Abstract
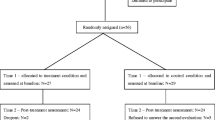
Thirty-eight institutionalized male delinquents evidencing verbal and physical aggression in response to anger provocations were randomly assigned to one of three experimental conditions: stress inoculation training, a treatment elements condition (which left out certain ingredients of stress inoculation), or a no-treatment control condition. Both active treatments reduced anger and aggression on three self-report scales. Only stress inoculation lowered verbal aggression in laboratory role-played provocations. Two demand analyses suggest that the latter difference is not artifactual. The social psychology of the institution may have been at least partly responsible for null effects on institutional behavior ratings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference Note
Meichenbaum, D.The nature and modification of impulsive children. Paper presented to the Society for Research in Child Development, Minneapolis, 1971.
References
Goodwin, S. E., & Mahoney, M. J. Modification of aggression through modeling: An experimental probe.Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry 1975,6 200–202.
Hackett, G., & Horan, J. J. Stress-inoculation for pain: What's really going on?Journal of Counseling Psychology 1980,27(2), 107–116.
Hackett, G., Horan, J. J., Buchanan, J. D., & Zumoff, P. Improving the exposure component and generalization potential of stress-inoculation for pain.Perceptual and Motor Skills 1979,48 1132–1134.
Hamburger, K., & Lohr, J. M. Rational restructuring for anger control: A quasi-experimental case study.Cognitive Therapy and Research 1980,4 99–102.
Hartman, C. H. Group relaxation training for control of impulsive behavior in alcoholics.Behavior Therapy 1973,4 173–174.
Hector, M. A., Davis, K. L., Denton, E. A., Hayes, T. W., Patton-Crowder, C., & Hinkle, W. K. Helping counselor trainees learn to respond consistently to anger and depression.Journal of Counseling Psychology 1981,28 53–58.
Horan, J. J., Hackett, G., Buchanan, J. D., Stone, C. I., & Demchik-Stone, D. Coping with pain: A component analysis of stress-inoculation.Cognitive Therapy and Research 1977,1 211–221.
Jaremko, M. E. A component analysis of stress inoculation for pain: Review and prospectus.Cognitive Therapy and Research 1979,3 35–48.
Jones, R. G.A factored measure of Ellis's irrational belief system with personality and maladjustment correlates. Doctoral dissertation, Texas Technological College, 1969.
Kaufmann, L. M., & Wagner, R. R. Barb: A systematic treatment technique for temper control disorders.Behavior Therapy 1972,3 84–90.
Meichenbaum, D., & Goodman, J. The developmental control of operant motor responding by verbal operants.Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 1969,7 553–565. (a)
Meichenbaum, D., & Goodman, J. Reflection-impulsivity and verbal control of motor behavior.Child Development 1969,40 785–797. (b)
Meichenbaum, D., & Goodman, J. Training impulsive children to talk to themselves: A means of developing self-control.Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1971,77 115–126.
Meichenbaum, D., & Turk, D. The cognitive-behavioral management of anxiety, anger, and pain. In P. O. Davidson (Ed.),The behavioral management of anxiety, depression, and pain. New York: Brunner/Mazel, 1976.
Novaco, R.A treatment program for the management of anger through cognitive and relaxation controls. Doctoral dissertation, Indiana University, 1974.
Novaco, R. Treatment of chronic anger through cognitive and relaxation controls.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1976,44 681.
Novaco, R. Training of probation counselors for anger problems.Journal of Counseling Psychology 1980,27 385–391.
O'Donnell, C. R., & Worell, L. Motor and cognitive relaxation in the desensitization of anger.Behaviour Research and Therapy 1973,11 473–481.
Repucci, N. D., & Saunders, J. T. Social psychology of behavior modification: Problems of implementation in natural settings. In C. M. Franks & G. T. Wilson (Eds.),Annual review of behavior therapy, theory, and practice (Vol. 3). New York: Brunner/Mazel, 1975.
Rimm, D. C., DeGrott, J. C., Boord, P., Heiman, J., & Dillow, P. V. Systematic desensitization of an anger response.Behaviour Research and Therapy 1971,9 273–280.
Smith, R. E. The use of humor in the counterconditioning of anger responses: A case study.Behavior Therapy 1973,4 576–580.
Worthington, E. L., & Shumate, M. Imagery and verbal counseling methods in stress inoculation training for pain control.Journal of Counseling Psychology 1981,28 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Appreciation is extended to Rus Bauer and Jim Raczynski for their help in the conduct of this research. An earlier circulated draft of this manuscript erroneously reported a null effect on the first dependent variable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlichter, K.J., Horan, J.J. Effects of stress inoculation on the anger and aggression management skills of institutionalized juvenile delinquents. Cogn Ther Res 5, 359–365 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01173687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01173687