitted.)
Straus, S., Fritz, S., Dale, J., Gould, B., Strober, W., (1993). Lymphocyte phenotype and function in the chronic fatigue syndrome.Journal of Clinical Immunology 13:30–40.
Straus, S., Tosato, G., Armstrong, G., Lawley, T., Preble, O., Henle, W., Davey, R., Pearson, G., Epstein, J., Brus, I., Blaese, R. (1985). Persisting illness and fatigue in adults with evidence of Epstein-Barr virus infection.Annals of Internal Medicine 102:7–16.
Tirelli, U., Marotta, G., Improta, S. (1994). Immunologic abnormalities in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 40:601–608.
Vaux, D., Strasser, A. (1996). The molecular biology of apoptosis.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 93:2239–2244.
Zubay, G.L., Parson, W.W., Vance, D.E. (1995). Principles of biochemistry: Metabolism, Volume 2. Dubuque, Iowa: Wm. C. Brown Publishers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dr. See is an Independent Mannatech Associate.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
See, D.M., Cimoch, P., Chou, S. et al. The in vitro immunomodulatory effects of glyconutrients on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 33, 280–287 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688668
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688668