Abstract
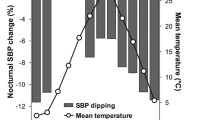
The record was studied of a 71-year-old, diurnally active (0700–2200 hours) male psychiatrist (G.N.) who self-measured systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BPS and BPD) mostly but not exclusively on Sunday mornings, from 1969 to 1994. A large about-yearly change was revealed which increased with age and was accompanied by a decreasing trend in the yearly rhythm-adjusted mean (MESOR;P<0.01). According to conventional criteria that specify only upper limits of acceptability, G.N. was hypertensive in summer and normotensive in other seasons. Since changes in both MESOR and circannual amplitude occurred, a systematic surveillance of BP is the chronobiological recommendation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartter FC, Delea CS, Baker W, Halberg F, Lee JK (1976) Chronobiology in the diagnosis and treatment of mesor-hypertension. Chronobiologia 3:199–213
Brennan PJ, Greenberg G, Miall WE, Thompson SG (1982) Seasonal variation in arterial blood pressure. Br Med J 285:919–923
Breus TK, Komarov FI, Musin MM, Naborov IV, Rapoport SI (1989) Heliogeophysical factors and their influence on cyclical processes in biosphere. Itogi Nauki i Techniki: Med Geog 18:138–142, 145, 147, 148, 172–174
Cornélissen G (1987) Instrumentation and data analysis methods needed for blood pressure monitoring in chronobiology. In: Scheving LE, Halberg F, Ehret CF (eds) Chronobiotechnology and chronobiological engineering. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 241–261
Cornélissen G, Halberg F (1994) Introduction to chronobiology. Medtronic Chronobiology Seminar 7
Cornélissen G, Haus E, Halberg F (1992) Chronobiologic blood pressure assessment from womb to tomb. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biological rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Berlin, pp 428–452
Engel R, Sothern RB, Halberg F (1985) Circadian and infradian aspects of blood pressure in a treated elderly mesor-hypertensive physician. Chronobiologia 12:243
Halberg F (1969) Chronobiology. Annu Rev Physiol 31:675–725
Halberg F, Carandente F, Cornélissen G, Katinas GS (1977) Glossary of chronobiology. Chronobiologia 4 [Suppl 1]:1–189
Halberg F, Cornélissen G, Sothern RB, Wallach LA, Halberg E, Ahlgren A, Kuzel M, Radke A, Barbosa J, Goetz F, Buckley J, Mandel J, Schuman L, Haus E, Lakatua D, Sackett L. Berg H, Wendt HW, Kawasaki T, Ueno M, Uezono K, Matsuoka M, Omae T, Tarquini B, Cagnoni M, Garcia Sainz M, Perez Vega E, Wilson D, Griffiths K, Donati L, Tatti P, Vasta M, Locatelli I, Camagna A, Lauro R, Tritsch G, Wetterberg L (1981) International geographic studies of oncological interest on chronobiological variables. In: Kaiser H (ed) Neoplasms — comparative pathology of growth in animals, plants and man. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 553–596
Halberg F, Drayer JIM, Cornélissen G, Weber MA (1984) Cardiovascular reference data base for recognizing circadian mesorand amplitude-hypertension in apparently healthy men. Chronobiologia 11:275–298
Halberg F, Bakken E, Cornélissen G, Halberg J, Halberg E, Wu J, Sánchez de la Peña S, Delmore P, Tarquni B (1990) Chronobiologic blood pressure assessment with a cardiovascular summary, the sphygmochron. In: Meyer-Sabellek W, Anlauf M, Gotzen R, Steinfeld L (eds) Blood pressure measurements. Steinkopff, Darmstadt, pp 297–326
Halberg F, Breus TK, Cornélissen G, Bingham C, Hillman DC, Rigatuso J, Delmore P, Bakken E, International Womb-to-Tomb Chronome Initiative Group (1991) Chronobiology in space. University of Minnesota/Medtronic Chronobiology Seminar Series, 1
Halberg F, Bingham C, Cornélissen G (1993) Clinical trials: the larger the better? Chronobiologia 20:193–212
Halberg F, Cornélissen G, Haus E, Northrup G, Portela A, Wendt H, Otsuka K, Kumagai Y, Watanabe Y, Zaslavskaya R (1996) Clinical relevance of about-yearly changes in blood pressure and the environment. Int J Biometerol: (in press)
Haus E, Nicolau G, Lakatua DJ, Jackimowicz A, Plinga L, Sackett-Lundeen L, Petrescu E, Ungureanu E (1987) Circannual variations in blood pressure, urinary catecholamine excretion, plasma aldosterone, and serum sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium in children 11±1.5 years of age. Prog Clin Biol Res 227B:3–19
King JW (1975) Sun-weather relationships. Aeronaut Astronaut 13:104–124
Levine H, Halberg F (1972) Circadian rhythms of the circulatory system, literature review. Computerized case study of transmeridian flight and medication effects on a mildly hypertensive subject. US Air Force Report SAM-TR-72-3
Nicolau GY, Haus E, Bogdan C, Plinga L, Robu E, Ungureanu E, Sackett-Lundeen L, Petrescu E (1986) Circannual rhythms of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, in relation to plasma aldosterone and urinary norepinephrine in elderly subjects and in children. Endocrinologie 24:97–107
Roberts WO (1979) Variations in the sun and their effects on weather and climate. Proc Am Philos Soc 123:151–159
Rose G (1961) Seasonal variation in blood pressur in man. Nature 189:235
Scheider RA, Costiloe JP (1972) Seasonal variation in cardiovascular functioning. Arch Environ Health 24:10–16
Sothern RB, Halberg F (1986) Circadian and infradian blood pressure rhythms of a man 20 to 37 years of age. In: Halberg F, Reale L, Tarquini B (eds) Proceedings 2nd International Conference Medico-Social Aspects of Chronobiology. Istituto Italiano di Medico Sociale, Rome, pp 395–416
Wendt HW (1987) Interplanetary magnetic field sector polarity, season and emotional state surrounding tumor operation: factors in the ecology of cancer progression? In: Hildebrandt G, Moog R, Raschke F (eds) Chronobiology and chronomedicine: basic research and applications. Lang, Frankfurt, pp 375–381
Wetterberg L, Halberg F, Halberg E, Haus E, Kawasaki T, Ueno M, Uezono K, Cornélissen G, Matsuoka M, Omae T (1986) Circadian characteristics of urinary melatonin from clinically healthy women at different civilization disease risk. Acta Med Scand 220:71–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Portela, A., Northrup, G., Halberg, F. et al. Changes in human blood pressure with season, age and solar cycles: A 26-year record. Int J Biometeorol 39, 176–181 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01221388
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01221388