Abstract
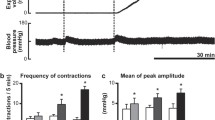
Colonic smooth muscle spike potentials and contractility were recorded during the periods of stress by a bipolar electrode-perfused catheter apparatus placed in the rectosigmoid colon. Healthy subjects and patients with the irritable colon syndrome (ICS) were exposed to three standardized stressful conditions: (1) ice-water immersion, (2) Stroop stimulus differentiation test, and (3) ball sorting. In healthy controls, colonic motility. An increase in colonic motility occurred in patients with the irritable colon <0.5), or ball sorting. Respiratory frequency also increased after exposure to the stressful stimuli. However, repeat exposures to the stress tests did not stimulate colonic motility. An increase in colonic motility occurred in patients with the irritable colon syndrome pretreated with a placebo after exposure to ice water (P<0.05), Stroop Test, or ball sorting (P<0.05). However, after exposure to the stressful situations patients pretreated with chlordiazepoxide had a diminished increase in colonic motility or in respiratory frequency. These studies suggest: (1) in healthy controls habituation reduces the stress-related increase in colonic motility, and (2) in patients with the irritable colon syndrome, chlordiazepoxide decreases the stress-related increase in colonic motility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
White BV, Jones CM: Mucous colitis: A delineation of the syndrome with certain observations on its mechanism and on the role of emotional tension as a precipitating factor. Ann Intern Med 14:854–872, 1940
Waller SL, Misiewicz JJ: Prognosis in the irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet 2:753–756, 1969
Mendeloff AI, Monk M, Singh CI, Lilienfeld A: Illness experience and life stresses in patients with irritable colon and with ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 282:14–17, 1970
Ritchie JA, Truelove SC: Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with lorazepam, hyoscine butylbromide, and ispaghula husk. Br Med J 1:376–378, 1979
Deutsch E: Relief of anxiety and related emotions in patients with gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Dig Dis 16:1091–1094, 1971
Almy TP, Hinkel LE Jr, Berle B, Kern F Jr: Alterations in colonic fuction in man under stress. Gastroenterology 12:437–449, 1949
Almy TP, Kern F Jr, Tulin M: Alterations in colonic function in man under stress. Gastroenterology 12:425–436, 1949
Drossman DA, Powell DW, Sessions JT: The irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 73:811–822, 1977
Sarna SK, Latimer PR, Campbell D, Waterfall WE: Effect of stress, meal and prostigmine on rectosigmoid electrical control activity (ECA) in normals and irritable bowel syndrome patients. Dig Dis Sci 27:582–591, 1982
Thompson RF, Spencer WA: Habituation: A model phenomenon for the study of neuronal substrates of behavior. Psychol Rev 73:16–43, 1966
Neary RS, Zuckerman M: Sensation seeking, trait and state anxiety, and the electrodermal orienting response. Psychophysiology 13:205–211, 1976
Grings WN, Dawson ME: Emotion and Bodily Responses: A Psychophysiological Approach. New York, Academic Press, 1978
Snape WJ Jr, Carlson GM, Cohen S: Colonic myoelectric activity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 70:326–330, 1976
Jensen R, Rohwer J: Stroop color word test. Acta Psychol 25:36–93, 1966
Snape WJ Jr, Wright SH, Cohen S, Battle WM: The gastrocolic response: Evidence for a neural mechanism. Gastroenterology 77:1235–1240, 1979
Rostad H: Central and peripheral nervous control of colonic motility in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 89:79–181, 1973
Kopin KJ, Lake RC, Ziegler M: Plasma levels of norepinephrine. Ann Intern Med 88:671–680, 1978
Wienbeck M, Christensen J: Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat. Gastroenterology 61:670–678, 1971
Anuras S, Christensen J: Effects of autonomic drugs on cat colonic muscle. Am J Physiol 240:G361-G364, 1981
Cohen M, Pickar D, Dubois M, Roth YF, Naber D, Bunney WE: Surgical stress and endorphins. Lancet 1:213–214, 1981
Stacher G, Steinringer H, Schmierer G: Stimulatory effects of the synthetic enkephalin analogue FK 33–824 on colonic motor activity antagonized by naloxone. Hepato-Gastroenterology 28:110–115, 1981
Wienbeck M, Dunzen R, Korner M, Berges W, Strohmeyer G: Enkephalins affect colonic motility. Gastroenterology 78:1290, 1980
Sun EA, Snape WJ Jr, Cohen S, Renny A: The role of opiate receptors and cholinergic neurons in the gastrocolonic response. Gastroenterology 82:689–693, 1982
Renny A, Snape WJ Jr, Sun EA, London R, Cohen S: Neurohumoral interaction in the gastrocolonic response to a fat meal. Gastroenterology 85:17–21, 1983
Snape WJ Jr, Carlson GM, Matarazzo SA, Cohen S: Evidence that abnormal myoelectrical activity produces colonic motor dysfunction in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 72:383–387, 1977
Whitehead WE, Engel BT, Schuster MM: Irritable bowel syndrome: Physiological and psychological differences between diarrhea-predominant and constipation-predominant patients. Dig Dis Sci 25:404–414, 1980
Bueno-Miranda F, Cerulli M, Schuster MM: Operant conditioning of colonic motility in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Gastroenterology 70:867, 1976
Leeuwin RS, Djojodibroto D, Groenewoud ET: The effects of three benzodiazepines and of meprobamate on the action of smooth muscle stimulants on the guinea pig ileum. Arch Pharmacodyn 271:18–21, 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narducci, F., Snape, W.J., Battle, W.M. et al. Increased colonic motility during exposure to a stressful situation. Digest Dis Sci 30, 40–44 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01318369
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01318369