Summary
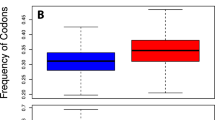
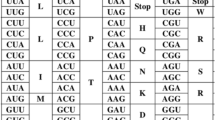
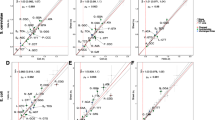
We have analyzed the correlation that exists between the GC levels of third and first or second codon position for about 1400 human coding sequences. The linear relationship that was found indicates that the large differences in GC level of third codon positions of human genes are paralleled by smaller differences in GC levels of first and second codon positions. Whereas third codon position differences correspond to very large differences in codon usage within the human genome, the first and second codon position differences correspond to smaller, yet very remarkable, differences in the amino acid composition of encoded proteins. Because GC levels of codon positions are linearly correlated with the GC levels of the isochores harboring the corresponding genes, both codon usage and amino acid composition are different for proteins encoded by genes located in isochores of different GC levels. Furthermore, we have also shown that a linear relationship with a unity slope and a correlation coefficient of 0.77 exists between GC levels of introns and exons from the 238 human genes currently available for this analysis. Introns are, however, about 5% lower in GC, on average, than exons from the same genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aïssani B, D'Onofrio G, Mouchiroud D, Gardiner K, Gautier C, Bernardi G (1991) The compositional properties of human genes. J Mol Evol 32:493–503
Bernardi G (1989) The isochore organization of the human genome. Annu Rev Genet 23:637–661
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1985) Codon usage and genome composition. J Mol Evol 22:363–365
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1986) Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol 24:1–11
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1991) Compositional properties of nuclear genes from cold-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol (in press)
Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial M, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier F (1985) The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228:953–958
Bulmer M (1987) A statistical analysis of nucleotide sequences of introns and exons in human genes. Mol Biol Evol 4:395–405
Gouy M, Gautier C, Attimonelli N, Lanave C, Di Paola G (1985) ACNUC-portable retrieval system for nucleic acid sequence database: logical and physical design and usage. Cabios 1:167–172
Grantham R (1980) Workings of the genetic code. Trends Biochem Sci 5:327–333
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M, Mercier R, Paré A (1980) Codon catalogue usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res 8:r49-r62
Sueoka N (1961) Correlation between base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid and amino acid composition of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 47:1141–1149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D'Onofrio, G., Mouchiroud, D., Aïssani, B. et al. Correlations between the compositional properties of human genes, codon usage, and amino acid composition of proteins. J Mol Evol 32, 504–510 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02102652
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02102652