Summary
Stellate neurons in the outer two layers of the rat dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) were studied by the Golgi-EM method. Stellate cell bodies are usually spherical or ovoidal and range from 9 μm to 14 μm in mean diameter. The smallest cells are situated underneath the ependymal layer and the largest cells in layer 2. Primary dendrites are short, thin and smooth and arise abruptly from the perikaryon, without a tapering main stem. Meandering secondary and tertiary dendrites extend in all directions, carry few pleomorphic spines lacking a spine apparatus and often show artifactual beading. The axons are impregnated only for a short distance (10–45 μm). The nucleus is indented, the nucleolus varies in position, and the chromatin, evenly dispersed in the centre, forms small clumps along the nuclear envelope. The cytoplasm is rich in free polyribosomes and contains scattered cisterns of granular endoplasmic reticulum. Varicosities of thin fibres, containing round synaptic vesicles, form asymmetric synapses on perikarya, dendritic shafts and spines of stellate cells. Such fibres run parallel to the long axis of the DCN or are oriented radially and are interpreted as axons of cochlear granule cells. Two kinds of bouton containing pleomorphic vesicles, one kind electron lucent and the other electron dense, form symmetric synapses on perikarya and dendritic shafts of stellate cells. The lucent boutons occur more frequently than the dense boutons, especially on the distal dendritic branches. The boutons with pleomorphic vesicles presumably represent terminals of local circuit neurons, probably the stellate and cartwheel cells.
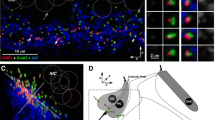
In addition, stellate cells show numerous dendro-somatic and dendro-dendritic appositions characterized by gap junctions and puncta adhaerentia. Most of the dendrites involved in these appositions resemble stellate cell dendrites and it is concluded that DCN stellate cells are coupled electrotonically with one another. The axons of stellate cells acquire a thin myelin sheath. Since the Golgi impregnation did not stain axons of stellate cells past this point, we were unable to demonstrate the synaptic targets of stellate cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. C. (1979) A fast, reliable silver-chromate Golgi method for perfusion-fixed tissue.Stain Technology 54, 225–6.
Altman, J. &Bayer, S. A. (1980) Development of the brain stem in the rat. III. Thymidine-radiographic study of the time of origin of neurons of the vestibular and auditory nuclei of the upper medulla.Journal of Comparative Neurology 194, 877–904.
Altman, J. &Das, G. (1966) Autoradiogrpahic and histological studies of postnatal histogenesis. II. A longitudinal investigation of kinetics, migration and transformation of cells incorporating thymidine in infant rats with special reference to postnatal neurogenesis in some brain regions.Journal of Comparative Neurology 126, 337–90.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1977) Electrical transmission: a functional analysis and comparison with chemical transmission. In:Cellular Biology of Neurons (edited byKandel, E. R.), Handbook of Physiology — The Nervous System, Vol. 1, pp. 357–416. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Blackstad, T. W., Osen, K. K. &Mugnaini, E. (1984) Pyramidal neurons of the dorsal cochlear nucleus: a Golgi and computer reconstruction study in the cat.Neuroscience (in press).
Brawer, R. J., Morest, D. K. &Kane, E. C. (1974) The neuronal architecture of the cochlear nucleus of the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 251–300.
Brodal, A. (1981) The auditory system (revised by K. K. Osen). InNeurological Anatomy (edited byBrodal, A.), pp. 692–739. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Browner, R. H. &Baruch, A. (1982) The cytoarchitecture of the dorsal cochlear nucleus in the 3-month- and 26-month-old C57B1/6 mouse. A Golgi impregnation study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 211, 115–38.
Cajal, S. R. Y. (1911)Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés, Vol. I. Paris: Maloine.
Cohen, E. (1972) The synaptic organization of the caudal cochlear nucleus in the cat: a light and electron microscopical study.Doctoral Dissertation. Harvard University, Cambridge.
Colonnier, M. (1968) Synaptic patterns on different cell types in different laminae of the cat visual cortex. An electron microscopic study.Brain Research 9, 268–87.
Disterhoft, J. F., Perkins, R. E. &Evans, S. (1980) Neuronal morphology of the rabbit cochlear nucleus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 192, 687–702.
Eccles, J. C., Ito, M. &Szentágothai, J. (1967)The Cerebellum as a Neuronal Machine. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Fairén, A., Defellpe, J. &Martinez-Ruiz, R. (1981) The Golgi-EM procedure: a tool to study neocortical interneurons. In:dial and Neuronal Cell Biology, Progress in Clinical and Biological Research, Vol. 59A (edited byAcosta Vidrio, E. andFedoroff, S.), pp. 219–301. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Fairén, A., Peters, A. &Saldanha, J. (1977) A new procedure for examining Golgi-impregnated neurons by light and electron microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 311–37.
Fiori, M. G. &Mugnaini, E. (1981) Subsurface and cytoplasmic. cisterns associated with mitochondria in pyramidal neurons of the rat dorsal cochlear nucleus.Neuroscience 6, 461–71.
Friedrich, V. L.JR, &Mugnaini, E. (1981) Electron microscopy: preparation of neural tissues for electron microscopy. In:Neuroanatomical Tract-Tracing Methods (edited byScheimer, L. andRobards, M. J.), pp. 345–376. New York: Plenum Press.
Gray, E. G. (1959) Axosomatic and axodendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex.Journal of Anatomy 93, 420–33.
Jones, L. S. &Disterhoft, J. F. (1979) Visualizing the rabbit auditory pathway with (14C)-2-deoxy-d-glucose.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 5, 23.
Kane, E. C. (1974a) Synaptic organization in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the cat: a light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 301–30.
Kane, E. C. (1974b) Patterns of degeneration in the caudal cochlear nucleus of the cat after cochlear ablation.Anatomical Record 179, 67–92.
Kane, E. C. &Finn, R. C. (1977) Descending and intrinsic inputs to dorsal cochlear nucleus of cats: a horseradish peroxidase study.Neuroscience 2, 897–912.
Larramendi, L. M. H. (1969) Analysis of synaptogenesis in the cerebellum of the mouse. In:Neurobiology of Cerebellar Evolution and Development (edited byLlinás, R.) pp. 803–843. Chicago: Ama-Erf Institute for Biomedical Reserach.
Lemkey-Johnston, N. &Laramendi, L. M. H. (1968) Types and distribution of synapses upon basket and stellate cells of the mouse cerebellum: an electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 134, 73–112.
Lorente de Nó, R. (1933) Anatomy of the eighth nerve. III. General plan of structure of the primary cochlear nuclei.Laryngoscope 43, 327–50.
Lorente de Nó, R. (1979) Central representation of the eighth nerve. InEar Diseases, Deafness and Dizziness (edited byGoodhill, V.), pp. 64–86. Hagerstown, Maryland: Harper & Row.
Lorente de Nó, R. (1981a)The Primary Acoustic Nuclei, pp. 1–177. New York: Raven Press.
Lorente de Nó, R. (1981b) Neurons with short axons in the adult human visual cortex.Frdburger Universitatsblatter 74, 59–61.
Marin-Padilla, M. (1969) Origin of pericullular baskets of the human motor cortex: a Golgi study.Brain Research 14, 633–46.
Mugnaini, E. (1969) Ultrastructural studies on the cerebellar histogenesis. II. Maturation of nerve cell populations and establishment of synaptic connections in the cerebellar cortex of the chick. In:Neurobiology of Cerebellar Evolution and Development (edited byLlinás, R.), pp. 749–782. Chicago: Ama-Erf Institute for Biomedical Research.
Mugnaini, E. (1972) The histology and cytology of the cerebellar cortex. In:The Comparative Anatomy and Histology of the Cerebellum: The Human Cerebellum, Cerebellar Connections and Cerebellar Cortex (edited byLarsell, O. andJansen, J.), pp. 201–265. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Mugnaini, E., Osen, K. K., Dahl, A.-L., Freidrich, V. L. Jr &Korte, G. (1980a) structure of granule cells and related interneurons (termed Golgi cells) in the cochlear nuclear complex of cat, rat and mouse.Journal of Neurocytology 9, 537–70.
Mugnaini, E., Warr, W. B. &Osen, K. K. (1980b) Distribution and light microscope features of granule cells in the cochlear nuclei of cat, rat and mouse.Journal of Comparative Neurology 191, 581–606.
Nudo, R. J. &Masterton, R. B. (1981) (14C)-2-deoxyglucose mapping of the dorsal cochlear nucleus in the kitten.Sodety for Neurostience Abstracts 7, 230.
Oliver, D. L., Potashner, S. J., Jones, D. R. &Morest, D. K. (1983) Selective labelling of spiral ganglion and granule cells withd-aspartate in the auditory system of cat and guinea pig.Journal of Neuroscience 3, 455–72.
Osen, K. K. &Mugnaini, E. (1981) Neuronal circuits in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. In:Neuronal Mechanisms of Hearing (edited byScsyka, J. andAitkin, L.). pp. 119–126. New York: Plenum Press.
Palay, S. L. &Chan-Palay, V. (1974)Cerebellar Cortex. Cytology and Organization, pp. 1–348. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Pappas, G. D. &Waxman, S. G. (1972) Synaptic fine structure: morphological correlations of chemical and electronic transmission. In:Structure and Function of Synapses (edited byPappas, G. D. andPurpura, D. P.), pp. 1–43. New York: Raven Press.
Peters, A. (1980) Morphological correlates of epilepsy: cells in the cerebral cortex. In:Antiepileptic Drugs. Mechanisms of Action (edited byGlaser, G. H., Tenzy, J. K. andWoodbury, D. N.), pp. 21–48. New York: Raven Press.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. &Webster, H.deF. (1976)The Fine Structure of the Nervous System, pp. 1–406. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Peters, A. &Proskauer, C. C. (1980) Synaptic relationships between a multipolar stellate cell and a pyramidal neuron in the rat visual cortex. A combined Golgi-electron microscopic study.Journal of Neurocytology 9, 185–205.
Pierce, E. T. (1967) Histogenesis of the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei in the mouse. An autoradiographic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 131, 27–54.
Rakic, P. (1972) Extrinsic cytological determinants of basket and stellate cell dendritic pattern in the cerebellar molecular layer.Journal of Comparative Neurology 146, 335–54.
Raviola, E. &Gilula, N. B. (1975) Intramembrane organization of specialized contacts in the outer plexiform layer of the retina. A freeze-fracture study in monkeys and rabbits.Journal of Cell Biology 65, 192–222.
Rhode, W. S., Smith, P. H. &Oertel, D. (1983) Physiological response properties of cells labeled intracellularly with horseradish peroxidase in cat dorsal cochlear nucleus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 213, 426–47.
Ribak, C. E. (1978) Aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase.Journal of Neurocytology 7, 461–78.
Schwartz, W. J. &Sharp, F. R. (1978) Autoradiographic maps of regional brain glucose consumption in resting, awake rats using (14C)-2-deoxy-glucose.Journal of Comparative Neurology 177, 335–60.
Sloper, J. J. (1972) Gap junctions between dendrites in the primate cortex.Brain Research 44, 641–6.
Sloper, J. J. &Powell, T. P. S. (1978a) Dendro-dendritic and reciprocal synapses in the primate motor cortex.Proceedings of the Royal Sodety of London, Series B 203, 23–38.
Sloper, J. J. &Powell, T. P. S. (1978b) Gap junctions between dendrities and somata of neurons in the primate sensori-motor cortex.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 203, 39–47.
Sotelo, C., Gentschev, T. &Zamora, A. J. (1976) Gap junctions in the ventral cochlear nucleus of the rat. A new example of electronic junctions in the mammalian CNS.Neuroscience 1, 5–7.
Sotelo, C. &Llinás, R. (1972) Specialized membrane junctions between neurons in the vertebrate cerebellar cortex.Journal of Cell Biology 53, 271–89.
Webster, D. B. &Trune, D. R. (1982) Cochlear nucleus complex of mice.American Journal of Anatomy 163, 103–30.
Willard, F. H. &Ryugo, D. K. (1983) Anatomy of the central auditory system. In:The Auditory Psychobiology of the Mouse (edited byWillot, J. F.), pp. 201–304. Springfield, Illinois: Thomas.
Wouterlood, F. G. (1979) Light microscopical identification of Golgi impregnated QMS neurons during sectioning for electron microscopy.Stain Technology 54, 325–9.
Wouterlood, F. G. &Mugnaini, E. (1984) Cartwheel neurons of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. A Golgi-electron microscopic study in rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology (in press).
Wouterlood, F. G., Nederlof, J. &Paniry, S. (1983) Chemical reduction of silver chromate: a procedure for electron microscopical analysis of Golgi-impregnated neurons.Journal of Neuroscience Methods 7, 295–308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wouterlood, F.G., Mugnaini, E., Osen, K.K. et al. Stellate neurons in rat dorsal cochlear nucleus studied with combined Golgi impregnation and electron microscopy: synaptic connections and mutual coupling by gap junctions. J Neurocytol 13, 639–664 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148083
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148083