Abstract
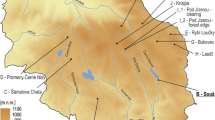
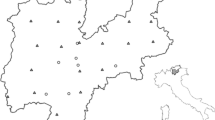
Ozone measurements have been apart of EMEP since its third phase in 1984–1986 and since 1988 data have been collected systematically. By 1992 data for 76 sites were being collected by the Chemical Co-ordinating Centre in NILU. The mean ozone concentration increases from 20–25ppb in the western and northern fringes to 30–35 in central areas of Europe. There is also evidence from the last decade of an upward trend of up to 0.5ppb y−1 at rural sites in the UK. The data have been analysed to estimate the spatial patterns in AOT 40 for ozone effects on crops and forests. The data show that the critical level for cereal crops of 5300 ppb.h above a threshold of 40 ppb is exceeded over almost all of continental Europe south of 65°N and over most of S.Britain. A similar exercise for the AOT 40 for the forest again shows exceedances of the critical load of 104 ppb.h across all the mapped area of Continental Europe south of 65°N including S.Britian. As land use for forestry and ozone dose both increase with altitude, and these effects have not so far been incorporated in the AOT 40 assessment for forests, the degree of exceedence for forests may have been significantly under-estimated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashmore, M.R.:1994, “Critical Levels and Agriculture in Europe.” In:Critical Levels for ozone a UN-ECE workshop report. (J.Fuhrer and B.Achermann Eds.), p.22–4.
Beck, J.P. and Grenfelt, P.: 1994, “Estimate of ozone production and destruction over northwestern Europe.”Atmos. Environ.,28, 129–140.
Cartalis, C. and Varotsos, C.: 1994, “Surface ozone in Athens, Greece, at the beginning and the end of the twentieth century.”Atmos. Environ.,28, 3–8.
Fowler, D., Smith, R.I., Coyle, M., Weston, K.J., Davies, T.D., Ashmore, M.A. and Brown, M.: 1995, “Quantifying the fine scale (1km × 1km) exposure and effects of ozone. Part 1. Methodology and application of effects on forests”.Water, Air, Soil Pollut. (In press).
Fuhrer, J.:1994, “The critical level for ozone to protect agricultural crops — An assessment of data from European open-top chamber experiments.” In:Critical Levels for ozone a UN-ECE workshop report. (J.Fuhrer and B.Achermann Eds.), p.42–57.
Garland, J.A. and Derwent, R.G.: 1979, “Destruction at the ground and the diurnal cycle of concentration of ozone and other gases”Quart J.R. Met Soc. 105,169–183.
Lefohn, A.S., Laurence, J.A. and Kohut, R.J.: 1988, “A comparison of indices that describe the relationship between exposure to ozone and reduction in the yield of agricultural crops.”Atmos Environ.,22, 1229–1240.
Oltmans, S.J. and Levy II, H.: 1994, “Surface ozone measurements from a global network”Atmos Environ.,28, 9–24.
Skarby, L.: 1994, “Critical levels for ozone to protect forest trees.” InCritical Levels for ozone a UN-ECE workshop report. (J. Fuhrer and B. Achermann Eds.), p.74–87.
Voltz, A. and Kley, D.: 1988, “Evaluation of the Montsouris series of ozone measurements made in the nineteenth century”.Nature,332, 240–242.
WMO: 1995, “Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 1994”. World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project — Report No 37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dollard, G., Fowler, D., Smith, R.I. et al. Ozone measurements in Europe. Water Air Soil Pollut 85, 1949–1954 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186119
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186119