Abstract
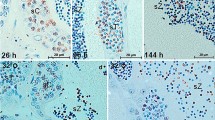
This study involves a histological examination of the testicular tissue to assess, both quantitatively and qualitatively, the effects of an 18-day exposure of juvenile male rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri, to cyanide in laboratory flow-through aquaria at 12.5°C. Test concentrations of 0.01 and 0.03 mg/L HCN reduced the number of dividing spermatogonia by 13 and 50% respectively. The exposure to cyanide led to an increase in the prophase stage spermatogonia which appeared to be due to a blockage of mitotic progress.
Cyanide also affected the formation of the mitotic spindle at the lower cyanide concentration as evidenced by the presence of multipolar spindles and multinucleate interphase cells. Cellular damage was evident in spermatogonia in all phases of the cell cycle accompanied by a high incidence of necrosis at the higher cyanide concentration. It is suggested that short-term exposure to sublethal concentrations of cyanide may cause permanent damage to the fixed number of primary spermatogonia within the testis, thereby reducing the reproductive capacity of this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deysson, G.: Antimitotic substances. In G. H. Bourne and J. F. Danielli (ed.): International review of cytology, Vol. 24, p. 99. New York-London: Academic Press (1968).
Dixon, D. G.: Some effects of chronic cyanide poisoning on the growth, respiration, and liver tissue of rainbow trout. M.Sc. thesis, Concordia University, Montreal (1975).
Doudoroff, P.: Toxicity to fish of cyanides and related compounds: A review. Ecol. Res. Ser. EPA-600/3-76-038. U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Technical Information Service. PB-253528 (1976).
Doxey, D.: The effect of isopropyl phenyl carbamate on mitosis in ryeSecale cereale and onionAllium cepa.Ann. Bot. 131, 329 (1949).
Elias, H., and A. Henning: Sterology of the human renal glomerulus. In E. R. Weibel and H. Elias (ed.): Quantitative methods in morphology, p. 130. New York: Springer-Verlag (1967).
Ennis, W. B.: Some cytological effects of o-isopropyl N-phenyl carbamate uponAvena. Am. J. Bot.35, 15 (1948).
Epstein, J.: Estimation of microquantities of cyanide. Anal. Chem.19, 272 (1947).
Galligher, A. E., and E. N. Kozloff: Essentials of practical microtechnique. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger (1971).
Hepler, P. K., and W. T. Jackson: Isopropyl N-phenylcarbamate affects spindle microtubule orientation in dividing endosperm cells ofHaemanthus katerinae Baker. J. Cell Sci.5, 727 (1969).
Koenst, W. M., L. L. Smith, Jr., and S. J. Broderius: Effect of chronic exposure of brook trout to sublethal concentrations of hydrogen cyanide. Environ. Sci. Tech.11, 883 (1971).
Kovacs, T. G.: Thermal influence on cyanide toxicity to rainbow trout. M.Sc. thesis. Concordia University. In preparation (1979).
Kruzynski, G. M.: Effects of dietary methoxychlor on brook trout,Salvelinus fontinalis. M.Sc. thesis. Sir George Williams University, Montreal (1972).
Leduc, G.: Une bouteille à débit constant pour petits volumes de liquides. Nat. Can.93, 61 (1966a).
: Some physiological and biochemical responses of fish to chronic poisoning by cyanide. Ph.D. thesis. Oregon State University, Corvallis (1966b).
: The role of cyanide as an ecological stressing factor to fish,In Recent Advances in Fish Toxicology. A symposium, p. 152. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Corvallis, Oregon. EPA-600/3-77-085 (1977).
: Deleterious effects of cyanide on early life stage of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Fish. Res. Board. Can.35, 166 (1978).
Lesniak, J. A.: A histological approach to the study of sublethal cyanide effects on rainbow trout ovaries. M.Sc. thesis. Concordia University, Montreal (1977).
Lind, D.T., L. L. Smith, Jr., and S. J. Broderious: Chronic effects of hydrogen cyanide on the fathead minnow. J. Water. Pollut. Control Fed.49, 262 (1977).
Mann, J. D., and W. B. Storey: Rapid action of carbamate herbicides upon plant cell nuclei. Cytologia31, 203 (1966).
Meyers, F. H., E. Jawetz, and A. Goldflen: Review of Medical Pharmacology. 6th ed., p. 685. Los Altos, Calif.: Lange Medical Publications (1976).
National Academy of Science and National Academy of Engineering. Water Quality Criteria (1972). EPA-R3-73-033 (1974).
Prosser, C. L.: Comparative Animal Physiology. 3rd ed., p.95, 332. Philadelphia-London-Toronto: Saunders (1973).
Ruby, S. M., and D. B. McMillan: The interstitial origin of germinal cells in the testis of the stickleback. J. Morph.145, 295 (1975).
Ruby, S. M., J. Aczel, and G. R. Craig.: The effects of depressed pH on spermatogenesis in flagfish,Jordanella floridae. Water Res.12, 621 (1978).
Sprague, J. B.: The ABC's of pollutant bioassay using fish. P. 6.In Biological Methods for the Assessment of Water Quality. ASTM STP 528, American Society for Testing Materials. Philadelphia (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruby, S.M., Dixon, D.G. & Leduc, G. Inhibition of spermatogenesis in rainbow trout during chronic cyanide poisoning. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 8, 533–544 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055034
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055034