Abstract
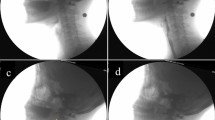
Cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has revealed patchy periventricular white matter lesions or “unidentified bright objects” (UBOs) in otherwise neurologically intact individuals. Quantitative videofluoroscopic swallowing evaluations and cranial MRI examinations were studied in 49 neurologically normal volunteers (ages 43 to 79 years). Total swallowing duration (TSD) and its subcomponents of oral transit duration (OTD), stage transition duration (STD), and pharyngeal response duration were measured for liquid and semisolid swallows. MRIs were graded from 0, or no UBOs, to 3, or multiple and confluent lesions. The effect of the presence of UBOs on swallowing durational measures and risk factors was analyzed with age differences accounted for statistically (AN-COVA). TSD and OTD for semisolids were significantly differentiated by MRI score (P<0.009 andP<0.047, respectively). That is, a demonstrable effect was found for an increased number of UBOs on duration of oropharyngeal swallowing in normal individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robbins J, Levine RL: Swallowing after unilateral stroke of the cerebral cortex: preliminary experience.Dysphagia 3:11–17, 1988
Awad I, Modic M, Little JR, Furlan AJ, Weinstein M: Focal parenchymal lesions in transient ischemic attacks—correlation of CT and MRI.Stroke 17:399–403, 1986
Kim WS, Buchholz D, Kumar AJ, Donner M, Rosenbaum AE: Magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating neurogenic dysphagia.Dysphagia 2:40–45, 1987
Awad IA, Johnson PC, Spetzler RF, Hodak JA: Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. II. Postmortem pathological correlations.Stroke 17:1090–1097, 1986
Kirkpatrick JB, Hayman LA: White-matter lesions in MR imaging of clinically healthy brains of elderly subjects: possible pathologic basis.Radiology 162:509–511, 1987
Brant-Zawadzki M, Kucharczyk W: Vascular disease: ischemia. In Brant-Zawadzki M, Norman D (eds):Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Central Nervous System. New York, NY: Raven Press, 1987
Marshall VG, Bradley WG, Marshall CE, Bhoopat T, Rhodes RH: Deep white matter infarction: correlation of MR imaging and histopathological findings.Radiology 167:517–522, 1988
Braffman BH, Zimmerman RA, Trojanowski JQ, Gonatas NK, Hickey WF, Schlaepfer WW: Brain MR: pathologic correlation with gross and histopathology, 2: hyperintensive white-matter foci in the elderly.AJR 151:559–566, 1988
Jungreis CA, Kanal E, Hirsch WL, Martinez AJ, Mossy J: Normal perivascular spaces mimicking lacunar infarction: MR imaging.Radiology 169:101–10, 1988
Awad IA, Chimowitz M, Akrawi WA, Estes M: Pathologic spectrum of subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in the elderly (abstract).Stroke 20:155, 1989
Miyashita K, Naritomi H, Sawada T, Nakamura M, Kuriyama Y, Ogawa M, Imakita S: Identification of recent lacunar lesions in cases of multiple small infarctions by magnetic resonance imaging.Stroke 19:834–839, 1988
Awad IA, Spetzler RF, Hodak JA, Awad CA, Carey R: Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. I. Correlation with age and cerebrovascular risk factors.Stroke 17:1084–1089, 1986
Gerard G, Weisberg LA: MRI periventricular lesions in adults.Neurology 36:998–1001, 1986
Kertesz A, Black SE, Tokar G, Benke T, Carr T, Nicholson L: Periventricular and subcortical hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. Rims, caps, and unidentified bright objects.Arch Neurol 45:404–408, 1988
Lechner H, Schmidt R, Bertha G, Justich E, Offenbacher H, Schneider G: Nuclear magnetic resonance image white matter lesions and risk factors for stroke in normal individuals.Stroke 19:263–265, 1988
Fazekas F, Niederkorn K, Schmidt R, Offenbacher H, Horner S, Bertha G, Lechner H: White matter signal abnormalities in normal individuals: correlation with carotid ultrasonography, cerebral blood flow measurements, and cerebrovascular risk factors.Stroke 19:1285–1288, 1988
Herholz K, Heindel W, Rackl A, Neubauer I, Steinbrich W, Pietrzyk U, Erasmi-Korber H, Heiss WD: Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with leukoaraiosis and atherosclerotic carotid artery disease.Arch Neurol 47:392–396, 1990
Jernigan TL, Press GA, Hesselink JR: Methods for measuring brain morphologic features in magnetic resonance images.Arch Neurol 47:27–32, 1990
Leys D, Saetaert G, Petit H, Faquette A, Pruvo JP, Steinling M: Periventricular and white matter magnetic resonance imaging hyperintensities do not differ between Alzheimer's disease and normal aging.Arch Neurol 47:524–527, 1990
Meguro K, Hatazawa J, Yamaguchi T, Itoh M, Matsuzawa T, Ono S, Miyazawa H, Hishinuma T, Yanai K, Sekita Y, Yamada K: Cerebral circulation and oxygen metabolism associated with subclinical periventricular hyperintensity as shown by magnetic resonance imaging.Ann Neurol 28:378–383, 1990
Sarpel G, Chaudry F, Hindo W: Magnetic resonance imaging of periventricular hyperintensity in a Veterans Administration Hospital population.Arch Neurol 44:725–728, 1987
Robbins J, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster G: Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages.Gastroenterology (in press)
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR: “Mini-mental State.” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician.J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198, 1975
Wilkinson C:SYSTAT, the System for Statistics. Evanston, IL: Systat, Inc., 1988
Junque C, Pujol J, Vendrell P, Bruno O, Jodar M, Ribas JC, Vinas J, Capdevila A, Marti-Vilatta JL: Leukoaraiosis on magnetic resonance imaging and speed of mental processing.Arch Neurol 47:151–156, 1990
Kertesz A, Polk M, Carr T: Cognition and white matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging in dementia.Arch Neurol 47:387–39, 1990
Rao SM, Mittenberg W, Bernardin L, Haughton V, Leo GJ: Neuropsychological test findings in subjects with leukoaraiosis.Arch Neurol 46:40–44, 1989
Hunt AL, Orrison WW, Yeo RA, Haaland KY, Rhyne RL, Gary PJ, Rosenberg GA: Clinical significance of MRI white matter lesions in the elderly.Neurology 39:1470–1474, 1989
Potvin AR, Tourtelotte WW: Quantitative examination of neurologic functions.CRC Press 2:25–41, 1985
Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Logemann JA, Shaker R: Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition.Gastroenterology 95:52–62, 1988
Dodds W, Mann K, Cook I, Kahrilas PJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK: Influence of bolus volume on swallow induced hyoid movement in normal subjects.Am J Radiol 150:1302–1309, 1988
Sullivan P, Pary R, Telang F, Rifai AH, Zubenko GS: Risk factors for white matter changes detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly.Stroke 21:1424–1428, 1990
Kozachuk WE, DeCarli C, Schapiro MB, Wagner EE, Rapoport SH, Horwitz B: White matter hyperintensities in dementia of Alzheimer's type and in healthy subjects without cerebrovascular risk factors. A magnetic resonance imaging study.Arch Neurol 47:1306–1310, 1990
Grafton ST, Sumi SM, Stimac GK, Alvord EC, Shaw CM, Nochlin D: Comparison of postmortem magnetic resonance imaging and neuropathological findings in the cerebral white matter.Arch Neurol 48:293–298, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by The National Institute of Health (NS24427).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levine, R., Robbins, J.A. & Maser, A. Periventricular white matter changes and oropharyngeal swallowing in normal individuals. Dysphagia 7, 142–147 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02493446
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02493446