Abstract
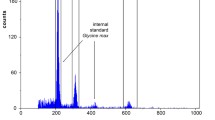
A wild-type (WT) strain of the moss Physcomitrella patens (Hedw.) B.S.G., two mutants derived from it (PC22 and P24), and a somatic hybrid, PC22(+)P24, were analysed. Staining of metaphases revealed 54±2 chromosomes in the somatic hybrid and 27 chromosomes in the wild type and the two mutants. Using flow cytometry (FCM), DNA contents were calculated to be 0.6 pg (WT, PC22), 1.2 pg (P24), and 1.6 pg (PC22(+)P24) per nucleus, respectively. Southern hybridization provided evidence for at least one family of highly repetitive DNA and, furthermore, revealed different amounts of repetitive DNA in the four genotypes. However, these sequences cannot account for the 100% increase in the nuclear DNA amount in mutant P24, relative to wild type. In FCM analyses every moss geno-type generated just one single peak of fluorescence, indicating an arrest in the cell cycle during the daytime. Thermal denaturation of wild-type DNA revealed a G+C content of 34.6% for total DNA and 38.6% for plastid DNA. A cDNA library of 1.2 × 106 independent clones was established, from which sequences homologous to cab and rbcS, respectively, were isolated. These genes show significant homologies to those of higher plants, and, likewise, comprise multigene families. No restriction fragment length polymorphisms could be detected between the four moss genotypes using these cDNA probes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel WO, Knebel W, Koop H-U, Marienfeld JR, Quader H, Reski R, Schnepf E, Spörlein B (1989) A cytokinin-sensitive mutant of the moss, Physcomitrella patens, defective in chloroplast division. Protoplasma 152:1–13
Allen CE (1917) A chromosome difference correlated with sex differences in Sphaerocarpos. Science 46:466–467
Auerbach C (1976) Mutation research. Chapman and Hall, London
Barthelmess A (1940) Mutationsversuche mit einem Laubmoos Physcomitrium piriforme. II. Mophologische und physiologische Analyse der univalenten und bivalenten Protonemen einiger Mutanten. Z Vererbl 79:153–170
Belling J (1926) The iron-acetocarmine method of fixing and staining chromosomes. Biol Bull 50:160–162
Bennett MD, Smith JB, Heslop-Harrison JS (1982) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Proc R Soc Lond B 216:179–199
Bopp M (1981) Entwicklungsphysiologie der Moose. In: SchultzeMotel W (ed) Advances in Bryology. Cramer, Braunschweig, pp 11–77
Bopp M (1990) Hormones of the moss protonema. In: Chopra RN, Bhatla SC (eds) Bryophyte development: physiology and biochemistry. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 55–77
Bowen WR (1963) The demonstration of mitotic figures in green algae. Proc Iowa Acad Sci 70:138–142
Bryan VS (1957) Cytotaxonomic studies in the Ephemeraceae and Funariaceae. Bryologist 60:103–126
Burgeff H (1943) Genetische Studien an Marchantia. Einführung einer neuen Pflanzenfamilie in die genetische Wissenschaft. Gustav Fischer, Jena
Cashmore AR (1986) Structure and expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2960–2964
Chasan R (1992) Ceratopteris: a model plant for the 90s. Plant Cell 4:113–115
Cove DJ (1983) Genetics of Bryophyta. In: Schuster RM (ed) New manual of Bryology. Hatt Botanical Laboratory, Tokyo, pp 222–231
Cove DJ (1992) Regulation of development in the moss, Physcomitrella patens. In: Russo VEA, Brody S, Cove D, Ottolenghi S (eds) Development. The molecular genetic approach. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest, pp 179–193
Cove DJ, Knight CD (1993) The moss Physcomitrella patens, a model system with potential for the study of plant reproduction. Plant Cell 5:1483–1488
Engel PP (1968) The induction of biochemical and morphological mutants in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Am J Bot 55:438–446
Featherstone DR, Cove DJ, Ashton NW (1990) Genetic analysis by somatic hybridisation of cytokinin overproducing mutants of the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Mol Gen Genet 222:217224
Ganal M, Hemleben V (1986) Comparison of the ribosomal RNA genes in four closely related Curcubitaceae. Plant Syst Evol 154:63–77
Goldberg RB (1988) Plants: novel developmental processes. Science 240:1460–1467
Grimsley NH, Ashton NW, Cove DJ (1977a) The production of somatic hybrids by protoplast fusion in the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Mol Gen Genet 154:97–100
Grimsley NH, Ashton NW, Cove DJ (1977b) Complementation analysis of auxotrophic mutants of the moss, Physcomitrella patens, using protoplast fusion. Mol Gen Genet 155:103–107
Hansen S, Koop H-U, Abel WO (1988) Electrofusion of two selected single moss protoplasts. Mitt Inst Allg Bot Hamburg 22:29–34
Heitz E (1928) Das Heterochromatin der Moose I. Jahrb Wiss Bot 69:782–818
Kasten B, Wehe M, Reski R, Abel WO (1991) trnR-CCG is not unique to the plastid DNA of the liverwort Marchantia: gene identification from the moss Physcomitrella patens. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5074
Kasten B, Wehe M, Kruse K, Reutter K, Abel WO, Reski R (1992) The plastome-encoded zfpA gene of a moss contains procaryotic as well as eucaryotic promoter consensus sequences and its RNA abundance is modulated by cytokinin. Curr Genet 22:327–333
Knapp E (1935) Untersuchungen über die Wirkung von Röntgenstrahlen an dem Lebermoos Sphaerocarpos, mit Hilfe der Tetraden-Analyse. Z Vererbl 70:309–349
Knapp E (1936) Zur Genetik von Sphaerocarpus (Tetradenanalytische Untersuchungen). Berl Dtsch Bot Ges 54:58–69
Knapp E (1937) Crossing over und Chromosomenreduktion. Z Vererbl 73:409–418
Knapp E, Reuss A, Risse O, Schreiber H (1939) Quantitative Analyse der mutationsauslösenden Wirkung monochromatischen UV-Lichtes. Naturwissenschaften 27:307
Kumar A, Cocking EC (1987) Protoplast fusion: a novel approach to organelle genetics in higher plants. Am J Bot 74:1289–1303
de Laat AMM, Göhde W Vogelzang MJDC (1987) Determination of ploidy of single plants and plant populations by flow cytometry. Plant Breeding 99:303–307
Leutwiler LS, Hough-Evans BR, Meyerowitz EM (1984) The DNA of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 194:15–23
Long Z, Wang S-Y, Nelson N (1989) Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of genes coding for the major chlorophyllbinding protein of the moss Physcomitrella patens and the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina. Gene 67:299–312
Marienfeld JR, Reski R, Friese C, Abel WO (1989) Isolation of nuclear, chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA from the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Sci 61:235–244
Marienfeld JR, Reski R, Abel WO (1991) The first analysed archegoniate mitochondrial gene (cox3) exhibits extraordinary features. Curr Genet 20:319–329
Marienfeld JR, Reski R, Abel WO (1992) Chondriom analysis of the moss Physcomitrella patens. Crypt Bot 3:23–26
Marmur JP, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of DNA from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Mejia A, Spangenberg G, Koop HU, Bopp M (1988) Microculture and electrofusion of defined protoplasts of the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Bot Acta 101:166–173
Oda K, Yamato K, Ohta E, Nakamura Y, Takemura M, Nozato N, Akashi K, Kanegae T, Ogura Y, Kohchi T, Ohyama K (1992) Gene organization deduced from the complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha mitochondrial DNA. A primitive form of plant mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol 223:1–7
Oehlkers F, Bopp M (1957) Entwicklungsphysiologische Untersuchungen an Moosmutanten: II. Die Korrelation zwischen Sporogon und Kalyptra bei- Mutanten von Funaria und Physcomitrium. Z Vererbl 88:608–618
Ohyama K, Fukuzawa H, Kohchi T, Shrai H, Sano T, Sano S, Shiri H, Umesono K, Shiki Y, Takeuchi M, Chang Z, Aota S, Inokuchi H, Ozeki H (1986) Chloroplast gene organization deduced from complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA. Nature 322:572–574
Reski R (1994) Plastid genes and chloroplast biogenesis. In: Mok DWS, Mok MC (eds) Cytokinins. Chemistry, activity, and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton Ann Arbor London Tokyo, pp 179–195
Reski R, Abel WO (1985) Induction of budding on chloronemata and caulonemata of the moss, Physcomitrella patens, using isopentenyladenine. Planta 165:354–358
Reski R, Wehe M, Hadeler B, Marienfeld JR, Abel WO (1991) Cytokinin and light quality interact at the molecular level in the chloroplast-mutant PC22 of the moss Physcomitrella. J Plant Physiol 138:236–243
Rother S, Hadeler B, Orsini JM, Abel WO, Reski R (1994) Fate of a mutant macrochloroplast in somatic hybrids. J Plant Physiol 143:72–77
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Schaefer D, Zryd J-P, Knight CD, Cove DJ (1991) Stable transformation of the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Mol Gen Genet 226:418–424
Templaar MJ, Drenth-Diephuis LJ, Saar TAWM, Jakobsen E (1991) Spontaneous and induced loss of chromosomes in slowgrowing somatic hybrid calli of Solanum tuberosum and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Euphytica 65:287–296
Thomas AJ, Sherrat HSA (1956) The isolation of nucleic acid fractions from plant leaves and their purine and pyrimidine composition. Biochem J 62:1–4
Ulrich I, Ulrich W (1991) High-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA in higher plants. Protoplasma 165:212–215
Wang X-H, Lazzeri PA, Lörz H (1992) Chromosomal variation in dividing protoplasts derived from cell suspensions of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 85:181–185
Watts JW, Doonan JH, Cove DJ, King JM (1985) Production of somatic hybrids of moss by electrofusion. Mol Gen Genet 199:349–351
Wettstein F von (1925) Genetische Untersuchungen an Moosen. Bibl Genet 1:1–38
Wettstein F von (1928) Über plasmatische Vererbung und über das Zusammenwirken von Genen und Plasma. Berl Dtsch Bot Ges 46:32–49
Wettstein F von (1932) Genetik. In: Verdoorn F (ed) Manual of bryology. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague, pp 233–273
Wolter FP, Fritz CC, Wilmitzer L, Schell J, Schreier PH (1988) rbcS genes in Solanum tuberosum: conservation of transit peptide and exon shuffling during evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:846–850
Ye F, Gierlich J, Reski R, Marienfeld J, Abel WO (1989) Isoenzyme analysis of cytokinin sensitive mutants of the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Sci 64:203–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
This article is based in part on doctoral studies of M.F. and MW at the University of Hamburg, Faculty of Biology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reski, R., Faust, M., Wang, XH. et al. Genome analysis of the moss Physcomitrella patens (Hedw.) B.S.G.. Molec. Gen. Genet. 244, 352–359 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286686
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286686