Abstract
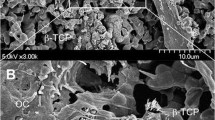
This study was designed to evaluate the effects of specific and potent cathepsin inhibitors on osteoclastic resorptive functions in vitro by means of a novel ultrastructural assay system. Mouse bone marrow cell-derived osteoclasts were suspended on dentine slices and cultured for 48 hours in the presence of either E-64 (a generalized cysteine proteinase inhibitor) or Z-Phe-Phe-CHN2 (a selective cathepsin L inhibitor). After the removal of cultured osteoclasts, co-cultured dentine slices were examined using electron microscopy: backscattered (BSEM), scanning (SEM), and atomic force (AFM). In morphometric analyses of BSEM images, there were no significant differences in the areas of demineralized dentine surfaces between control and inhibitor-treated groups, suggesting that cathepsin inhibitors had no effect on dentine demineralization by cultured osteoclasts. However, in SEM and AFM observations, both inhibitors remarkably reduced to the same extent, the formation of deep resorption lacunae on dentine slices that had resulted from degradation of matrix collagen. In addition, Z-Phe-Phe-CHN2 treatment produced deeper, ring-like grooves with little collagen exposure in shallow resorption lacunae. These results strongly suggest that (1) cathepsins released by osteoclasts are involved in the formation of deep resorption lacunae, and (2) cathepsin L plays a key role in bone resorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delaisse JM, Vaes G (1992) Mechanism of mineral solubilization and matrix degradation in osteoclastic bone resorption. In: Rifkin BR, Gay CV (eds) Biology and physiology of the osteoclast. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 289–314
Blair HC, Teitelbaum SL, Ghiselli R, Gluck S (1989) Osteoclastic bone resorption by a polarized vacuolar proton pump. Science 245:855–857
Vaananen HK, Karhukorpi EK, Sundquist K, Wallmark B, Roininen I, Hentunen T, Tuukkanen J, Lakkakorpi P (1990) Evidence for the presence of a proton pump of the vacuolar H+-ATPase type in the ruffled borders of osteoclasts. J Cell Biol 111:1305–1311
Sasaki T (1994) Recent advances in ultrastructural assessment of osteoclastic resorptive functions. Microsc Res Techn (in press)
Sasaki T, Hong MH, Udagawa N, Moriyama Y (1994) Expression of vacuolar H+-ATPase in osteoclasts and its role in resorption. Cell Tissue Res 278:265–271
Barrett AJ (1973) Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J 131:809–822
Burleigh MC, Barrett AJ, Lazarus GS (1974) Cathepsin B1: a lysosomal enzyme that degrades matrix collagen. Biochem J 137:387–398
Mott JS, Reckless AD, Poole AR (1984) Extracellular presence of the lysosomal proteinase cathepsin B in rheumatoid synovium and its activity at neutral pH. Arthritis Rheum 27:509–515
Delaisse JM, Eeckhout Y, Vaes G (1984) In vivo and in vitro evidence for the involvement of cysteine-proteinase in bone resorption. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 125:441–447
Delaisse JM, Boyde A, Maconnachie E, Ali NN, Sear CHJ, Eeckhout Y, Vaes G, Jones SJ (1987) The effects of inhibitors of cysteine-proteinases and collagenase on the resorptive activity of isolated osteoclasts. Bone 8:305–313
Jilka RL, Hamilton JW (1985) Evidence for two pathways for stimulation of collagenolysis in bone. Calcif Tissue Int 37:300–306
Rifkin BR, Vernillo AT, Kleckner AP, Auszmann JM, Rosenberg LR, Zimmerman M (1991) Cathepsin B and L activities in isolated osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 179:63–69
Everts V, Delaisse JM, Korper W, Niehof A, Vaes G, Beersten W (1992) Degradation of collagen in the bone-resorbing compartment underlying the osteoclast involves both cysteine-proteinase and matrix metalloproteinases. J Cell Physiol 150: 221–231
Goto T, Tsukuba T, Kiyoshima T, Nishimura Y, Kato K, Yamamoto K, Tanaka T (1993) Immunocytochemical localization of cathepsins B, D and L in the rat osteoclast. Histochemistry 99:411–414
Sasaki T, Ueno-Matsuda E (1993) Cysteine-proteinase localization in osteoclasts: an immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 271:177–179
Sasaki T, Debari K, Hasemi M (1993) Measurement of Howship's resorption lacunae by a scanning probe microscope system. J Electron Microsc 42:356–359
Tamura T, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, Sasaki T, Udagawa N, Tanaka S, Suda T (1993) New resorption assay with mouse osteoclast-like multinucleated cells formed in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 8:953–960
Akatsu T, Tamura T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Tanaka S, Sasaki T, Yamaguchi A, Nagata N, Suda T (1992) Preparation and characterization of a mouse osteoclast-like multinucleated cell population. J Bone Miner Res 7:1297–1306
Delaisse JM, Eeckhout Y, Neff L, Francois-Gillet Ch, Henriet P, Su Y, Vaes G, Baron R (1993) (Pro)collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1) is present in rodent osteoclasts and in the underlying bone-resorbing compartment. J Cell Sci 106:1071–1082
Eeckhout Y, Vaes G (1977) Further studies on the activation of procollagenase, the latent precursor of bone collagenases: effects of lysosomal cathepsin B, plasmin and kallinkrein, and spontaneous activation. Biochem J 166:21–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debari, K., Sasaki, T., Udagawa, N. et al. An ultrastructural evaluation of the effects of cysteine-proteinase inhibitors on osteoclastic resorptive functions. Calcif Tissue Int 56, 566–570 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298591
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298591