Abstract
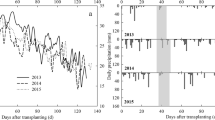
The goals of sustainable food production and mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions may be in conflict when green manures are used in flooded rice systems. A field study was initiated in early spring 1992 near Sacramento, California to quantify the potential for enhanced methane emissions following a green manure amendment to rice. Replicate flux measurements were made twice a day every 3–4 days throughout the growing season in four treatment plots: burned rice straw, spring incorporated rice straw, burned straw plus purple vetch and spring incorporated straw plus vetch. Seasonal methane emissions ranged from 66–136 g CH4 m−2 and were 1.5 to 1.8 times higher from the straw plus vetch treatments relative to the straw only treatments. No significant differences in emissions were found between the two straw only treatments or the straw plus vetch treatments. Methane fluxes were exponentially related to soil temperature, but no effect of redox potential or floodwater depth were observed. The potential impact of these results on the global methane budget is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blake DR & Rowland FS (1988) Continuing worldwide increase in tropospheric methane, 1978 to 1987. Science 239: 1129–1131
Bouwman AF (1990) Sources and sinks of greenhouse gases. In: Bouwman AF (Ed) Soils and the Greenhouse Effect, John Wiley, New York
Cicerone RJ and Ormland RS (1988) Biogeochemical aspects of atmospheric methane. Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 2 (4): 299–327
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1990) Production Yearbook. Vol 43. FAO, Rome
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1993) Report of the regional expert consultation on the sustainability of the rice-wheat production system in different agro-ecological settings in Asia. RAPA Report: 120. FAO. Bangkok, Thailand
Flinn JC and DeDatta SK (1984) Trends in irrigated-rice yields under intensive cropping at Philippine research stations. Field Crops Res. 9: 1–15
Garrity DP and Flinn JC (1988) Farm-level management systems for green manure crops in Asian rice environments. In: Green Manure in Rice Farming (pp 111–129). Proc. Symposium on Sustainable Agriculture. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Los Baños, Philippines
Giri GS, Acharya GP, Regmi AP and Hobbs PR (1993) Results of a long term rice-rice-wheat soil fertility experiment in the Terai of Nepal. Paper for Conference on “Rice-Wheat Systems of Warmer Areas” Nashipur, Bangladesh. Feb 14–15, 1993 (In Press)
Holzapfel-Pschorn A and Seiler W (1986) Methane emission during a cultivation period from an Italian rice paddy. J. Geophys. Res. 91: 11803–11841
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R and Seiler W (1986) Effects of vegetation on the emission of methane from submerged paddy soil. Plant Soil 92: 223–233
International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) (1989) IRRI Towards 2000 and Beyond. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines
Khalil MAK, Rasmussen RA, Wang MX and Ren L (1991) Methane emissions from rice fields in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 25: 979–981
Lauren JG, Duxbury JM (1993) Methane emissions from flooded rice amended with a green manure. In: Rolston D, Duxbury JM, Mosier AR and Harper LA (Eds) Agricultural Ecosystem Effects on Trace Gases and Global Climate Change (pp 183–192). Am. Soc. Agron. Spec. Pub. 55
Lindau CW, Bollich PK, Delaune RD, Patrick Jr. WH and Law VJ (1991) Effect of urea fertilizer and environmental factors on CH4 emission from a Louisiana, USA rice field. Plant Soil 136: 195ℓ203
Lizhi C (1988) Green manure cultivation and use for rice in China. In: Green Manure in Rice Farming (pp 63–70). Proc. Symposium on Sustainable Agriculture. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Los Baños, Philippines
Meelu OP, Palaniappan SP, Singh Y and Singh B (1992) Integrated nutrient management in crops and cropping sequences for sustainable agriculture. In: Bajwa M, Sidhu P, Benbi D, Pasricha N, Chaudhary M and Beri V, (Eds) Nutrient Management for Sustained Productivity (pp 101–114). Proc. Int. Symp. Punjab Agric. Univ., Indian Council Agric. Res. and Indian Soil Sci., Ludhiana, India. January 1992. Punjab Agric. Univ. Press, Ludhiana
Patrick WH (1981) The role of inorganic redox systems in controlling reduction in paddy soils. In: Proc. Symposium on Paddy Soil (pp 107–117). Inst. Soil Sci., Academia Sinica. Science Press. Beijing, China
Qixiao W and Tianren Y (1988) Effect of green manure on physiochemical properties of irrigated rice soils. In: Green Manure in Rice Farming (pp 275–287). Proc. Symposium on Sustainable Agriculture. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Los Baños, Philippines
Reddy KR, Feijtel TC and Patrick Jr. WH (1986) Effect of soil redox conditions on microbial oxidation of organic matter. In: Chen Y and Avnimelech Y (Eds) The Role of Organic Matter in Modern Agriculture. Dev. Plant Soil Sci. 25: 117–156
Rolston DE (1986) Gas flux. In: Klute A (Ed) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods. Agron. 9: 1103–1119
SAS Institute (1990) SAS user’s guide: Statistics. SAS Institute, Inc. Cary, NC
Sass RL, Fisher FM, Harcombe PA and Turner FT (1991) Mitigation of methane emissions from rice fields: Possible adverse effects of incorporated rice straw. Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 5 (3): 275–287
Schütz H, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Rennenberg H and Seiler W (1989) A 3-year continuous record on the influence of daytime, season and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy. J. Geophys. Res. 94 (D13): 16405–16406
Sebacher DI, Harriss RC, Bartlett KB, Sebacher SM and Grice SS (1986) Atmospheric methane sources: Alaskan tundra bogs, an alpine fen and a subarctic boreal marsh. Tellus. 38B: 1–10
Seiler W, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R and Scharffe D (1984) Methane emission from rice paddies. J. Atmos. Chem. 1: 241–268
Shine KP, Derwent RG, Wuebbles DJ and Morchrette J-J (1990) Radiative forcing of climate. In: Houghton JT, Jenkins GJ and Ephraums JJ (Eds) Climate Change - The IPCC Scientific Assessmentn (pp 45–68). Cambridge Univ. Press. Cambridge, UK
Swarup A (1988) Influence of organic matter and flooding on the chemical and electrochemical properties of sodic soil and rice growth. Plant Soil. 106: 135–141
Tsutsuki K and Ponnamperuma FN (1987) Behavior of anaerobic decomposition products in submerged soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 33 (1): 13–33
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1990a) Methane emissions and opportunities for control (pp 50–53). Workshop Results of Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change-Response Strategies Working Group. USEPA. Washington, DC
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1990b) Greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural systems. Vol 1, Summary report. In: IPCC-RSWG Workshop (pp 1–2). Washington DC. 12–14 Dec. 1989. USEPA Climate Change Div., Washington, DC
Watson RT, Meira Filho LG, Sanhueza E and Janetos A (1992) Greenhouse gases: sources and sinks. In: Houghton JT, Callander BA and Varney SK (Eds) Climate Change 1992. The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment (pp 29–460). Cambridge Univ. Press. Cambridge, UK
Yagi K and Minami K (1990) Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 36: 599–610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lauren, J.G., Pettygrove, G.S. & Duxbury, J.M. Methane emissions associated with a green manure amendment to flooded rice in California. Biogeochemistry 24, 53–65 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02390179
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02390179