Summary
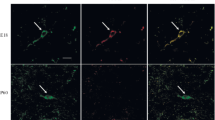
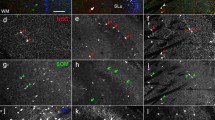
In situ hybridization was used to study dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) mRNA expression in neurons of the rat forebrain, both on control animals and after a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesion of midbrain dopamine neurons. D2R mRNA expressing neurons were seen in regions which are known to be heavily innervated by midbrain dopamine fibers such as caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. ChAT mRNA expressing neurons were seen in caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens and septal regions including vertical limb of the diagonal band. In caudate-putamen, approximately 55% of the medium sized neurons, which is the predominating neuronal cell-size in this region, were specifically labeled with the D2R probe. In addition, approximately 95% of the large size neurons in caudate-putamen were specifically labeled with both the D2R and ChAT probes, suggesting that most cholinergic neurons in the caudate-putamen express D2R mRNA. After a unilateral lesion of midbrain dopamine neurons, no change in the level of either D2R or ChAT mRNA were seen in the large size intrinsic cholinergic neurons in caudate-putamen. Similarily, no evidence was obtained for altered levels of D2R mRNA in medium size neurons in medial caudate-putamen, or nucleus accumbens. However, an increase in the number of medium size neurons expressing D2R mRNA was observed in the lateral part of the dopamine deafferented caudateputamen. Thus, it appears that midbrain dopamine deafferentation causes an increase in D2R mRNA expression in a subpopulation of medium size neurons in the lateral caudate-putamen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid Y, Guyenet P, Glowinsky J, Beaujouan J, Javoy-Agid F (1975) Inhibitory influence of the nigrostriatal dopamine system on the striatal cholinergic neurons in the rat. Brain Res 86:488–492
Andén N-E, Dahlström A, Fuxe K, Hillarp NA, Larsson K (1964) Demonstrating and mapping out of nigro-neostriatal dopamine neurons. Life Sci 3:523–530
Björklund A, Lindvall O (1984) Catecholaminergic brain stem regulatory systems. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemichal neuroanathomy, Vol 2. Elsevier, New York, pp 55–122
Brann MR, Emson PC (1980) Microiontophoretic injection of flouroscent tracer combined with simoltaneous immunoflouroscent histochemistry for demonstration of efferents from caudate-putamen. Neurosci Lett 16:61–65
Brice A, Berrard S, Raynaud B, Ansieau S, Coppola T, Weber MJ, Mallet J (1989) Complete sequence of a cDNA encoding an active rat choline acetyltransferase: a tool to investigate the plasticity of cholinergic phenotypic expression. J Neurosci Res 23:266–273
Brownstein MJ, Mroz EA, Tappaz ML, Leeman SE (1977) On the origin of substance P and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in the substantia nigra. Brain Res 135:315–323
Bunzow JR, VanTol HHM, Grandy DK, Albert P, Salon J, Christie M, Machida CA, Neve KA, Civelli O (1988) Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor. Nature 336:783–787
Chang HT (1988) Dopamine-acetylcholine interactions in the rat striatum: a dual-labeling immunocytochemichal study. Brain Res Bull 21:295–304
Christenson-Nylander I, Herrera-Marschitz M, Staines W, Hökfelt T, Terenius L, Ungerstedt U, Cuello C, Oertel WH, Goldstein M (1986) Striato-nigral dynorphine and substance P pathways in the rat. I. Biochemichal and immuno-histochemichal studies. Exp Brain Res 380:34–41
Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH (1977) Dopamine receptor binding enhancement accompanies lesion-induced behavioural supersensitivity. Science 197:596–598
Cuello AC, Paxinos G (1978) Evidence for a long Leu-enkephaline striopallidal pathway in rat brain. Nature 271:178–180
Dahlstöm A, Fuxe K (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 232:1–55
Dal Toso R, Sommer B, Ewert M, Herb A, Pritchet DB, Bach A, Shivers B, Seeburg PH (1989) The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative spxlicing. EMBO 8:4025–4039
Del Fiacco M, Paxinos G, Cuello AC (1982) Neostriatal enkephalin-immunoreactive neurons project to the globus pallidus. Brain Res 231:1–17
DiFiglia M, Aronin N, Leeman SE (1981) Immunoreactive substance P in the substantia nigra of the monkey: light and electron microscopic lokalization. Brain Res 233:381–388
DiFiglia M, Aronin N, Martin JB (1982) Light and electron microscopic localization of immunoreactive leuenkephaline in the monkey basal ganglia. J Neurosci 2:303–320
DiFiglia M, Aronin N (1982) Ultrastructural features of immunoreactive somatostatin neurons in the rat caudate nucleus. J Neurosci 2:1267–1274
Fibiger HC (1982) The organisation and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mamalian forebrain. Brain Res Rev 4:327–388
Fonnum F, Gottesfeld Z, Grofova I (1978) Distribution of glutamate decarboxylase, choline acetyltransferase and aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in the basal ganglia of normal and operated rat: evidence for striatopallidal, striatoentopeduncular and striatonigral GABAergic fibers. Brain Res 143:125–138
Gerlach J (1985) Pathophysiological mechanisms underlying tardive dyskinesia. In: Casey DE, Christensen AV, Gerlach J (eds) Dyskinesia research and treatment. Psychopharmacology Suppl 2:98–103
Giros B, Sokloff P, Martress M-P, Riou J-F, Emorine LJ, Schwartz J-C (1989) Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature 342:923–926
Grandy DK, Marchionni MA, Makam H, Stofko RE, Alfano M, Frothingham L, Fischer JB, Burke-Howie KJ, Bunzow JR, Server AC, Civelli O (1989) Cloning of the cDNA and gene for a human D2 dopamine receptor. Proc Acad Sci USA 86:9762–9766
Groves PM, Synaptic endings and their postsynaptic targets in neostriatum: synaptic specializations revealed from analysis of serial sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6926–6929
Hattori T, Singh VK, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1976) Immunohistochemichal localization of choline acetyltransferase containing striatal neurons and their relationship with dopaminergic synapses. Brain Res 102:164–173
Herrera-Marschitz M, Ungerstedt U (1984a) Evidence that striatal efferents relate to different dopamine receptors. Brain Res 323:269–278
Herrera-Marschitz M, Ungerstedt U (1984b) Evidence that apomorphine and pergolide induce rotation in rats by different actions on D1 and D2 receptor sites. Eur J Pharmacol 98:165–176
Hong JS, Yang HY, Racagni G, Costa E (1977) projections of substance P containing neurons from neostriatum to substantia nigra. Brain Res 122:541–544
Jessel TM, Emson PC, Paxinos G, Cuello AC (1978) Topographic projections of substance P and GABA pathways in the striatopallido-nigral system: a biochemical and immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 152:487–498
Joyce JN, Marshall JF (1985) Striatal topography of D2 receptors correlates with indexes of cholinergic neuron localization. Neurosci Lett 53:127–131
Kanazawa I, Emson PC, Cuello C (1977) Evidense for existence of substance P containing fibers in striato-nigral and pallido-nigral pathways in rat brain. Brain Res 119:447–453
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Kemp JM, Powell TPS (1971) The structure of caudate nucleus of the cat: light and electron microscopy. Phil Trans R Soc Ser B 262:383–401
Kim JS, Bak IJ, Hassler R, Okada Y (1971) Role of γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) in the extrapyramidal motor system: some evidence for the existence of a type of GABA-rich striato-nigral neurons. Exp Brain Res 14:95–104
Laihinen A, Rinne UK (1986) Function of dopamine response in Parkinsons disease: prolactin responses. Neurology 36:393–395
Lehmann L, Langer SZ (1983) The striatal cholinergic interneuron: synaptic target of dopaminergic terminals. Neuroscience 10:1105–1120
Le Moine C, Normand E, Guitteny AF, Fouque B, Teolle R, Bloch B (1989) Dopamine receptor gene expression by enkephaline neurons in rat forebrain. Proc Acad Sci USA 87:230–234
Lindefors N, Brodin E, Ungerstedt U (1986) Neurokinin A and substance P in striato-nigral neurons in rat brain. Neuropeptides 8:127–132
Lindefors N, Brené S, Herrera-Marschitz M, Persson H (1989) Region specific regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA expression by dopamine neurons in rat brain. Exp Brain Res 77:611–620
Lindefors N, Brené S, Herrera-Marschitz M, Persson H (1990) Neuropeptide gene expression in brain is differentially regulated by midbrain dopamine neurons. Exp Brain Res 80:489–500
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Fibiger HG, Vicksin V (1971) Neostriatal choline acetyltransferase following selective brain lesions. Brain Res 35:308–314
Meandor-Woodruff JH, Mansour A, Bunzow JR, Van Tol HHM, Watson S, Civelli O (1989) Distribution of D2 dopamine receptor mRNA in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7625–7628
Mengod G, Martinez-Mir MI, Vilario MT, Palacios JM (1989) Localization of the mRNA for the dopamine D2 receptor in the rat brain by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Proc Acad Sci USA 86:8560–8564
Mishra RK, Marshall AM, Varmuza SL (1980) Supersensitivity in rat caudate nucleus: effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on the time course of dopamine receptor and cyclic AMP changes. Brain Res 200:47–57
Monsma Jr FJ, McVittie LD, Gerfen CR, Mahan LC, Sibley DR (1989) Multiple D2 dopamine receptors produced by alternative RNA splicing. Nature 342:926–929
Nagai T, McGeer PL McGeer HC (1983) Distribution of GABA-T-intensive neurons in the rat forbrain and midbrain. J Comp Neurol 218:220–238
Nagy JI, Carter DA, Fibiger HC (1978) Anterior striatal projections to globus pallidus, entopeduncular nucleus and substantia nigra in the rat: the GABA connection. Brain Res 158:25–29
Nagy JI, Fibiger HC (1978) A striatal source of glutamic acid decarboxylase in the substantia nigra. Brain Res 35:237–242
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in sterotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Pickel VM, Beckley S, Joh TH, Reis DJ (1981) Ultrastructural immunocytochemichal localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in the neostriatum. Brain Res 225:373–385
Satoh K, Staines A, Atmadja S, Fibiger HC (1983) Ultrastructural observations of the cholinergic neuron in the rat striatum as identified by acetylcholinesterase pharmacohistochemistry. Neuroscience 10:1121–1136
Ungerstedt U (1971a) Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathwayss in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 367:1–48
Ungerstedt U (1971b) Postsynaptic Supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine induced degeneration of nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 367:69–93
Young III WS, Bonner TI, Brann MR (1986) Mescencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNA in the rat forebrain. Proc Acad Sci USA 83:9827–9831
Vernier P, Julien J-F, Rataboul, P, Fourrier O, Feuerstein C, Mallet J (1988) Similar time course changes in striatal levels of glutamic acid decarboxylase and proenkephalin mRNA following dopaminergic deafferentation in the rat. J Neurochem 51:1375–1380
Vincent SR, Hökfelt T, Christensson I, Terrenius L (1982a) Immunohistochemichal evidence for a dynorphine immunoreactive striato-nigral pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 85:251–252
Vincent SR, Skirboll L, Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Lundberg JM, Elde RP, Terrenius L, Kimmel J (1982b) Coexistence of somatostatin and avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP)-like immunoreactivity in some forebrain neurons. Neuroscience 7:439–446
Weiner DM, Brann MR (1989) The distribution of a dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in rat brain. FEBS Lett 253:207–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brené, S., Lindefors, N., Herrera-Marschitz, M. et al. Expression of dopamine D2 receptor and choline acetyltransferase mRNA in the dopamine deafferented rat caudate-putamen. Exp Brain Res 83, 96–104 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232197
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232197