Summary
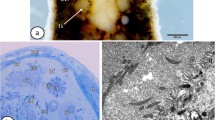
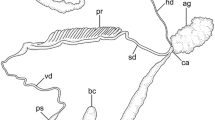
In Drosophila melanogaster, the cyst cell that surrounds the head region of sperm bundle becomes spheroidal or ellipsoidal and is trapped by the terminal epithelium of the testicular wall during the synchronous coiling of sperm. Extensions of this cyst cell are projected caudally into the interspaces between sperm heads probably to anchor the heads. Coiling of sperm tails is initiated at the head region and proceeds by the progressive retraction of the linear portion from the apical testicular region into the coiled portion at the base. The addition of one turn of coil is accompanied by one full rotation of the sperm bundle. When coiled, normal tails are tightly packed into a hexagonal lattice, and minute tubular structures of about 150 Å in diameter occupy the space between them. Sperm with abnormal tails are separated from those with normal ones and isolated into a separate part of the cyst lumen. Acid phosphatase is involved in the dissolution of the minute tubules for the liberation of sperm from the cyst. Sperm are released leaving the major portion of the cyst cells intact. This portion contains degenerating abnormal tails and the waste products of the individualization process. This detritus is ingested by the terminal epithelium and eventually degenerates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius, B. A.: Thoughts on comparative spermatology. In: Comparative spermatology (B. Baccetti, ed.). New York: Academic Press 1970.
Amann, R., Almonist, J.: Reproductive capacity of dairy bulls. VI. Effect of unilateral vasectomy and ejaculation frequency on sperm reserves; aspects of epididymal physiology. J. Reprod. Fertil. 3, 260–268 (1962).
Anderson, W. A.: Cytodifferentiation of spermatozoa in Drosophila melanogaster: the effect of elevated temperature on spermiogenesis. Molec. gen. Genet. 99, 257–273 (1967).
Anderson, W. A., Personne, P.: The localization of glycogen in the spermatozoa of various invertebrate and vertebrate species. J. Cell Biol. 44, 29–51 (1970).
Bairati, A.: Struttura ed ultrastruttura dell'apparato genitale maschile di Drosophila melanogaster. Meig. I. Il testicolo. Z. Zellforsch. 76, 56–99 (1967).
Blandau, R. J., Rummery, R. E.: The relationship of swimming movements of epididymal spermatozoa to their fertilizing capacity. Fertil. and Steril. 15, 571–579 (1964).
Burgos, M. H., Fawcett, D. W.: Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. I. Differentiation of the spermatids in the cat (Felis domestica). J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 287–300 (1955).
Essner, E., Novikoff, A. B.: Cytological studies on two functional hepatomas. Interrelations of endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 15, 289–312 (1967).
Fawcett, D. W., Ito, S., Slautterback, D.: The occurrence of intercellular bridges in groups of cells exhibiting synchronous differentiation. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 5, 453–460 (1959).
Fawcett, D. W., Hollenberg, R. D.: Changes in the acrosome of guinea pig spermatozoa during passage through the epididymis. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 276–292 (1963).
Fawcett, D. W., Phillips, D. M.: Observations on the release of spermatozoa and on changes in the head during passage through the epididymis. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 6, 405–418 (1969).
Franzén, Å.: Phylogenic aspects of the morphology of spermatozoa and spermiogenesis. In: Comparative spermatology (B. Baccetti, ed.). New York; Academic Press 1970.
Kiefer, B. I.: Ultrastructural abnormalities in developing sperm of X/0 Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 54, 1441–1452 (1966).
Leblond, C. P., Clermont, Y.: Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 55, 548–573 (1952).
Lindsley, D. L., Grell, E. H.: Genetic variations of Drosophila melanogaster. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Publ. No 627, Washington, D. C. (1968).
Loewenstein, W. R., Kanno, Y.: Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction. I. Modification of surface membrane permeability. J. Cell Biol. 22, 565–586 (1964).
Manton, I.: Plant spermatozoids. In: Comparative spermatology (B. Baccetti, ed.). New York: Academic Press 1970.
Miller, A.: The internal anatomy and histology of the imago of Drosophila melanogaster. In: Biology of Drosophila (M. Demerec, ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons 1950.
Moses, M. J., Wilson, M. H.: Spermiogenesis in an iceryine coccid, Steatococcus tuberculatus Morrison. Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 373–429 (1970).
Nicoletti, B.: Il controllo genetico della meiosi. Atti Assoc. Genet. Ital. 13, 1–71 (1968).
Perotti, M. E.: Ultrastructure of the mature sperm of Drosophila melanogaster Meig. J. Submicr. Cytol. 1, 171–196 (1970).
Smith, R. E., Farquhar, M. G.: Lysosome function in the regulation of the secretory process of the anterior pituitary gland. J. Cell Biol. 31, 319–348 (1966).
Tates, A. D.: Cytodifferentiation during spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: An electron microscope study. S-Gravenhage: Drukkerij J. H. Pasmans 1971.
Tokuyasu, K. T., Peacock, W. J., Hardy, R. W.: Dynamics of Spermiogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Individualization Process. Z. Zellforsch. 124, 479–506 (1972).
Vilar, O., Perez del Cerro, M. I., Mancini, R. E.: The Sertoli cell as a “bridge cell” between the basal membrane and the germinal cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 158–161 (1962).
Warner, F. D.: New observations on flagellar fine structure. J. Cell Biol. 47, 159–182 (1970).
Warner, F. D.: Spermatid differentiation in the blowfly Sarcophaga buallta with particular reference to flagellar morphogenesis. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 35, 210–232 (1971).
Wiener, J., Spiro, D., Loewenstein, W. R.: Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction. II. Surface structure. J. Cell Biol. 22, 587–598 (1964).
Young, W. C.: A study of the function of the epididymis. I. Is the attainment of full spermatozoan maturity attributable to some specific action of the epididymal secretion? J. Morph. 47, 479–495 (1929).
Young, W. C.: A study of the function of the epididymis. III. Functional changes undergone by spermatozoa during their passage through the epididymis and vas deferens in the guinea pig. J. exp. Biol. 8, 151–162 (1931).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (USPHS-HD 03015 and GM-15971) and a contract from the Atomic Energy Commission, AT(04-3)-34, P.A. 150.
Graduate training grant USPHS GM-00702.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokuyasu, K.T., Peacock, W.J. & Hardy, R.W. Dynamics of spermiogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster . Z.Zellforsch 127, 492–525 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306868
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306868