Summary
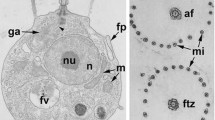
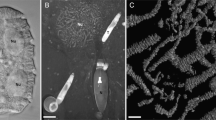
A short cylindrical pocket arises as an infolding from the ventral surface of the reservoir near the canal in several species ofEuglena (E. mutabilis, E. gracilis strain T,E. spec.). The structure is linked to a band of microtubules which is shown to be identical to the ventral flagellar root of the euglenoid flagellar root system. An absolute configuration analysis of the flagellar root system inE. mutabilis and a comparison with the flagellar apparatus of colourlessEuglenophyceae and the bodonids (Kinetoplastida) reveals structural and positional homology between the reservoir pocket ofEuglena and the cytostome of these organisms and strongly supports the phylogenetic derivation of theEuglenophyceae from theKinetoplastida and the evolution of greenEuglenophyceae from phagotrophic colourless taxa. The functional significance of the cryptic cytostome ofEuglena is discussed in relation to the occurrence of intracellular endosymbiotic bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brugerolle G, Lom J, Nohýnková E, Joyon L (1979) Comparison et évolution des structures cellulaires chez plusieurs espèces de bodonidés et cryptobiidés appartenant aux genresBodo, Cryptobia etTrypanoplasma (Kinetoplastida, Mastigophora). Protistologica 15: 197–221
Gibbs SP (1978) The chloroplasts ofEuglena may have evolved from symbiotic green algae. Can J Bot 56: 2883–2889
Häder D-P, Melkonian M (1983) Phototaxis in the gliding flagellate,Euglena mutabilis. Arch Microbiol 135: 25–29
Kies L (1967) Über Zellteilung und Zygotenbildung beiRoya obtusa (Bre.) West & West. Mitt Staats Allg Bot Hamburg 12: 35–42
Kivic PA, Walne PL (1984) An evaluation of a possible phylogenetic relationship between theEuglenophyta andKinetoplastida. Origins of Life 13: 269–288
Leedale GF (1967) Euglenoid flagellates. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.
— (1969) Observations on endonuclear bacteria in euglenoid flagellates. Österr Bot Z 116: 279–294
— (1978) Phylogenetic criteria in euglenoid flagellates. Biosystems 10: 183–187
— (1982) Ultrastructure. In:Buetow DE (ed) The biology ofEuglena, vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–27
Margulis L (1981) Symbiosis in evolution. Freeman and Co, San Francisco
Melkonian M (1975) The fine structure of the zoospores ofFritschiella tuberosa Iyeng. (Chaetophorineae, Chlorophyceae) with special reference to the flagellar apparatus. Protoplasma 86: 391–404
— (1982) Effect of divalent cations on flagellar scales in the green flagellateTetraselmis cordiformis. Protoplasma 111: 221–233
— (1984) Flagellar apparatus ultrastructure in relation to green algal classification. In:Irvine DEG, John DM (eds) Systematics of the green algae. Academic Press, New York Orlando, pp 73–120
—,Robenek H, Rassat J (1982) Flagellar membrane specializations and their relationship to mastigonemes and microtubules inEuglena gracilis. J Cell Sci 55: 115–135
Mignot J-P (1966) Structure et ultrastructure de quelques euglenomonadines. Protistologica 2: 51–117
Moestrup Ø (1982) Flagellar structure in algae: A review, with new observations on theChrysophyceae, Phaeophyceae (Fucophyceae), Euglenophyceae, andReckertia. Phycologia 21: 427–528
Nohýnková E (1984) A new pathogenicCryptobia from freshwater fishes: A light and electron microscopic study. Protistologica 20: 181–195
O'Kelly CJ, Floyd GL (1984) Flagellar apparatus absolute orientations and the phylogeny of the green algae. BioSystems 16: 227–251
Robenek H, Melkonian M (1983) Structural specialization of the paraflagellar body membrane ofEuglena. Protoplasma 117: 154–157
Schlösser UG (1982) Sammlung von Algenkulturen. Ber dtsch bot Ges 95: 181–276
Solomon JA,Walne PL,Kivic PA (1986) Euglenoid flagellar root systems:Entosiphon sulcatum (Euglenophyceae). J Phycol (in press)
Stewart KD, Mattox KR (1980) Phylogeny of Phytoflagellates. In:Cox ER (ed) Phytoflagellates, vol II, Developments in marine biology. Elsevier-North Holland, New York, pp 433–462
Surek B, Melkonian M (1983) Intracellular bacteria in theEuglenophyceae: Prolonged axenic culture of an algal-bacterial system. In:Schenk HEA, Schwemmler W (eds) Endocytobiology II. De Gruyter & Co, Berlin New York, pp 475–486
Taylor FJR (1976) Flagellate phylogeny: A study in conflicts. J Protozool 23: 28–40
Walne PL (1980) Euglenoid flagellates. In:Cox ER (ed) Phytoflagellates, vol II, Developments in marine biology. Elsevier-North Holland, New York, pp 165–212
Willey RL, Wibel RG (1985 a) A cytostome/cytopharynx in green euglenoid flagellates (Euglenales) and its phylogenetic implications. Biosystems 18: 369–376
— — (1985 b) The reservoir cytoskeleton and a possible cytostomal homologue inColacium (Euglenophyceae). J Phycol 21: 570–577
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surek, B., Melkonian, M. A cryptic cytostome is present inEuglena . Protoplasma 133, 39–49 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01293186
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01293186