Abstract
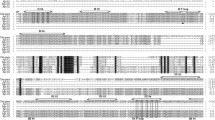
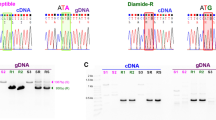
Using reverse transcription polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCR), the DNA sequence for the main membrane-spanning region (IS3 through IVS6) of the gene encoding theα-subunit of thepara sodium channel of the German cockroach,Blattella germanica, has been determined. The overall structure of the open reading frame region of thisB. germanica gene is very similar to that of thepara gene ofDrosophila melanogaster, and that of the partially sequencedpara gene ofMusca domestica. On the other hand, it is distinctly different from that of theDSC gene (Drosophila sodium channel). As a result of a side-by-side comparison of thepara gene sequences of the susceptible CSMA strain and thekdr resistant VT strain ofB. germanica, one mutation (TTG to TTC) at the approximate center of the IIS6 membrane-spanning segment was found to result in an amino acid change from L to F. While the functional meaning of this mutation for the operation of thepara sodium channel remains to be studied, this region is very highly conserved among all sodium channels identified so far, and is one of the most hydrophobic areas of the entireα-subunit. For comparison, we have studied the same region of thepara sodium channel of bothkdr and susceptible SBO strain of the housefly,Musca domestica. We found the homologous type of mutation, CTT to TTT, resulting in the same amino acid alteration (L to F) at this site. However, in the case of houseflies bothkdr and susceptible strains contained both L and F versions of the protein. The ratio of TTT to CTT was significantly higher in thekdr strain ofM. domestica than in the three susceptible strains examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed CM, Ware DH, Lee SC, Patten CD, Ferrer-Montiel AV, Schinder AF, McPherson JD, Wagner-McPherson CB, Wasmuth JJ, Evans GA, Mental M (1992) Primary structure, chromosomal localization, and functional expression of a voltage-gated sodium channel from human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8220–8224
Badley JE, Bishop GA, St. John T, Frelinger JA (1988) A simple, rapid method for the purification of Poly(A)+ RNA. Biotechniques 6:114–116
Dong K, Scott JG (1994) Linkage ofkdr-type resistance and the para-homologous sodium channel gene in German cockroaches (Blattella germanica). Insect Biochem Molec Biol 24:647–654
Doyle K, Knipple DC (1991) PCR-based phylogenetic walking: isolation ofpara-homologous sodium channel gene sequence from seven insect species and an arachnid. Insect Biochem 21:689–696
Elliott M, Janes NF, Potter C (1978) The future of pyrethroids in insect control. Annu Rev Entomol 23:443–469
Gautron S, Santo GD, Pinto-Henrique DP, Koulakoff A, Gros F, Berwald-Netter Y (1992) The glial voltage-gated sodium channel: cell- and tissue-specific mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7272–7276
Gellens ME, George AL, Chen L, Chahine M, Horn R, Barchi RL, Kallen RG (1992) Primary structure and functional expression of the human cardiac tetrodotoxin-insensitive voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:554–558
George AL, Komisarol J, Kallen RG, Barchi RL (1992a) Primary structure of adult human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent sodium channel. Ann Neurol 31:131–137
George AL, Knittle TJ, Tamkun MM (1992b) Molecular cloning of an atypical voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in human heart and uterus: evidence for a distinct gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4893–4897
Georghiou GP, Saito T (1983) Pest resistance to pesticides. Plenum Press, New York
Kallen RG, Sheng Z, Yang J, Chen L, Rogart RB, Barchi RL (1990) Primary structure and expression of a sodium channel characteristic of denervated and immature rat skeletal muscle. Neuron 4:233–242
Kaku K, Matsumura F (1995) Identification of the site of mutation within the M2 region of the GABA receptor of the cyclodience resistant German cockroach. Comp Biochem Physiol 108C:367–376
Kayano T, Noda M, Flockerzi V, Takahashi H, Numa S (1988) Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett 228:187–194
Knipple DC, Payne LL, Soderlund DM (1991) PCR-generated conspecific sodium channel gene probe for the housefly homologue of thepara locus ofDrosophila melanogaster. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 16:45–53
Knipple DC, Doyle KE, Marsella-Herrick PA, Soderlund DM (1994) Tight genetic linkage between thekdr insecticide resistance trait and a voltage-sensitive sodium channel gene in the housefly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2483–2487
Loughney K, Dreber R, Ganetzky B (1989) Molecular analysis of thepara locus, a sodium channel gene in Drosophila. Cell 58:1143–1154
Lu C-M, Han J, Rado TA, Brown GB (1992) Differential expression of two sodium channel subtypes in human brain. FEBS Lett 303:53–58
Matsumura F (1971) Studies on the biochemical mechanisms of resistance in strains of the German cockroach. Proceedings Second Pesticide Chemistry Congress 2:95–116
Matsumura F, Kaku K, Enan E, Charalambous P, Miyazaki M, Muralidhara, Inagaki S (1993) Molecular basis of toxic action of insecticides. In: Mitsui T, Matsumura F, Yamaguchi I (eds) Pesticides/Environment: molecular biological approaches. Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Pesticide Science. Pesticide Science Society of Japan, Tokyo, pp 3–16
Matsumura F, Mizutani A, Kaku K, Miyazaki M, Inagaki S, Dunlap DY (1995) Molecular biological investigations of the properties of sodium channels ofBlattella germanica. In: Marshall Clark J (ed) Molecular actions of insecticides on ion channels. ACS Symposium Series 591, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 109–127
Milani R (1954) Comportamento mendeliano della resistenza alla azione abbattante del DDT: correlazione tran abbattimento e mortalia inMusca domestica. L. Riv Parasitol 15:513–542
Miyazaki M, Matsumura F, Beeman RW (1995) Identification of the DNA sequence and the site of mutation at the M2 region of the GABA receptor of the cyclodience-resistant red flour beetleTribolium castaneum through polymerase chain reactions. Comp Biochem Physiol B 23:3177–3204
Noda M, Numa S (1987) Structure and function of sodium channel. Receptor Res 7:467–497
Noda M, Shimizu S, Tanabe T, Takai T, Kayano T, Ikeda T, Takahashi H, Nakayama H, Kanaoka Y, Minamino N, Kanagawa K, Matsuo H, Raftery MA, Hirose T, Inayama S, Hayashida H, Miyata T, Numa S (1984) Primary structure ofElectrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature 312:121–127
Noda M, Ikeda T, Kayano T, Suzuki H, Takeshima H, Kurasaki M, Takahashi H, Numa S (1986) Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature 320:188–192
Ramaswami M, Tanouye MA (1989) Two sodium-channel genes inDrosophila: implication for channel diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2079–2082
Rashatwar S, Matsumura F (1985) Reduced calcium sensitivity of the sodium channel and the Na+/Ca2+ exchange system in thekdr-type, DDT and pyrethroid-resistant German cockroachBlattella germanica. Comp Biochem Physiol C 81:97–103
Rogart RB, Cribbs LL, Muglia LK, Kephart DD, Kaiser MW (1989) Molecular cloning of a putative tetrodotoxin-resistant rat heart Na+ channel isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8170–8174
Salgado VL, Irving SN, Miller TA (1983) Depolarization of motor nerve terminals by pyrethroids in susceptible andkdr-resistant houseflies. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 20:100–114
Salkoff L, Butler A, Scavarda N, Wei A (1987a) Nucleotide sequence of the putative sodium channel gene fromDrosophila: the four homologous domains. Nucleic Acids Res 15:8569–8572
Salkoff L, Butler A, Wei A, Scavarda N, Giffen K, Ifune C, Goodman R, Mandel G (1987b) Genomic organization and deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel gene inDrosophila. Science 237:744–749
Sato C, Matsumoto G (1995) Sodium channel functioning based on an octagonal structure model. J Membrane Biol 147:45–70
Sills MN, Xu YC, Baracchini E, Goodman RH, Cooperman SS, Mandel G, Chien KR (1989) Expression of diverse Na+ channel messenger RNAs in rat myocardium: evidence for a cardiac-specific Na+ channel. I Clin Invest 84:331–336
Stern M, Kreber R, Ganetzky B (1990) Dosage effects of aDrosophila sodium channel gene on behavior and axonal excitability. Genetics 124:133–143
Taylor MFJ, Heckel DG, Brown TM, Kreitman ME, Black B (1993) Linkage of pyrethroid insecticide resistance to a sodium channel locus in the tobacco budworm. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 23:763–775
Telford JN, Matsumura F (1970) Dieldrin binding in subcellular nerve components of cockroaches: an electron microscopic and autoradiographic study. J Econ Entomol 63:795–800
Trimmer JS, Cooperman SS, Tomiko SA, Zhou J, Crean SM, Boyle MB, Kallen RG, Shenge Z, Barchi RL, Sigworth FJ, Goodman RH, Agnew WS, Mandel G (1989) Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron 3:33–49
Williamson MS, Denholm I, Bell CA, Devonshire AL (1993) Knockdown resistance (kdr) to DDT and pyrethroid insecticides maps to a sodium channel gene locus in the housefly (Musca domestica). Mol Gen Genet 240:17–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Ashburner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, M., Ohyama, K., Dunlap, D.Y. et al. Cloning and sequencing of thepara-type sodium channel gene from susceptible andkdr-resistant German cockroaches (Blattella germanica) and house fly (Musca domestica). Molec. Gen. Genet. 252, 61–68 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173205
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173205