Summary
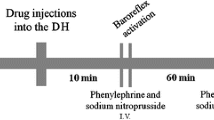
Excitatory amino acid receptors and l-glutamate in the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) may be involved in the regulation of baroreceptor reflexes. To evaluate this hypothesis, we microinjected amino acid antagonists unilaterally into the rat NTS, and examined their effects on cardiovascular responses to electrical stimulation of the aortic nerve and on depressor responses to excitatory amino acid agonists microinjected into the NTS. Male Wistar rats were anesthesized with urethane, paralyzed, and artifically ventilated. Kynurenate (227 ng), an excitatory amino acid antagonist, injected ipsilaterally but not contralaterally into the NTS, markedly inhibited the depressor response to aortic nerve stimulation. l-Glutamate diethylester (GDEE, 3 μg), another excitatory amino acid antagonist, injected ipsilaterally into the NTS, also markedly inhibited both reflex depressor and bradycardic responses. MK-801 (30 ng), an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channel blocker, slightly inhibited the baroreflex responses, while Joro spider toxin JSTX-3 (17 ng), a glutamate receptor antagonist, did not affect them. Kynurenate (227 ng) and GDEE (3 μg) markedly inhibited the depressor response to the NMDA receptor agonist NMDA (0.3 ng), the quisqualate receptor agonist quisqualate (0.1 ng), the kainate receptor agonist kainate (0.1 ng), and l-glutamate (10 ng), microinjected into the NTS, while MK-801 (30 ng) reduced only the depressor response to NMDA (0.3 ng), and JSTX-3 (17 ng) reduced only the depressor response to kainate (0.1 ng). These findings provide evidence for the presence of excitatory amino acid receptors involved in mediating the aortic baroreceptor reflex in the rat NTS. In addition, these observations are consistent with the hypothesis that l-glutamate or a related excitatory amino acid may be the neurotransmitter of baroreceptor information in the NTS. It appears that both NMDA and non-NMDA receptors in the rat NTS are responsible for the mediation of baroreflexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciriello (1983) Brainstem projections of aortic baroreceptor afferent fibers in the rat. Neurosci Lett 36: 37–42
Cotman CW, Iversen LL (1987) Excitatory amino acids in the brain — focus on NMDA receptors. Trends Neurosci 10: 263–265
Cottle MK (1964) Degeneration studies of primary afferents of the IXth and Xth cranial nerves in the cat. J. Comp Neurol 122: 329–345
Dale N, Roberts A (1985) Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol (Lond) 363: 35–59
Foster AC, Fagg CE (1984) Acidic amino acid binding sites in mammalian neuronal membranes: their characteristics and relationship to synaptic receptors. Brain Res Rev 7: 103–164
Furuya S, Ohmori H, Shigemoto T, Sugiyama H (1989) Intracellular calcium mobilization triggered by a glutamate receptor in rat cultured hippocampal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 414: 539–548
Guyenet PG, Filtz TM, Donaldson SR (1987) Role of excitatory amino acids in rat vagal and sympathetic baroreflexes. Brain Res 407: 272–284
Humphrey SJ, McCall RB (1984) Evidence that l-glutamic acid mediates baroreceptor function in the cat. Clin Exp Hypertens [A] 6: 1311–1329
Jackson H, Nemeth EF, Parks TN (1985) Non N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors mediating synaptic transmission in the avian cochlear nucleus: effects of kynurenic acid, dipicolinic acid and streptomycin. Neuroscience 16: 171–180
Kawai N, Niwa A, Abe T (1982) Spider venom contains specific receptor blocker of glutamineric synapses. Brain Res 247: 169–171
Kleinman LI, Radford EP (1964) Ventilation standards for small mammals. J Appl Physiol 19: 360–362
Kubo T, Amano H (1986) Vasopressin-induced pressor responses in rats to bilateral electrolytic lesioning of the caudal portion of the nucleus tractus solitarii. Brain Res 363: 183–187
Kubo T, Kihara M (1988a) Evidence of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated modulation of the aortic baroreceptor reflex in the rat nucleus tractus solitarii. Neurosci Lett 87: 69–74
Kubo T, Kihara M (1988b) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptors mediate tonic vasodepressor control in the caudal ventrolateral medulla of the rat. Brain Res 451: 366–370
Kubo T, Kihara M, Misu Y (1991) Ipsilateral but not contralateral blockade of excitatory amino acid receptors in the caudal ventrolateral medulla inhibits aortic baroreceptor reflex in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343: 46–51
Le Galloudec E, Merahi N, Laguzzi R (1989) Cardiovascular changes induced by the local application of glutamate-related drugs in the rat nucleus tractus solitarii. Brain Res 503: 322–325
Leone C, Gordon FJ (1989) Is l-glutamate a neurotransmitter of baroreceptor information in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250: 953–962
Miura M, Reis DJ (1969) Termination of secondary projections of carotid sinus nerve in the cat brainstem. Am J Physiol 217: 142–153
Monaghan DT, Cotman CW (1985) Distribution of N-methyl-d-aspartate-sensitive L-[3H]-glutamate-binding sites in rat brain. J Neurosci 11: 2909–2919
Nakagawa T, Shirasaki T, Tateishi N, Murase K, Akaike N (1990) Effects of antagonists on N-methyl-d-aspartate response in acutely isolated nucleus tractus solitarii neurons of the rat. Neurosci Lett 113: 169–174
Palkovits M, Zaborszky L (1977) Neuroanatomy of central cardiovascular control. Nucleus tractus solitarii: afferent and efferent neuronal connections in relation to the baroreceptor reflex arc. Prog Brain Res 47: 9–34
Perrone MH (1981) Biochemical evidence that l-glutamate is a neurotransmitter of primary vagal afferent nerve fibers. Brain Res 230: 283–293
Reis DJ, Granata AR, Perrone MH, Talman WT (1981) Evidence that glutamic acid is the neurotransmitter of baroreceptor afferents terminating in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS). J Auton Nerv Syst 3: 321–334
Sapru HN, Krieger AJ (1977) Carotid and aortic chemoreceptor function in the rat. J Appl Physiol 42: 344–348
Sapru HN, Gonzalez E, Krieger AJ (1981) Aortic nerve stimulation in the rat: cardiovascular and respiratory responses. Brain Res Bull 6: 393–398
Stone TW, Connick JH (1985) Quinolinic acid and other kynurenines in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 15: 597–618
Talman WT (1989) Kynurenic acid microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius of rat blocks the arterial baroreflex but not responses to glutamate. Neurosci Lett 102: 247–252
Talman WT, Perrone MH, Reis DJ (1980) Evidence for l-glutamate as the neurotransmitter of baroreceptor afferent nerve fibers. Science 209: 813–815
Zandberg P, Palkovits M, De Jong W (1978) Effect of various lesions in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat on blood pressure and heart rate, and cardiovascular reflex responses. Clin Exp Hypertens [A] 1: 355–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, T., Kihara, M. Unilateral blockade of excitatory amino acid receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii produces an inhibiton of baroreflexes in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343, 317–322 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251133
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251133