Abstract
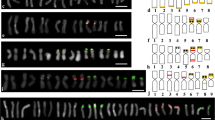
The 17s-5.8s-25s ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) loci in Oryza spp. were identified by the fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) method. The rDNA loci were located on one-to-three chromosomes (two-to-six sites) within the eight diploid Oryza spp. One of the rDNA loci gave the weakest hybridization signal. This locus is reported for the first time in the genus Oryza. The chromosomes containing the rDNA loci were determined to be numbers 9, 10 and 11 in descending order of the copy number of rDNA. The application of image analysis methods, after slide preparation treatments (post-treatments), and the use of a thermal cycler, greatly improved the reproducibility of the results. The evolutionary significance of the variability of rDNA loci among the Oryza spp. is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Gerlach WL, Dennis ES, Swift H, Peacock WJ (1980) Molecular and chromosomal organization of DNA sequence coding for the ribosomal RNAs in cereals. Chromosoma 78:293–311
Dvorak J, Zhang H-B, Kota RS, Lassner M (1989) Organization and evolution of the 5s ribosomal RNA gene family in wheat and related species. Genome 32:1003–1016
Fukui K (1984) In-situ hybridization. In: Uchimiya H, Tanaka K, Sugiura A (eds) Manual for plant genetic engineering. Kodansha Scientific, Tokyo, pp 165–168
Fukui K (1985) Identification of plant chromosomes by image analysis method. The Cell (Tokyo) 17:145–149
Fukui K (1986) Standardization of karyotyping plant chromosomes by a newly developed chromosome image analyzing system (CHIAS). Theor Appl Genet 72:27–32
Fukui K (1988) Analysis and utility of chromosome information by using the chromosome image analyzing system, CHIAS. Bull Natl Inst Agrobiol Resour 4:153–175
Fukui K (1990) Localization of rRNA genes on rice chromosomes. Rice Biotech Quart 1:18–19
Fukui K, Iijima K (1991) Somatic chromosome map of rice by imaging methods. Theor Appl Genet 81:589–596
Fukui K, Iijima K (1992) Manual on rice chromosomes. (2nd ed) Misc Pub Natl Inst Agrobiol Resour 4:1–25
Fukui K, Ito K (1989) Computer simulation for microscopic images of barley chromosomes. Bull Natl Inst Agrobiol Resour 5:21–35
Fukui K, Kakeda K (1990) Quantitative karyotyping of barley chromosomes by image analysis methods. Genome 33:450–458
Fukui K, Kamisugi Y (1991) Simulation of microscopic images by a desktop imaging system. In: Doyama M, Suzuki T, Yamamoto R (eds) Computer aided innovation of new materials. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp 101–104
Fukui K, Kakeda K, Hashimoto J, Matsuoka S (1987) In-situ hybridization of 125I-labelled rRNA to rice chromosomes. Rice Genet Newslett 4:114–116
Fukui K, Kadowaki K, Harada K (1989) Implication of the image analysis methods in biotechnology. Jpn Agr Res Quart 22:253–259
Gerlach WL, Peacock WJ (1980) Chromosomal location of highly-repeated DNA sequences in wheat. Heredity 44:269–276
Gustafson JP, Dillé JE (1992) Chromosome location of Oryza Sativa recombination linkage groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8646–8650
Heslop-Harrison JS (1990) Gene expression and parental dominance in hybrid plants. Development (suppl): 21–38
Hutchinson J, Miller TE (1982) The nucleolar organizers of tetraploid and hexaploid wheats revealed by in-situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 61:285–288
Iijima K, Kakeda K, Fukui K (1991) Identification and characterization of somatic rice chromosomes by imaging methods. Theor Appl Genet 81:597–605
Islam-Faridi MN, Ishii T, Kumar V, Sitch LA, Brar DS (1990) Chromosomal location of ribosomal RNA genes in rice by in-situ hybridization. Rice Genet Newslett 7:143–144
Kawase M, Kishimoto N, Tanaka T, Yoshimura A, Yoshimura S, Saito K, Saito A, Yano M, Takeda N, Nagamine T, Nakagahra M (1991) Intraspecific variation and genetic differentiation based on restriction fragment length polymorphism in Asian cultivated rice, Oryza sativa L. In: IRRI (ed) Rice genetics II, pp 467–473
Khush GS, Kinoshita T (1991) Rice karyotype, marker genes, and linkage groups. In: Khush GS, Toennieson GH (eds), Rice biotechnology. CAB International, Oxford, England, pp 83–108
Kurata N, Omura T (1978) Karyotype analysis in rice. A new method for identifying all chromosome pairs. Jpn J Genet 53:251–255
Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Physical mapping of the 18s-58s-26s rDNA genes in barley by in-situ hybridization. Genome 35:1013–1018
Mukai Y, Endo TR, Gill BS (1990) Physical mapping of the 5s rRNA multigene family in common wheat. J Hered 81:290–295
Mukai Y, Endo TR, Gill BS (1991) Physical mapping of the 18s.26s rRNA multigene family in common wheat: Identification of a new locus. Chromosoma 100:71–78
Oka HI (1958) Intervariatal variation and classification of cultivated rice. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 18:79–89
Oka HI (1983) Life-history characteristics and colonizing success in plants. Am Zool 23:99–109
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1985) Use of biotin-labeled probe to map specific DNA sequences on wheat chromosomes. J Hered 76:78–81
Sano Y, Sano R (1990) Variation of the intergenic spacer region of ribosomal DNA in cultivated and wild rice species. Genome 33:209–218
Sato S, Willson C, Dickinson HG (1988) Origin of nucleolus-like bodies found in the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm of Vicia faba meristematic cells. Biol Cell 64:321–329
Sato YI (1987) Character association patterns among japonica rice varieties of Asian origin. In: Hsieh SC (ed) Crop exploration and utilization of genetic resources. Taichung Agric Imp Sta, Taiwan, pp 21–29
Suzuki H, Futsuhara Y, Takaiwa F, Kurata N (1991) localization of glutelin gene in rice chromosome by in-situ hybridization. Jpn J Genet 66:305–312
Wang ZY, Tanksley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism in Oryza sativa L. Genome 32:1113–1118
Wu HK, Chung MC, Xie Y, Wu R (1986) Chromosomal localization of rice rbsS genes. Rice Genet Newslett 3:117–119
Wu HK, Chung MC, Chen MH (1985) Karyotype analysis of cultivar IR36. Rice Genet Newslett 2:54–57
Wu HK, Chung MC, Wu T, Ning CN, Wu R (1991) Localization of specific repetitive DNA sequences in individual rice chromosomes. Chromosoma 100:330–338
Yanagisawa T, Tano S, Fukui K, Harada K (1991) Marker chromosomes commonly observed in the genus Glycine. Theor Appl Genet 81:606–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukui, K., Ohmido, N. & Khush, G.S. Variability in rDNA loci in the genus Oryza detected through fluorescence in situ hybridization. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 87, 893–899 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225782