Summary
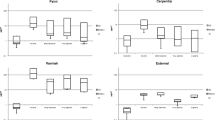
In a plastic boat company we studied workers' attitudes toward wearing respiratory protective equipment and differences in styrene exposure received with and without respirators. The workers studied used either half-facepiece air-purifying or full-face air-supplied respirators as much as possible during the first day of the study. On the second day respirators were used only for short periods or not at all. Individual styrene exposures were measured by personal air sampling in the breathing zone. When using respirators the exposure was measured both inside and outside the respirators. The styrene metabolites mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids were determined in urine samples collected during the workday. The eleven workers studied used the respirators 52% of the time on the first day and 7% of the time on the second. The reasons for not wearing respirators were that they delayed work, were too tight and uncomfortable, made it difficult to breath, and/or became too warm. The use of respirators during work operations such as spraying, laminating, and painting reduced the styrene exposure by 56%–92% . The excretion rate of mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids in urine collected at the end of the working day was 30%–99% lower when respirators were worn than when they were not.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åstrand I (1983) Effects of physical exercise on uptake, distribution and elimination of vapors in man. In: Fiserova-Bergerova V (ed) Modelling of inhalation exposure to vapors: uptake, distribution, and elimination, vol II. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl., pp 107–130
Bobjer O, Andersson I-M, Widholm B (1979) Painting in the ship-building industry: exposure to solvents and paint dust (in Swedish). NIGH (Sweden), Undersökningsrapport, 1979:14
Engström J, Bjurström R, Åstrand I, Övrum P (1978) Uptake, distribution and elimination of styrene in man. Concentration in subcutaneous adipose tissue. Scand J Work Environ Health 4:315–323
Flodin U, Ekberg K, Anderson L (1989) Neuropsychiatric effects of low exposure to styrene. Br J Ind Med 46:805–808
Galvin K, Selvin S, Spear RC (1990) Variability in protection afforded by half-mask respirators against styrene exposure in the field. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 51:625–631
Gwosdow AR, Nielsen R, Berglund LG, DuBois AB, Tremml PG (1989) Effect of thermal conditions on the acceptability of respiratory proctective devices on humans at rest. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 50:188–195
Harber P, Beck J, Brown C, Lou J (1991) Physiologic and subjective effects of respirator mask type. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 52:357–362
Jones JG (1991) The physiological cost of wearing a disposable respirator. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 52:219–225
Kjellberg A, Landström U, Löfstedt P, Wide P, Åkerlund E (1988) Estimation of noise and annoyance in working environments. A methodological study (in Swedish). Arbete och Hälsa 30:1–36
Lenhart SW, Campbell DL (1984) Assigned protection factors for two respirator types based upon workplace performance testing. Ann Occup Hyg 28:173–182
Moore DE, Smith TJ (1976) Measurement of protection factors of chemical cartridge, half-mask respirators under working conditions in a copper smelter. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 37:453–458
Morgan WP (1983) Psychological problems associated with the wearing of industrial respirators: a review. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 44:671–676
Myers WR, Peach MJ (1983) Performance measurements on a powered air-purifying respirator made during actual field use in a silica bagging operation. Ann Occup Hyg 27:251–259
Raven PB, Dodson AT, Davis TO (1979) The physiological consequences of wearing industrial respirators: a review. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 40:517–534
Sollenberg J, Baldesten A (1977) Isotachophoretic analysis of mandelic acid, phenylglyoxylic acid, hippuric acid and methylhippuric acid in urine after occupational exposure to styrene, toluene and/or xylene. J Chromatogr 132:469–476
Sollenberg J, Bjurström R, Wrangskog K, Vesterberg O (1988) Biological exposure limits estimated from relations between occupational styrene exposure during a workweek and excretion of mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids in urine. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 60:365–370
Stobbe TJ, daRoza RA, Watkins MA (1988) Facial hair and respirator fit: a review of the literature. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 49:199–204
Strindberg L, Johansson L, Carlsson A, Ljungqvist E, Åstrand I (1974) Physiological strain at increased respiratory resistance due to respirator with filter (in Swedish) Arbete och Hälsa 1974:5:1–28
Tossavainen A (1978) Styrene use and occupational exposure in the plastics industry. Scand J Work Environ Health 4 (Suppl 2):7–13
Vainio H, Hietanen E, Belvedere G (1984) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of styrene. In: Bridges JW, Chasseaud LF (eds) Progress in drug metabolism, vol 8. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 203–239
Wigaeus E, Löf A, Bjurström R, Byfält Nordqvist M (1983) Exposure to toluene. Uptake, distribution, metabolism and elimination in man. Scand J Work Environ Health 9:479–488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löf, A., Brohede, C., Gullstrand, E. et al. The effectiveness of respirators measured during styrene exposure in a plastic boat factory. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 65, 29–34 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586055
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586055