Summary
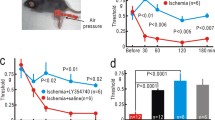
In the present study we examined the effect of systemic tocainide on sensory hypersensitivity in rats after spinal cord ischemia induced by a photochemical technique. After induction of spinal cord ischemia the rats exhibited a sensory disturbance which was mainly expressed as vocalization to innocuous cutaneous mechanical stimuli (allodynia) in the flank area during the following several days. Tocainide at 75 mg/kg i.p., but not 50 mg/kg i.p., significantly increased the vocalization threshold to mechanical pressure for 2 h. The effect of intraarterial (i.a.) tocainide on the responses of dorsal horn wide-dynamic-range (WDR) neurons to suprathreshold electrical stimulation of their receptive fields was also examined in normal rats and after transient spinal cord ischemia, at a time when the animals exhibited typical behavioral allodynia in the dermatomes innervated by the ischemic spinal segments. In normal rats, tocainide (50 mg/kg i.a.) strongly suppressed the responses of WDR neurons to C fiber input with lesser effect on A fiber input. In allodynic rats, tocainide suppressed the augmented A and C fiber mediated responses of WDR neurons to the extent that their responses were similar to those seen in normal rats without tocainide. There was no difference in the overall depression of A and C fiber mediated input by tocainide between normal and allodynic rats. The present results demonstrated the analgesic effect of systemic tocainide in relieving allodynia in rats and indicated that systemic local anesthetics, at doses that do not block nerve conduction, can be effective in suppressing dorsal horn WDR neuronal activity. Although such drugs primarily suppress C fiber induced activity, the depression by local anesthetics of increased A fiber induced responses in allodynic conditions mediated by myelinated afferents may explain the analgesic effect of such drugs on behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JL, Mason JW, Winkle RA (1978) Clinical electrophysiologic effects of tocainide. Circulation 57:685–691
Atkinson RL (1982) Intravenous lidocaine for the treatment of intractable pain of adiposis dolorosa. Int J Obes 6:351–365
Bartlett EE, Hutaserani O (1961) Xylocaine for the relief of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg 40:296–304
Boas RA, Covino BG, Shahnarian A (1982) Analgesic responses to i. v. lidocaine. Br J Anaesth 54:501–505
De Clive-Lowe SG, Desmond J, North J (1958) Intravenous lignocaine anesthesia. Anesthesiology 13:138–146
Defgard A, Petersen P, Kastrup J (1988) Mexiletine for treatment of chronic diabetic neuropathy. Lancet 1:9–11
De Jong RH (1970) Physiology and pharmacology of local anesthesia. Thomas, Springfield, Ill.
De Jong RH, Nace RA (1968) Nerve impulse conduction during intravenous lidocaine injection. Anesthesiology 29:22–28
De Jong RH, Robles R, Corbin RW (1969) Central actions of lidocaine-synaptic transmission. Anesthesiology 30:19–23
Hao J-X, Xu X-J, Aldskogius H, Seiger Å, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1991a) Allodynia-like effects in rat after ischaemic spinal cord injury photochemically induced by laser irradiation. Pain 45:175–185
Hao J-X, Xu X-J, Yu Y-X, Seiger Å, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1991b) Hypersensitivity of dorsal horn wide dynamic range neurons to cutaneous mechanical stimuli after transient spinal cord ischemia in the rat. Neurosci Lett 128:105–108
Holmes B, Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS (1983) Tocainide. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 26:93–123
Keats AS, D'Alessandro GL, Beecher HK (1951) A controlled study of pain relief by intravenous procaine. JAMA 147:1761–1763
Kuno M, Matsuura S (1982) Sites and mechanisms of action of lidocaine upon the isolated spinal cord of the frog. Brain Res 249:87–93
Lindström P, Lindblom U (1987) The analgesic effect of tocainide in trigeminal neuralgia. Pain 28:45–50
Moore EN, Speer JF, Horowitz CN, Ferdman HS, Moller RA (1978) Electrophysiologic properties of a new antiarrhythmic drug-tocainide. Am J Cardiol 41:703–709
Petersen P, Kastrup J, Zeeberg I, Boysen G (1986) Chronic pain treatment with intravenous lidocaine. Neurol Res 8:189–190
Sotgiu ML, Lacerenza M, Marchettini P (1991) Selective inhibition by systemic lidocaine of noxious evoked activity in rat dorsal horn neurons. Neuroreport 2:425–428
Sugimori M, Llinas R (1980) Lidocaine differentially blocks fast and slowly inactivating sodium conductance in Purkinje cells: an in vitro study in guinea pig cerebellum using iontophoretic glutamate. Soc Neurosci Abstr 6:468
Watson BD, Prado R, Dietrich WD (1988) Photochemically induced spinal cord injury in the rat. Brain Res 367:296–300
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Lindblom U (1985) The effect of systemic tocainide, lidocaine and bupivacaine on nociception in the rat. Pain 23:357–360
Woolf CJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1985) The systemic administration of local anaesthetics produces a selective depression of Cafferent fibre evoked activity in the spinal cord. Pain 23:361–374
Young MD, Haanchan Z, Horn HR, Johnson JL, Vasallo HG (1980) Treatment of arrhythmias with oral tocainide. Am Heart J 100:1041–1045
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, J.X., Yu, Y.X., Seiger, Å. et al. Systemic tocainide relieves mechanical hypersensitivity and normalizes the responses of hyperexcitable dorsal horn wide-dynamic-range neurons after transient spinal cord ischemia in rats. Exp Brain Res 91, 229–235 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231656
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231656