Abstract
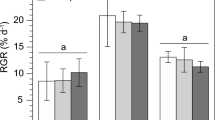
The growth rate and maximum yield of Skeletonema costatum (Grev.) Cleve in batch culture were inhibited by dissolved lead at concentrations of 0.05 to 10.0 μg Pb l-1. Growth rate, maximum yield, and respiration cell-1 decreased and photosynthesis cell-1 and cell volume increased in response to increased lead concentration in the medium. At 0.1 and 1.0 μg Pb l-1, the chlorophyll a:carbon and protein:carbon ratios did not significantly differ from the control and the increased cellular chlorophyll a, carbon and protein observed at these concentrations reflect an increased cell volume. However, at 10.0 μg Pb l-1, associated with an increase in cell volume, the chlorophyll a:carbon ratio was significantly lower and the protein:carbon ratio was significantly higher than in the control, reflecting a changed cellular chemical composition. The rates of cell division and dark respiration decreased relative to photosynthesis and to carbon and protein production, resulting in an alteration of the cellular chemical composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abdullah, M.J., L.G. Royle and A.W. Morris: Heavy metal concentrations in coastal waters. Nature, Lond. 235, 158–160 (1972)
Antia, N.J., C.D. McAllister, T.R. Parsons, K. Stephens and J.D.H. Strickland: Further measurements of primary production using a large-volume plastic sphere. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8, 166–182 (1961)
Barber, R.I.: Organic ligands and phytoplankton growth in nutrient-rich seawater. In: Trace metals and metal-organic interactions in natural waters, pp 311–338. Ed. by P.C. Singer. Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Science Publishers 1973
Bentley-Mowat, J.A. and S.M. Reid: Survival of four marine phytoplankton in high concentrations of heavy metals, and uptake of copper. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 26, 249–264 (1977)
Berland, B.R., D.J. Bonin, O.J. Guérin-Ancey, V.I. Kapkov et D.P. Arlhac: Action de métaux lourds à des doses sublétales sur les charactéristiques de la crossiance chez la diatomée Skeletonema costatum. Mar. Biol. 42, 17–30 (1977)
Black, W.A.P. and R.L. Mitchell: Trace elements in the common brown algae and in seawater. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 30, 575–584 (1952)
Bowen, H.J.M.: Trace elements in biochemistry, 241 pp. New York: Academic Press 1966
Brewer, P.G.: Minor elements in seawater. In: Chemical oceanography, 2nd ed. Vol. 1. pp 415–496. Ed. by J.P. Riley and G. Skirrow. New York: Academic Press 1975
Bryan, G.W. and J.G. Hummerstone: Brown seaweeds as an indicator of heavy metals in estuaries in South-West England. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 53, 145–166 (1973)
Chow, T.J.: Lead accumulation in roadside soil and grass. Nature, Lond. 225, 295–296 (1970)
Conover, S.A.M.: Oceanography of Long Island Sound. 1952–1954. IV. Phytoplankton. Bull. Bingham oceanogr. Coll. 15, 62–112 (1956)
Davey, E.W., M.J. Morgan and S.J. Erickson: A biological measurement of the copper complexation capacity of seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 993–997 (1973)
Davies, A.G.: The growth kinetics of Isochrysis galbana in cultures containing sublethal concentrations of mercuric chloride. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 54, 157–169 (1974)
—: An assessment of the basis of mercury tolerance in Dunaliella tertiolecta. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 56, 39–57 (1976)
Dayton, L. and R.L. Lewin: The effects of lead on algae. III. Effect of lead on population growth curves in two-membered cultures of phytoplankton. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Suppl.) 49, 25–36 (1975)
Eisler, R. and M. Wapner: Second annotated bibliography on biological effects of metals in aquatic environments, 400 pp. Narragansett, Rhode Island: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development 1975
Erickson, S.J.: Toxicity of copper to Thalassiosira pseudonana in unenriched sea water. J. Phycol. 8, 318–323 (1972)
Fogg, G.E. and P.F. Westlake: The importance of extracellular products of algae in fresh water. Verh. int. Verein. theor. angew. Limnol. 12, 319–323 (1955)
Goyer, R.A., A. Krall and P. Kimball: The renal tubule in lead poisoning. I. Mitochondrial swelling and aminoaciduria. Lab. Invest. 19, 78–83 (1968)
Guillard, R.R.L. and J.H. Ryther: Studies of marine plankton diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervaces (Cleve.) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239 (1962)
Hammett, F.S.: Studies in the biology of metals. III. The localization of lead within the cells of the growing root. Protoplasma 5, 135–141 (1929a)
—: Studies in the biology of metals. IV. The influence of lead on mitosis and cell size in the growing root. Protoplasma 5, 535–542 (1929b)
Hellebust, J.A.: Excretions of some organic compounds by marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 10, 192–206 (1965)
Hessler, A.: The effects of lead on algae. I. Effects of Pb on viability and motility of Platymonas subcordiformis. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 3, 371–386 (1974)
Jensen, A., B. Rystad and S. Melson: Heavy metal tolerance of marine phytoplankton. I. The tolerance of three algal species in coastal sea water. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 15, 145–157 (1974)
Ketchum, B.H.: Relationship between circulation and planktonic populations in estuaries. Ecology 35, 191–200 (1954)
Knauer, G.A. and J.H. Martin: Seasonal variations of cadmium, copper, manganese, lead and zinc in water and phytoplankton in Monterey Bay, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 597–604 (1973)
Koeppe, D.E. and R.J. Miller: Lead effects on corn mitochondrial respiration. Science, N.Y. 167, p. 1378 (1970)
Levan, A.: Cytological reactions induced by inorganic salt solution. Nature, Lond. 156, 751–752 (1945)
Lowry, O.H., N.J. Rosenbrough, A.L. Farr and R.L. Randall: Protein measurements with folinphenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Lunan, K.T., T.A. Jorgenson and G.M. Goldstein: Lead and cadmium inhibition of DNA biosynthesis. In: International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment. Abstract, pp B61-B63. Toronto: Institute for Environmental Studies, University of Toronto 1975
Malanchuk, J.L. and G.K. Gruendling: Toxicity of lead nitrate to algae. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 2, 181–190 (1973)
Malone, C., D.E. Koeppe and R.J. Miller: Localization of lead accumulated by corn plants. Pl. Physiol., Lancaster 53, 388–394 (1974)
Monahan, T.H.: Lead inhibition of chlorophycean microalgae. J. Phycol. 12, 358–362 (1976)
Overnell, J.: The effect of heavy metals on photosynthesis and loss of cell potassium in two species of marine algae, Dunaliella tertiolecta and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mar. Biol. 29, 99–103 (1975)
Patterson, C.C.: Lead. In: Impingement of man on the oceans, pp 245–258. Ed. by D.W. Hood. New York: Wiley-Interscience 1971
—: Lead in seawater. Science, N.Y. 183, 553–554 (1974)
Piotrowicz, S.R., B.J. Ray, G.L. Hoffman and R.A. Duce: Trace metal enrichment of the sea surface microlayer. J. geophys. Res. 77, 5243–5254 (1972)
Prakash, A. and M.A. Rashid: Influence of humic substances on the growth of marine phytoplankton dinoflagellates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 13, 598–603 (1968)
Preston, A., D.F. Jeffries, S.W. Button, B.R. Harvey and A.K. Steele: British Isles coastal waters; concentrations of heavy metals in seawater, suspended matter and biological indicators. A pilot study. Envir. Pollut. 3, 69–82 (1972)
Riley, J.P. and I. Roth: The distribution of trace elements in some species of phytoplankton grown in culture. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 51, 63–72 (1971)
Schultz-Baldes, M. and R.A. Lewin: Lead uptake in two marine phytoplankton organisms. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 150, 118–127 (1976)
Sibley, T.H. and J.J. Morgan: Trace metal speciation in aquatic environments. In: International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment, Abstract, p. C-133, Toronto: Institute for Environmental Studies, University of Toronto 1975
Siegel, A.: Metal-organic interactions in the marine environment. In: Organic compounds in the aquatic environment, pp 265–295. Ed. by S.J. Faust and J.W. Hunter. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. 1971
Simola, L.K.: The effect of lead, cadmium, arsenate and fluoride ions on the growth and fine structure of Sphagnum nemoreum in aseptic culture. Can. J. Bot. 55, 426–436 (1977)
Skaar, H., E. Ophus and B.M. Gulvag: Lead accumulation within nuclei of moss leaf cells. Nature, Lond. 241, 215–216 (1973)
Smayda, T.J.: Phytoplankton studies in lower Narragansett Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2, 342–359 (1957)
Sokal, R.R. and J.F. Rohlf: Introduction to biostatistics, 368 pp. San Francisco: Freeman Press 1973
Spencer, C.P.: The chemistry of ethylenediamene tetra-acetic acid in sea water. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 37, 127–144 (1958)
Steeman Nielsen, E. and S. Wium-Andersen: Copper ions as poison in the sea and in freshwater. Mar. Biol. 6, 93–97 (1970)
——: The influence of Cu on photosynthesis and growth in diatoms. Physiologia Pl. 24, 480–484 (1971)
Stewart, J.: Relative sensitivity to lead of a naked green flagellate, Dunaliella tertiolecta. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 8, 243–247 (1977)
Strickland, J.D.H. and T.R. Parsons: A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 167, 1–311 (1968)
Sunda, W. and R.R.L. Guillard: The relationship between cupric ion activity and the toxicity of copper to phytoplankton. J. mar. Res. 34, 511–529 (1976)
Tatsumoto, M. and C. Patterson: Concentrations of common lead in some Atlantic and Mediterranean waters. Nature, Lond. 199, 350–352 (1963)
Thomas, W.H., O. Holm-Hansen, D.L.R. Siebert, F. Azam, R. Hodson and M. Takahashi: Effects of copper on phytoplankton standing crop and productivity: controlled ecosystem pollution experiment. Bull. mar. Sci. 27, 34–43 (1977)
— and D.L.R. Siebert: Effects of copper on the dominance and diversity of algae: controlled ecosystem pollution experiment. Bull. mar. Sci. 27, 23–33 (1977)
Tofflemire, T.J. and L.J. Hetling: Pollution sources in the Lower Hudson River. In: Proceedings of the Second Symposium on Hudson River Ecology, pp 78–146. Ed. by G.P. Howells and G.V. Lauer. Sterling Forest New York: Hudson River Environmental Society Inc. 1969. (Bull. N.Y. St. Dep. envirl Conserv.)
Vallee, B.L. and D.D. Ulmer: Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium and lead. A. Rev. Biochem. 41, 91–128 (1972)
Whitton, B.A.: Toxicity of heavy metals to freshwater algae: a review. Phykos 9, 116–125 (1970)
Woolery, M.L. and R.A. Lewin: The effects of lead on algae. IV. Effects of Pb on respiration and photosynthesis of Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae). Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 6, 25–51 (1976)
Zirino, A. and S. Yamamoto: A pH dependent model for the chemical speciation of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 661–671 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M.R. Tripp, Newark
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivkin, R.B. Effects of lead on growth of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum . Mar. Biol. 50, 239–247 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394205
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394205