Abstract
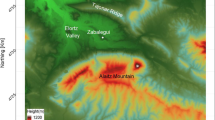
Vertical profiles of wind speed, temperature and humidity were used to estimate the roughness lengths for momentum (z 0), heat (z H ) and moisture (z Q) over smooth ice and snow surfaces. The profile-measurements were performed in the vicinity of a blue ice field in Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica. The values ofz 0 over ice (∼3·10−6 m) seem to be the smallest ever obtained over permanent, natural surfaces. The settling of snow on the ice and the loss of momentum at saltating snow particles serve as momentum dissipating processes during snow-drift events, expressed as a strong dependence ofz 0 on u#.
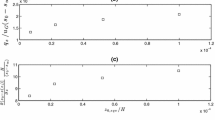
The scalar roughness lengths and surface temperature can be evaluated from the temperature and humidity profile measurements if the ratioz H /z Q is specified. This new method circumvents the difficult measurement of surface temperature. The scalar roughness lengths seem to be approximately equal toz0 for a large range of low roughness Reynolds numbers, despite the frequent occurrence of drifting snow. Possible reasons for this agreement with theory of non-saltating flow are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas, E. L.: 1987, ‘A Theory for the Scalar Roughness and the Scalar Transfer Coefficient over Snow and Sea Ice’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 38, 159–184.
Bintanja, R., Van den Broeke, M. R., and Portanger, M. J.: 1993, ‘A Meteorological and Glaciological Experiment on a Blue Ice Area in the Heimefront Range, Queen Maud Land, Antarctica’, Svea Field Report, I.M.A.U. report, Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research Utrecht, Utrecht University.
Bintanja, R. and Van den Broeke, M. R.: 1995, ‘The Surface Energy Balance of Antarctic Snow and Blue Ice’,J. Appl. Meteorol. (in press).
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1975, ‘The Roughness Length for Water Vapor, Sensible Heat and Other Scalars’,J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 2028–2031.
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1982,Evaporation into the Amosphere, Reidel, Dordrecht, 299 pp.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1983, ‘Roughness Length of Sea, Sand and Snow’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 405–409.
Charnock, H.: 1955, ‘Wind Stress on a Water Surface’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 639–640.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1991, ‘Radiation Fog: A Comparison of Model Simulation with Detailed Observations’,Mon. Wea. Rev. 119, 324–341.
Dyer, A. J.: 1974, ‘A Review of Flux-Profile Relationships’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 363–372.
Fortuin, J. P. F. and Oerlemans, J.: 1992, ‘An Atmospheric Model for Simulating the Mass Balance and Temperature on the Antarctic Ice Sheet’,Zeitschr. Gletscherk. Glazialgeol. 26, 31–56.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992,The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press. 316 pp.
Garratt, J. R. and Hicks, B. B.: 1973, ‘Momentum, Heat and Water Vapour Transfer to and from Natural and Artificial Surfaces’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 99, 680–687.
Hicks, B. B. and Martin, H. C.: 1972, ‘Atmospheric Turbulent Fluxes Over Snow’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2, 496–502.
Hinze, J. O.: 1975,Turbulence, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 790 pp.
Högström, U.: 1988, ‘Non-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Profiles in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Re-evaluation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 55–78.
Inoue, J.: 1989a, ‘Surface Drag over the Snow Surface of the Antarctic Plateau. 1: Factors Controlling Surface Drag over the Katabatic Wind Region’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 2207–2217.
Inoue, J.: 1989b, ‘Surface Drag over the Snow Surface of the Antarctic Plateau. 2: Seasonal Change of the Surface Drag in the Katabatic Wind Region’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 2219–2224.
Joffre, S. M.: 1982, ‘Momentum and Heat Transfers in the Surface Layer over a Frozen Sea’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 211–229.
King, J. C.: 1990, ‘Some Measurements of Turbulence over an Antarctic Ice Shelf’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 379–400.
King, J. C. and Anderson, P. S.: 1994, ‘Heat and Water Vapour Fluxes and Scalar Roughness Lengths over an Antarctic Ice Shelf’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 69, 101–121.
Kondo, J. and Yamazawa, H.: 1986, ‘Bulk Transfer Coefficient over a Snow Surface’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 123–135.
Liljequist, G. H.: 1957, ‘Energy Exchange over an Antarctic Snow Field’,Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition 1949–52, Scientfic Results, Vol. 1–4.
Munro, D. S.: 1989, ‘Surface Roughness and Bulk Heat Transfer on a Glacier: Comparison with Eddy Correlation’,J. Glaciol. 35, 343–348.
Owen, P. R.: 1964, ‘Saltation of Uniform Grains in Air’,J. Fluid Mech. 20, 225–242
Schmidt, R. A.: 1982, ‘Vertical Profiles of Wind Speed, Snow Concentration and Humidity in Blowing Snow’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 23, 223–246.
Schmidt, R. A.: 1986, ‘Transport Rate of Drifting Snow and the Mean Wind Speed Profile’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 213–241.
Tabler, R. D.: 1980, ‘Self-Similarity of Wind Profiles in Blowing Snow Allows Outdoor Modeling’,J. Glaciol. 26, 421–434.
Van den Broeke, M. R. and Bintanja, R.: 1995, ‘Summer Time Katabatic Flow and Local Circulation in the Vicinity of a Blue Ice Area in Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol.72 (in press).
Wendler, G., Ishikawa, N., and Kodama, Y.: 1988, ‘The Heat Balance of the Icy Slope of Adelie Land, Eastern Antarctica’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 27, 52–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bintanja, R., Van Den Broeke, M.R. Momentum and scalar transfer coefficients over aerodynamically smooth antarctic surfaces. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 74, 89–111 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00715712
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00715712