Summary
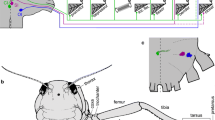
The skeletal morphology, musculature and innervation of the mandible of the common lobster,Homarus gammarus, are described as a basis for the functional study included in the two subsequent papers.
Although the mandible articulation takes the form of a hinge with movement in a single plane, the musculature of the mandible is complex. The main muscles are similar to those ofAstacus (Schmidt, 1915) but some smaller, previously undescribed muscles were found.
As forAstacus (Keim, 1915) andCambarus (Chaudonneret, 1956) the mandibular muscles are innervated by two nerve trunks, the inner and outer mandibular nerves. However, differences occur in the branching of these nerves and the muscles which they innervate.
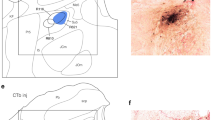
A group of sensory cells associated with the posterior stomach nerve (omn 4) are described. It is suggested that these form a proprioceptive organ associated with the hypodermis overlying the lateral mandible articulation.
An interesting group of neurones lying at the confluence of nerve branches from omn 2, omn 3, and omn 4 is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D.J., Hannam, A.G., Matthews, B.: Sensory mechanisms in mammalian teeth and their supporting structures. Physiol. Rev.50, 171–195 (1970)
Balss, H.: Crustacea, Decapoda. In: Bronn's Klassen und Ordnungen des Tierreichs. Bd. 5, Abt. 1, Buch 7 (1941)
Borradaile, L.A.: On the function of the mouth parts of the common prawn. Proc. Camb. phil. Soc. biol. Sci.19, 56 (1917)
Chaudonneret, J.: Le système nerveux de la région gnathale de l'écrevisseCambarus affinis (say). Ann. Sci. nat. (Zool.) (sér. 11)18, 33–61 (1956)
Dando, M.R., Laverack, M.S.: A mandibular proprioceptor in the lobster,Homarus vulgaris. Experientia (Basel)24, 931 (1968)
Dando, M.R., Laverack, M.S.: The anatomy and physiology of the posterior stomach nerve (p.s.n.) in some decapod Crustacea. Proc. roy Soc. B171, 465–482 (1969)
Ferrero, E., Wales, W.: The mandibular common inhibitor system. 1. Axon topography and the nature of coupling. (In preparation)
Keim, M.: Das Nervensystem vonAstacus fluviatilis (L.) (Potamobius astacus Leach.). Z. wiss. Zool.113, 485–545 (1915)
Laverack, M.S., Dando, M.R.: The anatomy and physiology of mouthpart receptors in the lobster,Homarus vulgaris. Z. vergl. Physiol.61, 176–195 (1968)
Macmillan, D.L., Wales, W., Laverack, M.S.: Mandibular movements and their control inHomarus gammarus. III. Effects of load changes. J. comp. Physiol.106, 207–221 (1976)
Manton, S.M.: Mandibular mechanisms and the evolution of arthropods. Phil. Trans. B.247, 1–184 (1964)
Mocquard, M.F.: L'estomac des Crustacéa podophthalmaires. Ann. Sci. nat. (Zool.) (6eme Series)16, 1–311 (1883)
Moulins, M., Dando, M.R., Laverack, M.S.: Further studies on mouthpart receptors in decapod Crustacea. Z. vergl. Physiol.69, 225–248 (1970)
Netz, W.: Das Skelett des Flusskrebses (Potamobius astacus, Leach). Thesis, Universität Marburg, Germany (1917)
Pabst, H., Kennedy, D.: Cutaneous mechanoreceptors influencing motor output in the crayfish abdomen. Z. vergl. Physiol.57, 190–208 (1967)
Pantin, C.F.A.: Notes on microscopical technique for zoologists. Cambridge: University Press 1948
Schmidt, W.: Die Muskulatur vonAstacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus). Z. wiss. Zool.113, 165–251 (1915)
Snodgrass, R.E.: Comparative studies on the jaws of mandibulate arthropods. Smithson, misc. Collns116, 1–85 (1950)
Snodgrass, R.E.: A textbook of arthropod anatomy. New York: Cornell University Press (1952)
Stormer, L.: On the relationships and phylogeny of fossil and recent arachnomorpha. Skr. norske Vidensk. Akad., I. Mat. nat. Kl.1, 158 (1944)
Wales, W., Clarac, F., Dando, M.R., Laverack, M.S.: Innervation of the receptors present at the various joints of the pereiopods and third maxilliped ofHomarus gammarus (L.) and other macruran decapods (Crustacea). Z. vergl. Physiol.68, 345–384 (1970)
Wales, W., Ferrero, E.: The mandibular common inhibitor system. 2. Input sensitivity. (In preparation)
Wales, W., Laverack, M.S.: The mandibular muscle receptor organ ofHomarus gammarus (L.) (Crustacea, Decapoda). Z. Morph. Tiere73, 145–162 (1972a)
Wales, W., Laverack, M.S.: Sensory activity of the mandibular muscle receptor organ ofHomarus gammarus (L.). I. Response to receptor muscle stretch. Mar. Behav. Physiol.1, 239–255 (1972b)
Wales, W., Macmillan, D.L., Laverack, M.S.: Mandibular movements and their control inHomarus gammarus. II. Normal feeding. J. comp. Physiol.106, 193–206 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wales, W., Macmillan, D.L. & Laverack, M.S. Mandibular movements and their control inHomarus gammarus . J. Comp. Physiol. 106, 177–191 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620497
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620497