Summary
To determine the effect of a taurine-enriched drink “Red Bull” on performance, 10 endurance-athletes performed three trials. After 60 min. cycling at approximately 70% VO2 max, the subjects pedalled to exhaustion on a cycle ergometer. During each exercise, the subjects received 500 ml of a test-drink after 30 min. submaximal cycling: “Red Bull” without taurine, without glucuronolacton (U1), “Red Bull” without taurine, without glucuronolacton, without caffeine (U2) and “Red Bull” original drink containing taurine, glucuronolacton and caffeine (U3).
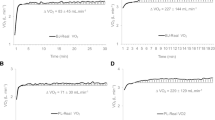
The heart rate level was significantly lower in U3 (p = 0,0031) 15 min. after application. The plasma catecholamines increased slightly from begin of exercise to 15 min. after application of the drinks in all trials but remained on a significantly lower level in U3 (epinephrine (p = 0,0011) and norepinephrine (p = 0,0003). Endurance time was significantly longer with “Red Bull” original in U3 (p = 0,015). The results of this study show a positive effect of a taurine-containing drink on hormonal responses which leads to a higher performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma J, Takahisa K, Awata N, Ohta H, Hamaguchi H, Harada H, Takihara K, Hasegawa H, Yamagami R, Ishiyama T, Iwata H, Kishimoto S (1985) Therapeutic effect of taurine in congestive heart failure: a double-blind crossover trial. Clin Cardiol 8: 276–282
Baba A, Lee E, Tatsuno T, Iwata H (1982) Cysteine sulfinic acid in the central nervous system: antagonistic effect of taurine on cysteine sulfinic acid-stimulated formation of cyclic AMP in guinea pig hippocampal slices. J Neurochem 38: 1280–1285
Bousquet P, Feldman J, Bloch R, Schwartz J (1981) Tag antagonises the central cardiovascular effects of taurine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 219: 213–218
Chazov EI, Malchikova LS, Lipiva NV, Asafov GB, Smirnov VN (1974) Taurine and electrical activity of the heart. Circ Res 35: 11–21
Costill DL, Palsky GP, Fink WJ (1978) Effects of caffeine ingestion on metabolism and exercise performance. Med Sci Sports 10: 155
Franconi F, Stendardi MI, Failli P, Antonini G, Bennardini F, Matucci R, Manzini S, Giotti A (1983) Taurine antagonizes the alpha-adrenergic positive inotropic effect of phenylephrine. In: Kuriyama K, Huxtable RJ, Iwata H (eds) Sulfur amino acids: Biochemical and clinical aspects: 51–60
Geiß K-R, Jester I, Askali F, Förster H, Hamm M, Böhmer D (1993) Auswirkungen fruktose- und glukosehaltiger Getränke auf die körperliche Leistungsfähigkeit bei 9 Triathleten. Dtsch Sportärztekongreß Paderborn (publication in preparation)
Geiß K-R, Nöcker J, Waag K-L, Queeney D (1991) Individual calorie calculation and sportspecific nutrient distribution in 100 high-performance athletes to increase performance. Int J Sports Med 12: 122
Huxtable RJ, Bressler R (1973) Effect of taurine on a muscle intracellular membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 323: 573–583
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiological Rev 72 1: 128
IBL (1993) Radioimmunoassays zur quantitativen Bestimmung der Katecholamine Noradrenalin und Adrenalin in Plasma und Urin. dbm bulletin: 1–20
Inoue A, Takahashi H, Lee L, Iyoda I, Sasaki S, Ijichi H (1985) Centrally induced vasodepressor and sympathetic nerve responses to taurine. Jpn Circ J 49: 1180–1184
Jacobs DS (ed) (1988) Laboratory test handbook. Laxi-Comp/Mosby, Cleveland, p 139
Livesey JH, Hodgkinson SC, Roud HR, Donald RA (1980) hGH-analysing methods. Clin Biochem 13: 151
Mal'Chikova LS, Elizarova EP (1981) Taurine and cAMP content in the heart. Kardiologiya 21: 85–89
Mal'Chikova LS, Speranskaia NV, Elizarova EP (1979) Effect of taurine on the cAMP and cGMP content in the rat heart in stress. Byull Eksp Biol Med 87: 134–137
Muramatsu M, Kakita K, Kuriyama K (1978) Amodulating tole of taurine on release of acetyl choline and norapinephrine from neuronal tissue. Jpn J Pharmacol 28: 259–268
Ono M, Watanabe M, Minato K (1987) Effects of taurine on the metabolism under physical exercise. Sulfur Amino Acids 10: 183–186
Pasantes-Morales H (1982) Taurine-calcium interactions in frog rod outer segments; taurine effects on an ATP-dependent calcium translocation process. Vision Res 22: 1487–1493
Pasantes-Morales H, Martin DL, Ordonez A (1982) Taurine activation of a bicarbonatcdependent, ATP-supported calcium uptake in frog rod outer segments. Neurochem Res 7: 317–328
Sherman WM, Brodowicz GR, Wright DA, Allen WK, Simonsen J, Dernbach A (1989) Effects of 4th preexercise carbohydrate feedings on cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exer 21: 598–604
Trout DL, Estes EH, Friedberg SJ (1969) Microdetermination of long chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Lipid Res 1: 199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geiß, K.R., Jester, I., Falke, W. et al. The effect of a taurine-containing drink on performance in 10 endurance-athletes. Amino Acids 7, 45–56 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00808445
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00808445