Summary
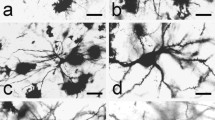
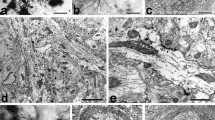
There have been few Golgi studies dealing with the cytoarchitecture of the supraoptic nucleus (SON). This is due in part to resistance of supraoptic neurons to impregnation by Golgi methods. In this study, the structure of the SON was examined in normal S/D rats by using both Nissl and Golgi-silver methods. The purpose was to correlate shape, size and location of neurons within the SON as revealed by these two techniques. On the basis of size, neurons of the SON can be divided into 3 populations: <200 μm2, (9%); 100–200 μm2, (64%); and <100 μm2, (27%). The larger neurons are located predominantly at mid-nuclear levels; the smaller at rostral and caudal levels of the nucleus. The perikarya of most SON neurons (64%) are only slightly elliptical in cross-section (L/W≤2). The large neurons, however, tend to be more spherical whereas the smaller neurons are more elongated (L/W≥3). In Golgi preparations, a variety of randomly distributed bipolar and multipolar neurons were identified. One form of bipolar neuron had a large spherical or oval cell body that was intimately associated with blood vessels. Its thick, varicose dendrites usually lacked spines and were not extensively branched. A second form of bipolar neuron was distinguished by its smaller more fusiform cell body and lengthy dendrites which were often spinous and more extensively branched. Axons, when present emerged from the cell body or a proximal dendrite and were uniformly thin except for fusiform swellings along their length. Among multipolar neurons, the following variants were distinguished: spherical and polygonal neurons of various sizes with 3–5 dendrites and small triangular neurons with dendrites arising from each of the poles. The results of this study demonstrate the heterogeneity of the rat SON and of its neuronal components, some of which appear suited to function in a nonendocrine capacity, possibly as interneurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong WE, Scholer J, McNeill TH (1982) Immunocytochemical, Golgi and electron microscopic characterization of putative dendrites in the ventral glial lamina of the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience 7(3):679–694
Bicknell HR, Beal JA (1981) Neurons with dual axons in the substantia gelatinosa (SG) of the adult cat lumbosacral spinal cord. Experientia 37:1198–1199
Dierickx K, Vandesande F (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of vasopressinergic and the oxytocinergic neurons in the human hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res 184:15–27
Dyball REJ, Kemplay SK (1982) Dendritic trees of neurons in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience 7:223–230
Enestrom S (1967) Nucleus supraopticus. A morphological and experimental study in the rat. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 186 (Suppl):1–99
Felten DL, Cashner KA (1979) Cytoarchitecture of the supraoptic nucleus: A Golgi study. Neuroendocrinology 29:221–230
Fox C, Zabors J (1960) Neurons of the supraoptic nucleus in Golgi preparations. Anat Rec 136:335–336
Gurdjian ES (1927) The diencephalon of the albino rat. Studies on the brain of the rat. J Comp Neurol 43:1–144
Hayward JN (1974) Physiological and morphological identification of hypothalamic magnocellular neuroendocrine cells in goldfish preoptic nucleus. J Physiol 239:103–124
Hayward JN, Vincent JD (1970) Activity of single cells in the osmoreceptor-supraoptic nuclear complex in the hypothalamus of the waking rhesus monkey. Brain Res 23:105–108
Ifft JO, McCarthy L (1974) Somatic spines in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus
Krieg WS (1932) The hypothalamus of the albino rat. J Comp Neurol 55:10–44
Lefranc GM (1966) Etude neurohistologique des noyaux supraoptique et paraventriculaire chez le cobaye et le chat par la technique de triple impregnation de Golgi. CR Acad Sci (Paris) 263:976–979
Leontovich TA (1969/1970) The neurons of the magnocellular neurosecretory nuclei of the dog's hypothalamus: A Golgi study. J Hirnforsch 11:499–517
Leranth Cs, Zaborszky L, Marton J, Palkovits M (1975) Quantitative studies on the supraoptic nucleus in the rat. I. Synaptic organization. Exp Brain Res 22:509–523
LuQui I, Fox CA (1976) The supraoptic nucleus and the supraopticohypophyseal tract in the monkey (Macaca mulatta). J Comp Neurol 168:7–40
McNeill TH, Sladek JR (1980) Simultaneous monoamine histofluorescence and neuropeptide immunocytochemistry: II. Correlative distribution of catecholamine varicosities and magnocellular neurosecretory neurons in the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. J Comp Neurol 193:1023–1033
Millhouse OE (1979) A Golgi anatomy of the rodent hypothalamus. In: Morgane PJ, Panksepp J (eds) Handbook of the hypothalamus, Vol. I. Anatomy of the hypothalamus. Marcel Dekker Inc. New York, p. 221–265
Montemurro DG (1966) Light microscopic observations on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland of the rat fixed in osmium tetroxide. J Endocrinol 35:271–279
Morton A (1969) A quantitative analysis of the normal neuron population of the hypothalamic magnocellular nuclei in man and of their projections to the neurohypophysis. J Comp Neurol 136:143–158
Peterson RP (1966) Magnocellular neurosecretory centers in the rat hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 128:181–185
Polenov AL, Senchik JI (1966) Synapses on neurosecretory cells of the supra-optic nucleus in white mice. Nature 211:1423–1424
Priymak EKh, Hajos F (1970) Synapses on the supraoptic neurosecretory neurons of the rat: An electron microscopic study. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung 18:55–61
Rhodes CH, Morrell JI, Pfaff DW (1981) Immunohistochemical analysis of magnocellular elements in rat hypothalamus: Distribution and numbers of cells containing neurophysin, oxytocin and vasopressin. J Comp Neurol 198:45–64
Silver J (1977) Abnormal development of the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in a strain of genetically anophthalmic mice. J Comp Neurol 176:589–606
Sokol HW, Zimmerman EA, Sawyer WH, Robinson AG (1976) The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial system of the rat: Localization and quantitation of neurophysin by light microscopic immunocytochemistry in normal rats and in brattleboro rats deficient in vasopressin and a neurophysin. Endocrinology 98:1176–1188
Swaab DF, Nijveldt F, Pool CW (1975) Distribution of oxytocin and vasopressin in the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus. J Endocrinol 67:461–462
Szentágothai J, Flerko B, Mess B, Halasz B (1962) Hypothalamic control of the anterior pituitary. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, p. 34–81
Vandesande F, Dierickx K (1975) Identification of vasopressin-producing and of the oxytocin-producing neurons in the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory system of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 164:153–162
Zaborszky L, Leranth C, Makara GB, Palkovits M (1975) Quantitative studies on the supraoptic nucleus in the rat. II Afferent fiber connections. Exp Brain Res 22:525–540
Zambrano D, De Robertis E (1966) The secretory cycle of supraoptic neurons in the rat. A structural-functional correlation. Z Zellforsch 73:414–431
Zambrano D, Mordoh J (1966) Neurosecretory activity in supraoptic nucleus of normal rats. Z Zellforsch 73:405–413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by grants from the Medical Research Council of Canada, the St. Boniface General Hospital and Mrs. James A. Richardson Research Foundations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruni, J.E., Perumal, P.M. Cytoarchitecture of the rat's supraoptic nucleus. Anat Embryol 170, 129–138 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318997
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318997