Abstract
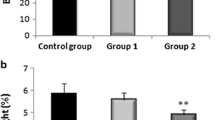
Endrin is a polyhalogenated cyclic hydrocarbon pesticide which produces hepatic and neurologic toxicity. Previous studies have indicated that endrin induces hepatic lipid peroxidation. In order to further assess the possible role of lipid peroxidation in the toxicity of endrin, the dose- and time-dependent effects of endrin on hepatic lipid peroxidation, membrane microviscosity and DNA damage in rats were examined. Rats were treated with 0, 3.0, 4.5, or 6.0 mg endrin/kg as a single oral dose in corn oil, and the animals were killed 0, 12, 24, 48, or 72 h post-treatment. Dose-dependent increases in hepatic mitochondrial and microsomal lipid peroxidation and microviscosity as well as nuclear DNA single strand breaks were observed as early as 12 h post-treatment. Maximum increases in these three parameters occurred 24 h after endrin administration at all three doses. While the incidence in DNA damage decreased with time after 24 h, the incidence of lipid peroxidation and microviscosity of microsomal and mitochondrial membranes remained relatively constant. Dose- and time-dependent increases in liver and spleen weight/body weight ratios with decreases in thymus weight/body weight ratios were observed. The data indicate that endrin administration induces hepatic lipid peroxidation which may be responsible for the increased membrane microviscosity as a result of membrane damage as well as enhanced DNA damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsharif NZ, Grandjean CJ, Murray WJ, Stohs SJ (1990) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induced decrease in the fluidity of rat liver membranes. Xenobiotica 20:979–988
Bagchi M, Prasad RM, Engelman RM, Das DK (1989) Effects of free radicals on the fluidity of myocardial membranes. Free Rad Res Comm 7:375–380
Bernet JT, Groce DF (1984) Acute response of rat liver microsomal lipids, lipid peroxidation and membrane anisotropy to a single oral dose of polybrominated biphenyls. J Toxicol Environ Hlth 13:673–687
Brooks GT (1976) In: Chlorinated insecticides—Biological and environmental aspects. CRC Press Inc., Cleveland, OH, pp 95–143
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Meth Enzymol 51:302–310
Casals C, Herrero LM, Soriano Y, Garcia-Barrero P, Munico AM (1985) Membrane regulation of liver and lung microsomes under low oxygen tension. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 126:551–558
Dobrestor GE, Borschevskaya TA, Petrov VA, Vladimirov YA (1977) The increase of phospholipid bilayer rigidity after lipid peroxidation. FEBS Lett 84:125–128
Engelman RM, Prasad RM, Rousou JA, Beyer HR, Bagchi M, Das DK (1989) Steroid induced myocardial preservation is associated with decreased cell membrane microviscosity. Circulation 80: 36–43
Hassan MQ, Numan IT, Nasiri NA, Stohs SJ (1991) Endrin-induced histopathological changes and lipid peroxidation in livers and kidneys of rats, mice, guinea pigs and hamsters. Toxicol Pathol 19:108–114
Hewett JA, Roth RA (1990) Dieldrin activates rat neutrophils in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 92:269–278
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr WL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Matsumura F (1976) In: Toxicology of Insecticides. Academic Press, NY, pp 127–186
Murphy SD (1986) Toxic effects of pesticides. In: Klassen et al. (eds) Toxicology: The basic science of poisons. McMillan Publishing Company, NY, pp 519–581
Numan IT, Hassan MQ, Stohs SJ (1990a) Endrin-induced depletion of glutathione and inhibition of glutathione peroxidase activity in rats. Gen Pharmacol 21:625–628
—, —, — (1990b) Protective effects of anti-oxidants against endrin induced lipid peroxidation, glutathione depletion and lethality in rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:302–306
Saffioti U, Terrachini D (1979) Endrin, IARC Monograph 5:15–171
Shintzky M, Barrenholz Y (1978) Dynamics of the hydrocarbon layer in liposomes of lecithin and sphingomyelin containing diacetyl phosphate. J Biol Chem 249:2652–2657
Spector AA, Yorek MA (1985) Membrane lipid composition and cellular function. J Lipid Res 26:1015–1035
Stohs SJ (1990) Oxidative stress induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Free Rad Biol Med 9:79–90
Stubbs CD (1983) Structure and dynamics of membrane lipids. Essays in Biochem 19:1–39
Trimenstein M, Reed DJ (1989) Effect of glutathione on the α-tocopherol-dependent inhibition of nuclear lipid peroxidation. J Lipid Res 30:959–965
Wahba ZZ, Lawson TA, Murray WJ, Stohs SJ (1989) Factors influencing the induction of DNA single strand breaks in rats by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Toxicology 58:57–69
White RD, Sipes IG, Gandolfi AJ, Bowden GT (1981) Characterization of the hepatic DNA damage caused by 1,2-dibromoethane using the alkaline elution technique. Carcinogenesis 2:839–843
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagchi, M., Hassoun, E.A., Bagchi, D. et al. Endrin-induced increases in hepatic lipid peroxidation, membrane microviscosity, and DNA damage in rats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 23, 1–5 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225988
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225988