Abstract
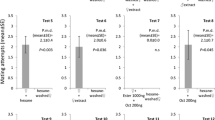
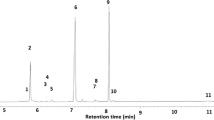
Amblyomma americanum andA. maculatum were studied to determine if genital sex pheromones were present, as reported inDermacentor species. Chemical analysis of methanol extracts of the anterior reproductive tracts (source of the genital sex pheromone) ofA. americanum andA. maculatum confirmed the presence of the same fatty acids that act as components of the genital sex pheromone inDermacentor variabilis andD. andersoni. In bothAmblyomma species, removal of the anterior reproductive-tract of fed females eliminated the male copulatory response. ForA. americanum, use of anterior reproductive tract extracts made with water, methanol, ether and hexane elicited significant probing and copulatory responses by conspecific males. However, inA. maculatum, use of anterior reproductive-tract extracts made with water, methanol, ether, chloroform: methanol (4∶1), hexane and pentane did not restore mating response by males. Treatment with known components ofDermacentor genital sex pheromones elicited weak but significant responses inA. americanum, but did not restore male mating responses inA. maculatum. These results indicate that genital sex pheromones exist inA. americanum and are not restricted to the genusDermacentor. Characteristics of theAmblyomma genital sex pheromone, however, do differ considerably from those inDermacentor. No genital sex pheromone was present inA. maculatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, S.A., Phillips, J.S., Taylor, D. and Sonenshine, D.E., 1988. Genital sex pheromones in ixodid ticks: evidence of the role of fatty acids from the anterior reproductive tract in mating ofDermacentor variabilis andDermacentor andersoni. J. Insect Physiol., 34: 315–323.
Allan, S.A., Phillips, J.S. and Sonenshine, D.E., 1989. Species recognition betweenDermacentor variabilis andDermacentor andersoni (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol., (in press).
Dees, W.H., Sonenshine, D.E. and Briedling, E.M., 1984. Ecdysteroids in the American dog tick,Dermacentor variabilis (Say), during different periods of tick development (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol., 21: 514–423.
Gladney, W.J., 1971. Mate-seeking by femaleAmblyomma maculatum (Acarina: Ixodidae) on a bovine. Nature, 232: 401–402.
Gladney, W.J. and Dawkins, C.C., 1973. Experimental interspecific mating ofAmblyomma maculatum andA. americanum. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 66: 1093–1097.
Gladney, W.J. and Drummond, R.O., 1970a. Mating behavior and reproduction in the Lone Star tick,Amblyomma americanum. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 63: 1036–1039.
Gladney, W.J. and Drummond, R.P. 1970b. Migration of male Lone Star ticks on the host in relation to mating. J. Econ. Entomol., 63: 1211–1216.
Gladney, W.J., Grabble, R.R., Erst, S.E. and Oehler, D.D., 1974a. The Gulf Coast tick: Evidence for a pheromone produced by males. J. Med. Entomol., 11: 303–306.
Gladney, W.J., Ernst, S.E. and Brabble, R.K., 1974b. The aggregation response of the Gulf Coast Tick on cattle. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 67: 750–752.
Hamilton, J.G.C. and Sonenshine, D.E., 1988. Evidence for the occurrence of a mounting sex pheromone on the body of femaleDermacentor variabilis Say andDermacentor andersoni (Stiles) Acari: Ixodidae). J. Chem. Ecol., 14: 401–410.
Hamilton, J.G.C., Sonenshine, D.E. and Lusby, W.R., 1990. Cholesteryl oleate: mounting sex pheromone of the hard tick,Dermacentor variabilis (Say) (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Insect. Physiol. (in press).
Homsher, P.J. and Sonenshine, D.E., 1976. The effect of the presence of females on spermatogenesis and mate-seeking behavior in two species ofDermacentor ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae). Acarologia, 18: 226–233.
Kellum, D. and Berger, R.S., 1977. Relationship of the occurrence and function of 2,6-dichlorophenol in two species ofAmblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol., 13: 701–705.
Khalil, G.M., Sonenshine, D.E., Sallam, D.A. and Homsher, P.J., 1983. Mating regulation and reproductive isolation in the ticksHyalomma dromedarii andH. anatolicum excavatum (Acari: Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol., 20: 136–145.
Lees, A.D. and Beament, J.W., 1948. An egg-waxing organ in ticks. Qld. J. Microsc. Sci., 89: 291–332.
McCamish, M., Cannell, G.R. and Cherry, L.M., 1977. The nonpolar egg wax lipids of the cattle tick,Boophilus microplus (Canestrini). Lipids, 12: 182–187.
Oliver, J.H. Jr., 1972. Cytogenetics of ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea). 6. Chromosomes of threeDermacentor species in the United States. J. Med. Entomol., 20: 177–182.
Sonenshine, D.E., 1985. Pheromones and other semiochemicals of the Acari. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 30: 1–28.
Sonenshine, D.E., Khalil, G.M. and Mason, S.N., 1982.Dermacentor variabilis andDermacentor andersoni: genital sex pheromones. Exp. Parasitol., 54: 317–330.
Sonenshine, D.E., Silverstein, R.M., Brossut, R.E., Davis, E., Taylor, D., Carson, K.A., Homsher, P.J. and Wang, J.B., 1985. Genital sex pheromones of ixodid ticks: 1. Evidence of occurrence in anterior reproductive tract of American dog ticks,Dermacentor variabilis (Say) (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Chem. Ecol., 11: 1669–1664.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allan, S.A., Phillips, J.S. & Sonenshine, D.E. Role of genital sex pheromones inAmblyomma americanum andA. maculatum (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 11, 9–21 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193725
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193725