Abstract
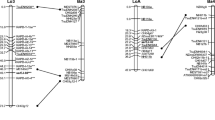
A genetic linkage map for radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don) has been constructed using segregation data from a three-generation outbred pedigree. A total of 208 loci were analyzed including 165 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), 41 random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and 2 microsatellite markers. The markers were assembled into 22 linkage groups of 2 or more loci and covered a total distance of 1382 cM. Thirteen loci were unlinked to any other marker. Of the RFLP loci that were mapped, 93 were detected by loblolly pine (P. taeda L.) cDNA probes that had been previously mapped or evaluated in that species. The remaining 72 RFLP loci were detected by radiata pine probes from a PstI genomic DNA library. Two hundred and eighty RAPD primers were evaluated, and 41 loci which were segregating in a 1∶1 ratio were mapped. Two microsatellite markers were also placed on the map. This map and the markers derived from it will have wide applicability to genetic studies in P. radiata and other pine species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn S, Tanksley SD (1993) Comparative linkage maps of the rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7980–7984
Ahuja MR, Devey ME, Groover AT, Jermstad KD, Neale DB (1994) Mapped DNA probes from loblolly pine can be used for restriction fragment length polymorphism in other conifers. Theor Appl Genet 88:279–282
Bradshaw HD Jr, Stettler RF (1995) Molecular genetics of growth and development in Populus. IV. Mapping QTLs with large effects on growth, form and phenology traits in a forest tree. Genetics 139:963–973
Conkle MT (1992) Genetic diversity — seeing the forests through the trees. New For 6:5–22
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Devey ME, Jermstad KD, Tauer CG, Neale DB (1991) Inheritance of RFLP loci in a loblolly pine three-generation pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 83:238–242
Devey ME, Fiddler TA, Liu B-H, Knapp SJ, Neale DB (1994) An RFLP linkage map for loblolly pine based on a three-generation outbred pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 88:273–278
Devey ME, Delfino-Mix A, Kinloch BB, Neale DB (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA markers tightly linked to a gene for resistance to white pine blister rust in sugar pine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2066–2070
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Green P, Falls K, Crooks S (1988) Documentation of CRI-MAP. Collaborative Research,
Groover A, Devey M, Fiddler T, Lee J, Megraw R, Mitchel-Olds T, Sherman B, Vujcic S, Williams C, Neale D (1994) Identification of quantitative trait loci influencing wood specific gravity in an outbred pedigree of loblolly pine. Genetics 138:1293–1300
Groover AT, Williams CG, Devey ME, Lee JM, Neale DB (1995) Sex-related differences in meiotic recombination frequency in Pinus taeda. J Hered 86:157–158
Heun M, Helentjaris T (1993) Inheritance of RAPDs in F1 hybrids of corn. Theor Appl Genet 85:985–993
Keim P, Diers BW, Shoemaker RC (1990) Genetic analysis of soybean hard seededness with molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 79:465–469
Manly K, Cudmore R (1994) Map manager: a program for genetic mapping. Roswell Park Cancer Institute, New York
Moran GF, Bell JC, Hilliker AJ (1983) Greater meiotic recombination in male vs. female gametes in Pinus radiata. J Hered 74:62
Moran GF, Bell JC, Eldridge KC (1987) The genetic structure and the conservation of the five natural populations of Pinus radiata. Can J For Res 18:506–514
Neale DB, Sederoff R (1991) Genome mapping in pines takes shape. Probe 1:1–3
Neale DB, Williams CG (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping in conifers and applications to forest genetics and tree improvement. Can J For Res 21:545–554
Nelson CD, Nance WL, Dourick RL (1993) A partial genetic linkage map of slash pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm. var ‘elliottii’) based on random amplified polymorphic DNAs. Theor Appl Genet 87:145–151
Nelson CD, Kubisiak TL, Stine M, Nance WL (1994) A genetic linkage map of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris Mill.) based on random amplified polymorphic DNAs. J Hered 85:433–439
Paterson AH, Damon S, Hewitt JD, Zamir D, Rabinowitch HD, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Tanksley SD (1991) Medelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations, and environments. Genetics 127: 181–197
Plomion C, O'Malley DM, Durel CE (1995) Genomic analysis in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster). Comparison of two RAPD maps using selfed and open-pollinated seeds of the same individual. Theor Appl Genet 90:1028–1034
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis F (1989) Molecular cloning:a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y.
Smith DN, Devey ME (1994) Occurrence and inheritance of microsatellites in Pinus radiata. Genome 37:977–983
Stam P (1993) Construction of integrated genetic linkage maps by means of a new computer package:JoinMap. Plant J 3:739–744
Stuber CW, Lincoln SE, Wolff DW, Helentjaris T, Lander ES (1992) Identification of genetic factors contributing to heterosis in a hybrid from two elite maize inbred lines using molecular markers. Genetics 132:823–839
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Patterson AH, Pineda O, Roder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High-density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Tulsieram LK, Glaubitz JC, Kiss G, Carlson JE (1992) Single tree genetic linkage mapping in conifers using haploid DNA from megagametophytes. Bio/Technology 10:686–690
van Ooijen JW (1994) Draw Map:a computer program for drawing genetic linkage maps. J Hered 85:66
Wakamiya I, Newton RJ, Johnston JS, Price HJ (1993) Genome size and environmental factors in the genus Pinus. Am J Bot 80:1235–1241
Whitkus R, Doebley J, Lee M (1992) Comparative genome mapping of sorghum and maize. Genetics 132:1119–1130
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak J, Rafalski JA, Tingey S (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley SD (1991) Tagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81:471–476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by P. M. A. Tigerstedt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devey, M.E., Bell, J.C., Smith, D.N. et al. A genetic linkage map for Pinus radiata based on RFLP, RAPD, and microsatellite markers. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 673–679 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226088
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226088