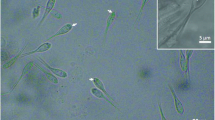
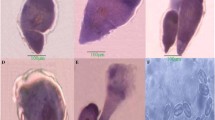
Abstract
The coccidian from the black beetle, Heteronychus arator (Fabricius), in New Zealand was identified as Adelina tenebrionis Sautet 1930. Its development occurs in the fat body of the host. Merogony produces bundles of 8–19 vermiform merozoites, which range in length from 12.0 to 24.1 Μm. Spherical macrogametocytes and small, vermiform microgametocytes fuse to form a zygote. Sporogony produces an oocyst 29.2–45.0 Μm in diameter, containing 3–13 sporocysts, 12.3–14.0 Μm in diameter. The life cycle takes about 46 days in an alternative host, Planotortrix excessana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), at 22‡ C. Electron micrographs of merozoites and gametocytes are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald RD (1976) The effect of pathogens on two populations of Heteronychus arator (F.) (Coleptera: Scarabaeidae). MS Thesis, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Archibald RD, Longworth JF, King PD, Mercer CF (1975) The effect of two pathogens on a black beetle population in kikuyu pasture. Proc N Z Weed Pest Control Conf 28:200–204
Bhatia ML (1937) On Adelina tribolii, a coccidian parasite of Tribolium ferrugineum F. Parasitology 29:239–246
King PD, Mercer CF (1979) Effect of Adelina sp. (Protozoa: Coccidia) on Heteronychus arator fecundity and populations (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Proceedings of the 2nd Australasian Conference on Grassland Invertebrate Ecology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, pp 200–202
King PD, Meekings JS, Phillip KC (1985) A protozoan pathogen of black beetle. Proceedings of the 4th Australasian Conference on Grassland Invertebrate Ecology, Christchurch, New Zealand, pp 201–209
Léger L (1900) Sur la présence d'une Coccidie coelomique chez Olocrates abbreviatus Ol. Arch Zool Exp Gen 8:i-iii
Léger L (1904) Sporozoaires parasites de l'Embia solieri Rambur. Arch Protistenkd 3:358
Longworth JF, Archibald RD (1975) A virus of black beetle, Heteronychus arator (F.) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). N Z J Zool 2:233–236
Malone LA, Wigley PJ (1987) A practical method for rearing Argentine stem weevil, Listronotus bonariensis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in the laboratory. N Z Entomol 11 (in press)
Moroff T (1907) Untersuchungen über Coccidien: I. Adelea zonula n. sp. Arch Protistenkd 8:17–51
Pérez C (1899) Sur une coccidie nouvelle, Adelea mesnili n. sp., parasite coelomique d'un Lépidoptère. C R Soc Biol (Paris) 51:694–696
Purrini K (1984) Two new coccidian parasites of the genus Adelina (Adeleidae, Coccidia) parasitizing oribatid mite Nothrus silvestris (Oribatei, Acarina) and springtail Neanura muscorum (Collembola, Apterygota). Arch Protistenkd 128:99–107
Rioux JA, Léger N, Manier JF, Croset H (1972) Adelina sp., parasite de phlebotomes. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 47:347–350
Sautet J (1930) A propos d'Adelina tenebrionis, coccidie coelomique de Tenebrio molitor. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 8:582–589
Schneider A (1875) Contribution à l'histoire des grÊgarines des invertebrés de Paris et de Roscoff. Arch Zool Exp Gen 4:493–599
Schulte E (1971) Cytochemische Untersuchungen an den Feinstrukturen von Klossia helicina (Coccidia, Adeleidea) I. Morphologie und Kulturhaltung von Klossia helicina. Z Parasitenkd 36:140–157
Tuzet O (1970) Recherches ultrastructurales sur les mérozoÏtes et les gamontes de la coccidie Adelina dimidiata Schneider, parasite du myriapode chilopode Scolopendra cingutata Latreille. Natur Can (Ottawa) 97:369–385
Tuzet O, Vago C, Ormieres R, Robert P (1965) Adelina melolonthae n. sp., coccidie parasite des larves de Melolontha melolontha. Arch Zool Exp Gen 106:513–521
Weiser J, Beard RL (1959) Adelina sericesthis n. sp., a new coccidian parasite of scarabaeid larvae. J Insect Pathol 1:99–106
Wigley PJ, Malone LA, Dhana S (1986) Screening insect pathogens for pest control. Proc N Z Weed Pest Control Conf 39:126–129
Yarwood EA (1937) The life cycle of Adelina cryptocerci sp. nov., a coccidian parasite of the roach Cryptocercus punctulatus. Parasitology 29:370–390
Zizka Z (1969) The fine structure of the macrogametocytes of Adelina tribolii Bhatia, 1937 (Eucoccidia, Telosporea) from the fat body of the beetle Tribolium castaneum Hbst. J Protozool 16:111–120
Zizka Z (1985) Ultrastructure of the sporozoite and the sporocyst wall of the coccidian species Adelina tribolii Bhatia, 1937 within the course of an autoinfection. Arch Protistenkd 129:119–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malone, L.A., Dhana, S. Life cycle and ultrastructure of Adelina tenebrionis (Sporozoea: Adeleidae) from Heteronychus arator (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Parasitol Res 74, 201–207 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539566
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539566