Summary
The properties of bee medulla and lobula neurons were investigated using intracellular recordings and light stimuli of different qualities. The intracellular injection of dye permitted the examination of the structure and position of neurons studied electrophysiologically. Examples of different coding mechanisms are given; transitional stages were also found.
-
1.
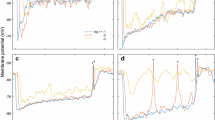
Broad band neurons have response/intensity curves for different wavelengths in the same range of intensity; the absolute value of intensity for this range may be different for ON and OFF reactions.
-
2.
Narrow band units show high sensitivity to only a small portion of the spectrum. The maximum sensitivity sometimes lies between the sensitivity maximum of different photoreceptors.
-
3.
Intensity band neurons react to a small intensity range, and show no reaction to light of neighboring intensities.
-
4.
Color specific mechanisms are evident in antagonistic reactions to different colors of the test light. In medullar neurons this component of reaction was phasic, in lobular neurons tonic.
-
5.
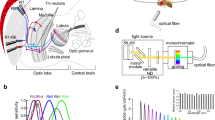
Receptive fields of 1/3 of medulla neurons are smaller than 30°; those of lobula neurons are greater than 30°.
-
6.
Some fibres show spatial antagonism: light elicits excitation in one part of the receptive field and inhibition in the other. Fields lack antagonistic center-surround structure.
-
7.
Several neurons are sensitive to movement of a light stimulus. In the medulla these always had small receptive fields, in the lobula wide receptive fields. Directional selectivity occasionally occurred in the lobula.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett, D.W.: Spatial and temporal integration properties of units in first optic ganglion of dipterans. J. Neurophysiol.35, 429–444 (1972)
Autrum, H., Zwehl, V. von: Spektrale Empfindlichkeit einzelner Sehzellen des Bienenauges. Z. Vergl. Physiol.48, 357–384 (1964)
Daumer, K.: Reizmetrische Untersuchungen des Farbensehens der Bienen. Z. Vergl. Physiol.38, 413–478 (1956)
DeValois, R.L.: Central mechanisms of colour vision. In: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VII/3A. Jung R. (ed.), pp. 209–254. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1973
Erber, J., Menzel, R.: Visual interneurons in the median protocerebrum of the bee. J. Comp. Physiol.121, 65–77 (1977)
Frisch, K. von: Der Farbensinn und Formensinn der Bienen. Zool. J. Physiol.37, 1–238 (1914)
Heiversen, O. von: Zur spektralen Unterschiedsempfindlichkeit der Honigbiene. J. Comp. Physiol.80, 439–472 (1972)
Hering, E.: Zur Lehre vom Lichtsinn. Wien: Karl Gerolds Sohn 1878
Honegger, H.-W.: Sustained and transient responding units in the medulla of the cricketGryllus campestris. J. Comp. Physiol.125, 259–266 (1978)
Hubel, D.H., Wiesel, T.N.: Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J. Physiol.160, 106–154 (1962)
Kaiser, W., Seidl, R., Vollmar, J.: Participation of all three colour receptors in phototactic behaviour of fixed walking honeybees. J. Comp. Physiol.122, 27–44 (1977)
Kien, J., Menzel, R.: Chromatic properties of interneurons in the optic lobes of the bee. I. J. Comp. Physiol.113, 17–34 (1977a)
Kien, J., Menzel, R.: Chromatic properties of interneurons in the optic lobes of the bee. II. J. Comp. Physiol.113, 35–53 (1977b)
McIlwain, J.T.: Large receptive fields and spatial transformations in the visual system. In: Neurophysiology II, Vol. 10. Porter, R. (ed.), pp. 223–248. Baltimore: University Park Press 1976
Menzel, R.: Spectral sensitivity of monopolar cells in the bee lamina. J. Comp. Physiol.93, 337–346 (1974)
Menzel, R.: Spectral sensitivity and colour vision in invertebrates. In: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VII/6A. Autrum, H. (ed.), pp. 504–566. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1979
Menzel, R., Blakers, M.: Colour receptors in the bee eye — morphology and spectral sensitivity. J. Comp. Physiol.108, 11–33 (1976)
Michael, C.R.: Color vision mechanisms in monkey striate cortex: simple cells with dual opponent-color receptive fields. J. Neurophysiol.41, 1233–1249 (1978)
Mimura, K.: Movement discrimination by the visual system of flies. Z. Vergl. Physiol.73, 105–138 (1971)
Mimura, K.: Analysis of visual information in lamina neurones of the fly. J. Comp. Physiol.88, 335–347 (1974)
Ribi, W.A.: The first optic ganglion of the bee. I. Correlation between visual cell types and their terminals in the lamina and medulla. Cell Tissue Res.165, 103–112 (1975)
Ribi, W.A.: The first optic ganglion of the bee. II. Topographical relationship of the monopolar cells within and between cartridges. Cell Tissue Res.171, 359–374 (1976)
Riehle, A.: Reaktionsmuster zentraler visueller Interneurone der Honigbiene (Apis mellifera c.) auf hetero-chromatisches Flickerlicht. Dissertation am FB 23 der Freien Universität Berlin (1980)
Strausfeld, N.: Atlas of an insect brain. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1976
Swihart, S.L.: Colour vision and the physiology of the superposition eye of a butterfly (Hesperiidae). J. Insect Physiol.15, 1347–1365 (1969)
Swihart, S.L.: Modelling the butterfly visual pathway. J. Insect Physiol.18, 1915–1928 (1972a)
Swihart, S.L.: The neural basis of colour vision in the butterflyHeliconius erato. J. Insect Physiol.18, 1015–1025 (1972b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
I am grateful to R. Menzel for helpful comments on the manuscript and R.D. Rose for critical reading the paper. I thank Mrs. G. Bollmus-Schnier and P. Jahn for technical assistance. This work was supported by DFG grant Me 365/6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hertel, H. Chromatic properties of identified interneurons in the optic lobes of the bee. J. Comp. Physiol. 137, 215–231 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657117
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657117