Summary
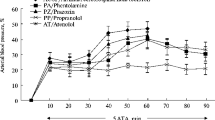
Amphetamine administration to rats anaesthetized with nitrous oxide resulted in protein extravasation in the brain, particularly in the frontoparietal cortex. The drug is known to increase the cerebral blood flow in the same areas, indicating a vasodilatory action on the cerebral vessels. Protein leakage could be prevented by lowering the blood pressure and, to a large extent, also by hyperventilation. This suggests that the permeability disturbance is caused by the mechanical stress which results from high intraluminal pressure in combination with vasodilatation.
The pharmacological effect of amphetamine is caused by a catecholamine release in the central nervous system and in the periphery. The vasodilatory effect of amphetamine could be either a direct effect on the cerebral vessels or could be secondary to an increased cerebral metabolism. The vasodilatory betaadrenergic receptors in the cerebral vessels are of beta1 type. Practolol, a selective beta1-receptor antagonist which can prevent the vasodilatory effect of isoprenaline on cerebral vessels, did not influence the amphetamine induced protein leakage. In contrast, propranolol, a non-selective beta-receptor blocking drug which earlier has been shown to prevent catecholamine induced increase of CBF and oxygen consumption, diminished or prevented the protein leakage. It is likely that the cerebral vasodilatation caused by amphetamine, at least in part, is secondary to an increased cerebral metabolism induced by a catecholamine release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N. E.: Effects of amphetamine and some other drugs on central catecholamine mechanisms. In: Amphetamines and Related Compounds (eds. E. Costa and S. Garattini), pp. 447–462. New York: Raven Press 1970
Benakis, A., Thomasset, M.: Metabolism of amphetamines and their interaction with barbiturates and SKF-525 A. In: Amphetamines and Related Compunds (eds. E. Costa and S. Garattini), 153–164, New York: Raven Press 1970
Berntman, L., Carlsson, C., Hägerdal, M., Siesjö, B. K.: Circulatory and metabolic effects in the brain induced by amphetamine sulphate. Acta physiol. scand. (in press)
Bolwig, T. G., Hertz, M. M., Westergaard, E.: Blood-brain barrier permeability to protein during epileptic seizures in the rat. Acta neurol. scand., Suppl.64, 56, 226–227 (1977)
Carlsson, A.: Amphetamine and brain catecholamines. In: Amphetamines and Related Compounds (eds. E. Costa and S. Garattini), 289–300. New York: Raven Press 1970
Carlsson, C., Hägerdal, M., Siesjö, B. K.: Influence of amphetamine sulphate on cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Acta physiol. scand.94, 128–129 (1975)
Carlsson, C., Hägerdal, M., Kaasik, A. E., Siesjö, B. K.: A catecholaminemediated increase in cerebral oxygen uptake during immobilisation stress in rats. Brain Res.119, 223–231 (1977)
Carlsson, C., Hägerdal, M., Siesjö, B. K.: The effect of nitrous oxide on oxygen consumption and blood flow in the cerebral cortex of the rat. Acta anaesth. scand.20, 91–95 (1976)
Chapman, A. G., Meldrum, B. S., Siesjö, B. K.: Cerebral metabolic changes during prolonged epileptic seizures in rats. J. Neurochem.28, 1025–1035 (1977)
Edvinsson, L., Owman, Ch.: Pharmacological characterization of adrenergic alpha and beta receptors mediating the vasomotor responses of cerebral arteries in vitro. Circulat. Res.35, 835–849 (1974)
Eklöf, B., Lassen, N. A., Nilsson, L., Norberg, K., Siesjö, B. K., Torlöf, P.: Regional cerbral blood flow in the rat measured by the tissue sampling technique; a critical evaluation using four indicators C14-antipyrine, C14-ethanol, H3-water and zenon133. Acta physiol scand.91, 1–10 (1974)
von Essen, C.: Effects of dopamine on the cerebral blood flow in the dog. Acta neurol. scand.50, 39–52 (1974)
Johansson, B.: Brain barrier pathology in acute arterial hypertension. In: Transport phenomena in the nervous system (eds. G. Levi, L. Battistin and A. Lajtha). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.69, 517–527. New York: Plenum Press 1976a
Johansson, B.: Some factors influencing the damaging effect of acute arterial hypertension on cerebral vessels in rats. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med.51, 41–43 (1976b)
Johansson, B., Li, Ch.-L., Olsson, Y., Klatzo, I.: The effect of acute arterial hypertension on the blood-brain barrier to protein tracers. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)16, 117–124 (1970)
Johansson, B., Nilsson, B.: The pathophysiology of the blood-brain barrier dysfunction induced by severe hypercapnia and by epileptic brain activity. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)38, 153–158 (1977)
MacKenzie, E. T., McCulloch, J., O'Keane, M., Pichard, J. D., Harper, A. M.: Cerebral circulation and norepinephrine: relevance of the blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Physiol.231, 483–488 (1976)
MacKenzie, E. T., McCulloch, J., Harper, A. M.: Influence of endogenous norepinephrine on cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Am. J. Physiol.231, 489–494 (1976)
McCulloch, J., Harper, A. M.: Cerebral circulatory and metabolism changes following amphetamine administration. Brain Res.121, 196–199 (1977)
Meldrum, B. S., Nilsson, B.: Cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate early and late in prolonged epileptic seizures induced in rats by bicuculline. Brain99, 523–542 (1976)
Petito, C., Schaefer, J. A., Plum, F.: Ultrastructural characteristics of the brain and blood-brain barrier in experimental seizures. Brain Res.127, 251–267 (1977)
Sercombe, R., Aubineau, P., Edvinsson, L., Mamo, H., Owman, Ch., Seylaz, J.: Pharmacological evidence in vitro and in vivo for functional beta1 receptors in the cerebral circulation. Pflügers Arch.368, 241–244 (1977)
Stein, L.: Self-stimulation of the brain and the central stimulant action of amphetamine. Fed. Proc.23, 836–850 (1964)
Steinwall, O., Klatzo, I.: Selective vulnerability of the blood-brain barrier in chemically induced lesions. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.25, 542–559 (1966)
Sulser, F., Sander-Bush, E.: Biochemical and metabolic considerations concerning the mechanism of action of amphetamine and related compounds. In: Psychomimetric Drugs (ed. D. H. Efron), 83–94. New York: Raven Press 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlsson, C., Johansson, B.B. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction after amphetamine administration in rats. Acta Neuropathol 41, 125–129 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689763
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689763