Abstract
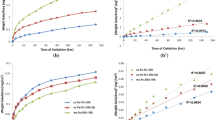
The role of chromium, carbon, chromium carbides, and phosphorus on the intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) resistance of Ni-Cr-Fe alloys in 50 pct NaOH at 140 °C is studied using controlled-purity alloys. The effect of carbon is studied using heats in which the carbon level is varied between 0.002 and 0.063 wt pct while the Cr level is fixed at 16.8 wt pct. The effect of Cr is studied using alloys with Cr concentrations between 5 and 30 wt pct. The effect of grain boundary Cr and C together is studied by heat-treating the nominal alloy composition of Ni-16Cr-9Fe-0.035C, and the effect of P is studied using a high-purity, P-doped alloy and a carbon-containing, P-doped alloy. Constant extension rate tensile (CERT) results show that the crack depth increases with decreasing alloy Cr content and increasing alloy C content. Crack- ing severity also correlates inversely with thermal treatment time at 700 °C, during which the grain boundary Cr content rises and the grain boundary C content falls. Phosphorus is found to have a slightly beneficial effect on IG cracking susceptibility. Potentiodynamic polarization and potentiostatic current decay experiments confirm that Cr depletion or grain boundary C enhances the dissolution at the grain boundary. Results support a film rupture-anodic dissolution model in which Cr depletion or grain boundary C (independently or additively) enhances dissolution of nickel from the grain boundary region and leads to increased IG cracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Serra: NP-2114-SR, Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA, Nov. 1981.
R. Bandy and D. van Rooyen:Proc. 9th Int. Congress on Metallic Corrosion, National Research Council, Toronto, CanActa, 1984, vol. 2, pp. 202–09.
G.S. Was:Corrosion, 1990, vol. 46, pp. 319–30.
N. Pessel, G.P. Airey, and B.P. Lingenfelter:Corrosion, 1979, vol. 356, pp. 100–07.
J.R. Crum:Corrosion, 1986, vol. 42, pp. 368–72.
K.H. Lee, G. Cragnolino, and D.D. Macdonald:Corrosion, 1985, vol. 41, pp. 540–53.
J.R. Crum: inCorrosion 81, National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, TX, 1981, Paper 24.
V.B. Rajan, J.K. Sung, and G.S. Was:Proc. 3rd Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1987, pp. 545–50.
G.P. Airey:Corrosion, 1980, vol. 36, pp. 9–17.
J.R. Crum:Corrosion, 1982, vol. 38, pp. 40–45.
A.R. McIlree, H.T. Michels, and P.E. Morris:Corrosion, 1975, vol. 31, pp. 441–48.
A.R. Mcllree and H.T. Michels:Corrosion, 1977, vol. 33, p. 60.
R.S. Pathania:Corrosion, 1978, vol. 34, pp. 149–56.
G.S. Was and R.M. Kruger:Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 841–54.
G.S. Was:Computer Simulation of Microstructure Evolution, TMS- AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 151–70.
G.S. Was and J.R. Martin:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 349–60.
X. Liu, J. Shao, G. Cragnolino, and D.D. Macdonald:Proc. Corrosion of Nickel-Base Alloys, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 1985, pp. 211–26.
T. Yonezawa, K. Onimura, N. Sasaguri, T. Kusakabe, H. Nagano, K. Yamanaka, T. Minami, and M. Inoue:Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 1986, pp. 593–600.
K. Hashimoto and K. Asami:Corros. Sci., 1979, vol. 19, p. 427.
K. Yamanaka and J. Murayama:Proc. 4th Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, TX, 1991, pp. 5–96-5-106.
H. Nagano, K. Yamanaka, K. Tokimasa, and H. Kiyuki: inEnvironment-Induced Cracking of Metals, R. Gangloff and M.B. Ives, eds., National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, TX, 1990, pp. 407–14.
R.M. Kruger, G.S. Was, J.F. Mansfield, and J.R. Martin:Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 3163–76.
R.M. Kruger and G.S. Was:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2555–66.
G.P. Airey:Corrosion, 1979, vol. 35, pp. 129–36.
M. Da Cunha Delo, D. Colin, M. Cornet, and Ph. Berge:7th Int. Symp. on Metallic Corrosion, ABRACO, Rio de Janeiro, 1978, p. 991.
L. Karlsson and H. Norden:Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 35–48.
S. Suzuki, M. Obata, K. Abiko, and H. Kimura:Scripta Metall., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 1325–28.
K. Yamanaka, K. Tokimasa, H. Miyuki, and H. Nagano:Proc. Intergranular Corrosion and Primary Water Intergranular Stress Corrosion Cracking Mechanisms, Washington, DC, 1987.
G. Cragnolino and D.D. Macdonald: EPRI Report NP-3998M, Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA, 1985.
R.J. Jacko: EPRI Report NP-4478, Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA, 1986, p. C3–1.
S.M. Bruemmer and C.H. Heneger, Jr.:Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 1986, pp. 293–300.
D. Lee and D.A. Vermilyea:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2565–71.
J.K. Sung and G.S. Was:Corrosion, 1992, vol. 47 (11), pp. 824–34.
J.M. Cookson, R.D. Carter, D.L. Damcott, M. Atzmon, and G.S. Was:Proc. 5th Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange, IL, 1992, pp. 806–13.
M. Fukuya, K. Nakata, and A. Horie:Proc. 5th Int. Symp. on Environmental DegrActation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, J.K., Koch, J., Angeliu, T. et al. The effect of grain boundary chemistry on Intergranular stress corrosion cracking of Ni-Cr-Fe alloys in 50 Pct NaOH at 140 °C. Metall Trans A 23, 2887–2904 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651767
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651767